Abstract
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most lethal malignant diseases. Gemcitabine‐based chemotherapy is still one of the first‐line systemic treatments, but chemoresistance occurs in the majority of patients. Recently, accumulated evidence has demonstrated the role of the tumour microenvironment in promoting chemoresistance. In the tumour microenvironment, pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) are among the main cellular components, and extracellular vesicles (EVs) are common mediators of cell‒cell communication. In this study, we showed that SP1‐transcribed miR‐31‐5p not only targeted LATS2 in pancreatic cancer cells but also regulated the Hippo pathway in PSCs through EV transfer. Consequently, PSCs synthesized and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteins (SPARC), which was preferentially expressed in stromal cells, stimulating Extracellular Signal regulated kinase (ERK) signalling in pancreatic cancer cells. Therefore, pancreatic cancer cell survival and chemoresistance were improved due to both the intrinsic Hippo pathway regulated by miR‐31‐5p and external SPARC‐induced ERK signalling. In mouse models, miR‐31‐5p overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells promoted the chemoresistance of coinjected xenografts. In a tissue microarray, pancreatic cancer patients with higher miR‐31‐5p expression had shorter overall survival. Therefore, miR‐31‐5p regulates the Hippo pathway in multiple cell types within the tumour microenvironment via EVs, ultimately contributing to the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, Hippo pathway, miR‐31‐5p, pancreatic cancer, pancreatic stellate cell
1. INTRODUCTION
Although cancer has been studied extensively, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, generally named pancreatic cancer, is still one of the most lethal malignant diseases. The current 5‐year survival rate of pancreatic cancer is still lower than 12% (Siegel et al., 2023). Radical surgery combined with chemotherapy is the only way to cure pancreatic cancer at present. However, during treatment, distant metastasis and local recurrence often occur due to chemoresistance, substantially shortening the survival of pancreatic cancer patients (Zeng et al., 2019). Therefore, it is necessary to explore the molecular mechanism underlying chemoresistance and develop novel therapeutics that can overcome chemoresistance.
Accumulated evidence indicates the key roles of miRNAs in pancreatic cancer progression, including roles in chemoresistance, which is mainly mediated by targeted inhibition of tumour suppressor mRNAs (Daoud et al., 2019). For example, our previous study suggested that miR‐10a‐5p could target TFAP2C and increase gemcitabine chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer (Xiong et al., 2018). In addition, miRNAs are preferably packaged into extracellular vesicles (EVs) or exosomes, affecting downstream pathways in recipient cells and modifying the tumour microenvironment (Zhang et al., 2015). EVs carrying miR‐155 could transmit chemoresistance ability among heterogeneous pancreatic cancer cells by targeting gemcitabine‐metabolizing genes, such as deoxycytidine kinase (Patel et al., 2017). Recently, many reports have suggested the vital role of EVs in communication in the tumour microenvironment, as they coordinate the behaviour of distinct cellular components and promote pancreatic cancer progression (Qin et al., 2023). Pancreatic cancer is characterized by extensive desmoplastic reactions and fibrosis, which are mainly mediated by collagen and cancer‐associated fibroblasts (CAFs) (Ho et al., 2020). CAFs can be divided into myofibroblastic CAFs, antigen‐presenting CAFs and inflammatory CAFs, depending on their markers and functions (Huang et al., 2022). Under physiological conditions, pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) are in the periacinar regions and participate in the maintenance of the pancreatic tissue architecture (Bynigeri et al., 2017). During the process of chronic pancreatitis and carcinogenesis, PSCs are stimulated and activated, show proliferative and contractile characteristics and differentiate into CAFs, contributing to pancreatic fibrosis (Bynigeri et al., 2017; Öhlund et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2022). A recent study further confirmed that myofibroblastic CAFs derived from PSCs could establish a tumour‐promoting desmoplastic milieu, indicating the key relationship between activated PSCs and pancreatic cancer cells (Helms et al., 2022).
Recent studies have shown that there is intense EV‐mediated communication between PSCs and pancreatic cancer cells. EV miR‐5703 derived from PSCs enhances pancreatic cancer progression by targeting CMTM4 and activating followed PI3K/Akt pathway (Li et al., 2020). Moreover, PSCs release miR‐21, which accelerates pancreatic cancer cell migration via indirectly regulating Ras/ERK pathway activity (Ma et al., 2020). However, the unidirectional transfer of EV miRNAs is not likely to reflect the complicated tumour microenvironment in vivo. The natural interaction between two cellular components is reciprocal, which can result in mutualistic symbiosis and deserves further study (Yan et al., 2018). In this study, we investigated our previously reported chemoresistance‐related miRNAs and focused on miR‐31‐5p and the Hippo pathway (Wang et al., 2016). Additionally, EV miR‐31‐5p derived from pancreatic cancer cells promotes secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteins (SPARC) release from PSCs, which also supports cancer cell survival (Munasinghe et al., 2020). Thus, the crosstalk between pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs establishes a chemoresistant tumour microenvironment.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Dataset sources
The miR‐31‐5p expression data and overall survival information of pancreatic cancer patients were analysed by CancerMIRNome website (http://bioinfo.jialab‐ucr.org/CancerMIRNome/) which contains The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (Li et al., 2022). The TransmiR2.0 website (http://www.cuilab.cn/transmir) containing public chromatin‐‑immunoprecipitation (ChIP)‐seq and Motif data was utilized to predict potential transcription factors of miR‐31‐5p (Tong et al., 2019). The Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) website (http://gepia.cancer‐pku.cn/) housing the TCGA database was employed to analyse the correlation between SP1 and SPARC expression (Li et al., 2021). Moreover, CRA001160, a single‐cell dataset from the Tumor Immune Single‐cell Hub (TISCH) database (http://tisch.comp‐genomics.org/) (Sun et al., 2021), was analysed to assess the cellular distribution of SP1 and SPARC expression (Peng et al., 2019).
2.2. Tissue microarray and clinical specimens
The tissue microarray (TMA, 5 μm thick), which includes 70 pairs of adjacent normal pancreatic tissues and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissues. Enrolled patients signed the informed consent form, and the study was approved by the ethical committees of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (I‐24PJ0401). Additionally, to investigate the transcription levels of miR‐31‐5p, the protein levels of SP1, large tumour suppressor kinase 2 (LATS2) and SPARC, the in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were performed on the TMA. The results were independently evaluated by two professional pathologists as follows: score = tumour cell (stromal cell for SPARC) proportion × staining intensity; proportion = 0 (no stained cells), 1 (< 10%), 2 (10%−25%), 3 (26%−49%) or 4 (≥50%); and staining intensity = 0 (negative), 1 (lightly yellow), 2 (brownish–yellow) or 3 (brown). Samples with staining scores between 0 and 4 were assigned to the low miR‐31‐5p group, while samples with scores ≥ 6 were assigned to the high miR‐31‐5p group. Plasma from 20 patients with pancreatic cancer and 10 healthy controls was utilized to analyse the miR‐31‐5p levels in plasma EVs. Informed consent was obtained from all patients before enrolment, and this study was approved by the ethical committees of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (I‐24PJ0401) (JS‐3349). All patients involved in this study received little preoperative treatment.
2.3. In situ hybridisation, immunohistