Abstract
Six patients with pseudomembranous entercolitis were seen at one institution over a six-month period. Clindamycin therapy preceded the diagnosis in all six patients and possibly caused the disease in five cases. Common clinical features included diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, leukocytosis, radiographic findings of large bowel dilatation with mucosal thickening and a characteristic sigmoidoscopic or gross pathologic demonstration of discrete yellow-white plaques on an otherwise normal mucosa. Complications included toxic megacolon and sigmoid colon perforation. Two of the six patients died. The literature since 1970 is tabulated to clarify the clinical and pathological features of pseudomembranous enterocolitis associated with newer antibiotic therapy. Lincomycin and clindamycin are strongly implicated in the recent resurgence of this formerly rare variety of colitis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRNBAUM D., LAUFER A., FREUND M. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis. A clinicopathologic study. Gastroenterology. 1961 Oct;41:345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
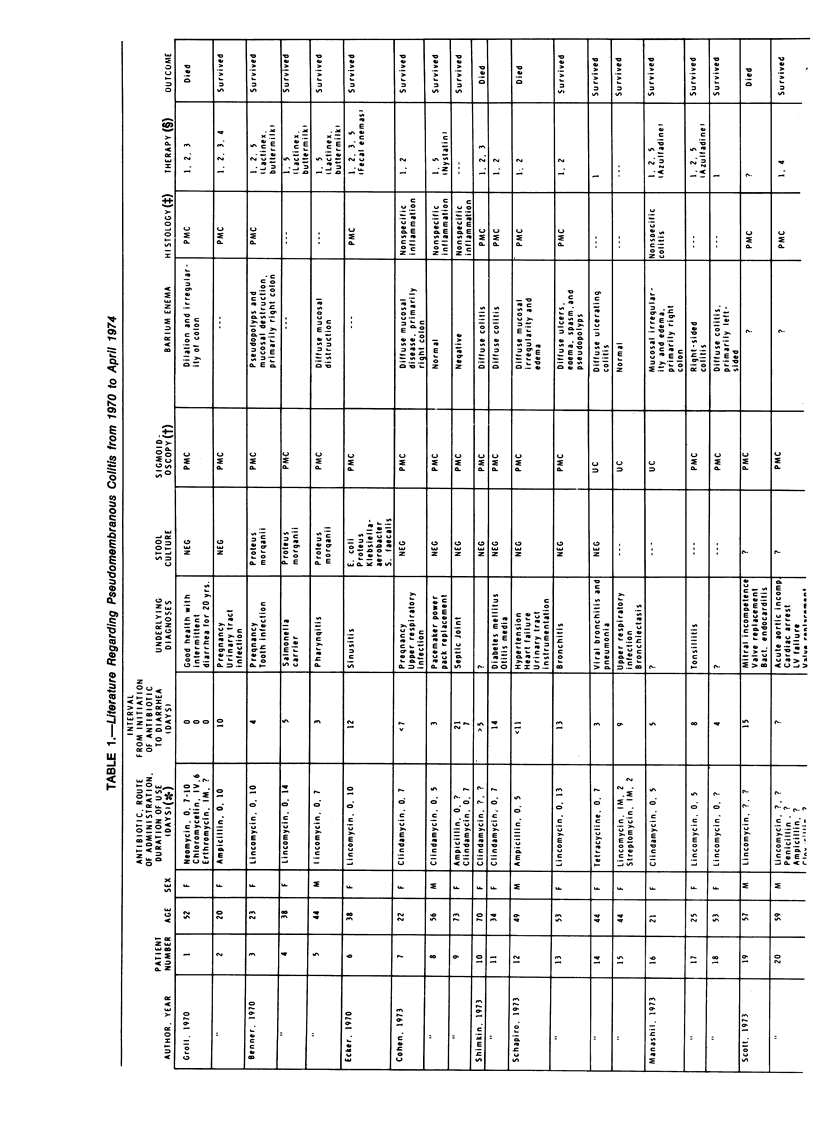
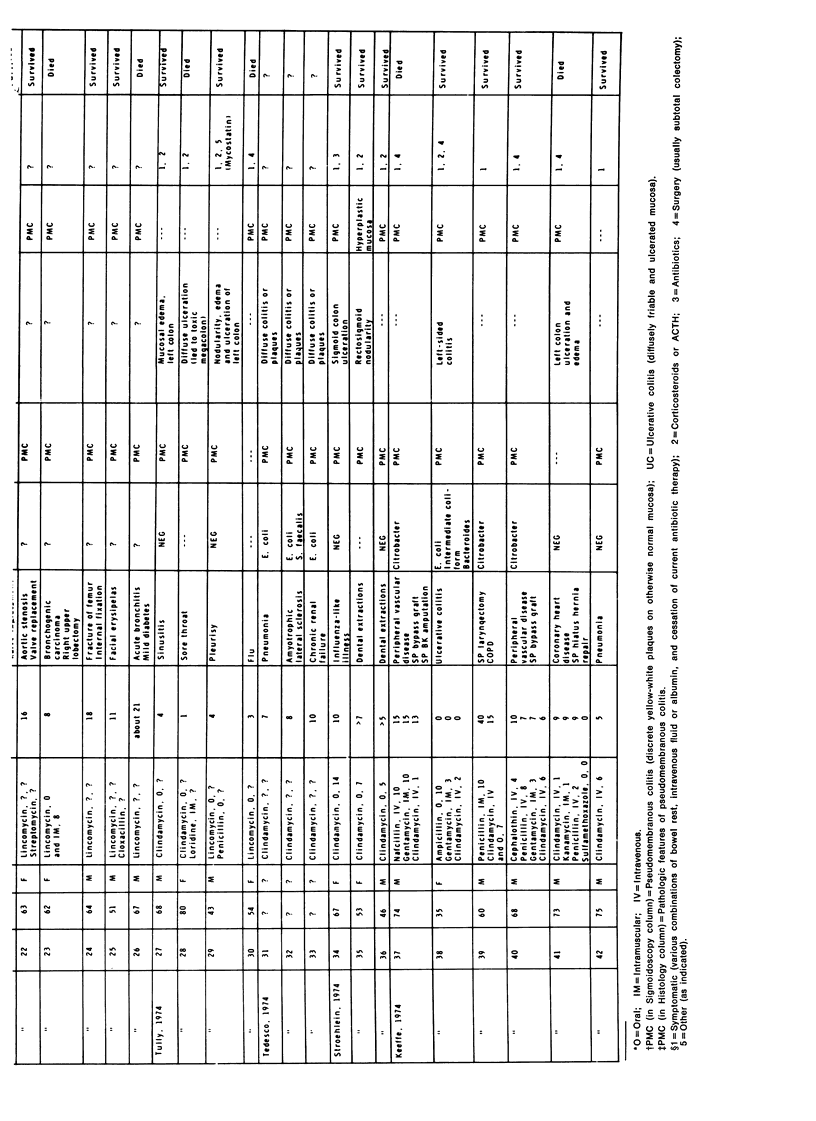
- Benner E. J., Tellman W. H. Pseudomembraneous colitis as a sequel to oral lincomycin therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1970 Jul;54(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHILDS S. B., BEATTY E. C., Jr Fatal enteritis; relation to antibiotic therapy. AMA Arch Surg. 1954 Apr;68(4):486–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. E., McNeill C. J., Wells R. F. Clindamycin-associated colitis. JAMA. 1973 Mar 19;223(12):1379–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. E., Smith C. J., Pister J. D., Wells R. F. Clindamycin (Cleocin) colitis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974 Jun;121(2):301–304. doi: 10.2214/ajr.121.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. A., Williams R. G., McKittrick J. E., Failing R. M. Pseudomembraneous enterocolitis--an unwelcome gastrointestinal complication of antibiotic therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1970 Sep;54(3):214–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety F. R., Jr Gastrointestinal complications of antibiotic therapy. JAMA. 1968 Jan 15;203(3):210–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes A. M., Bridgwater F. A., Williams D. N., Oon J., Grimshaw G. J. Clinical and bacteriological studies with clindamycin. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 20;2(5711):703–704. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5711.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. D., Krone C. L. Non-staphylococcal pseudomembranous colitis. Am J Dig Dis. 1969 Apr;14(4):278–281. doi: 10.1007/BF02235958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulston S. J., McGovern V. J. Pseudo-membranous colitis. Gut. 1965 Jun;6(3):207–212. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groll A., Vlassembrouck M. J., Ramchand S., Valberg L. S. Fulminating noninfective pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):88–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE H. W., Jr, COSGRIFF J. H., Jr Pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Am J Surg. 1957 Nov;94(5):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(57)90854-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLOTZ A. P., PALMER W. L., KIRSNER J. B. Aureomycin proctitis and colitis: a report of five cases. Gastroenterology. 1953 Sep;25(1):44–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K., Weinstein L. Lincomycin. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1968 Feb;15(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manashil G. B., Kern J. A. Nonspecific colitis following oral lincomycin therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1973 Oct;60(4):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARCE C., DINEEN P. A study of pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Am J Surg. 1960 Mar;99:292–300. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(60)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETTET J. D., BAGGENSTOSS A. H., DEARING W. H., JUDD E. S., Jr Postoperative pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1954 May;98(5):546–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., Pittman J. C., Humphrey C. D. Colitis following oral lincomycin therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Aug;134(2):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., Pittman J. C., Humphrey C. D. Letter: Lincomycin and pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1974 Mar 16;1(7855):451–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92402-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINER L., SCHLESINGER M. J., MILLER G. M. Pseudomembranous colitis following aureomycin and chloramphenicol. AMA Arch Pathol. 1952 Jul;54(1):39–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders E. Lincomycin versus erythromycin: a choice or an echo. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Mar;70(3):585–590. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-3-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapiro R. L., Newman A. Acute enterocolitis. A complication of antibiotic therapy. Radiology. 1973 Aug;108(2):263–268. doi: 10.1148/108.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. J., Nicholson G. I., Kerr A. R. Lincomycin as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 1;2(7840):1232–1234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90973-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
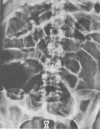
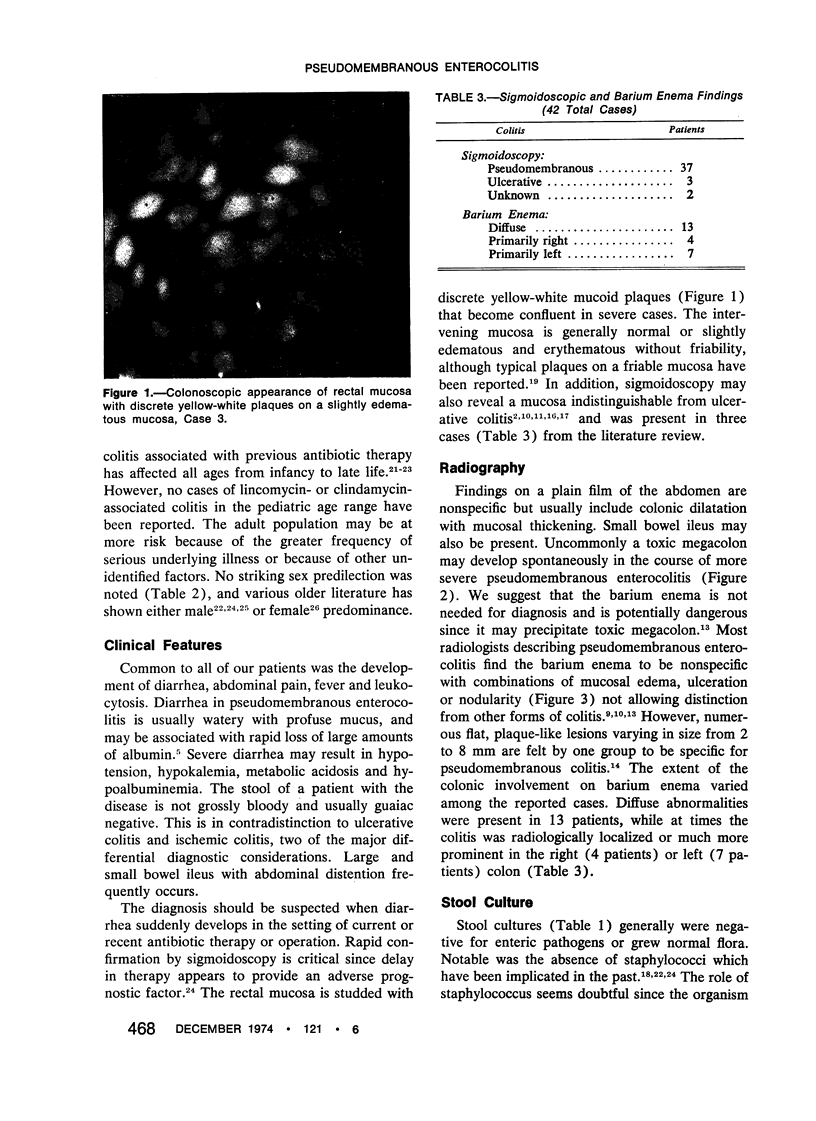
- Shimkin P. M., Link R. J. Pseudomembranous colitis: a consideration in the barium enema differential diagnosis of acute generalized ulcerative colitis. Br J Radiol. 1973 Jun;46(546):437–439. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-546-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroehlein J. R., Sedlack R. E., Hoffman H. N., 2nd, Newcomer A. D. Clindamycin-associated colitis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Apr;49(4):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F. J., Barton R. W., Alpers D. H. Clindamycin-associated colitis. A prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Oct;81(4):429–433. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-4-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F. J., Stanley R. J., Alpers D. H. Diagnostic features of clindamycin-associated pseudomembranous colitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 11;290(15):841–843. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404112901508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully T. E., Feinberg S. B. A reappearance of antibiotic-induced pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Radiology. 1974 Mar;110(3):563–567. doi: 10.1148/110.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]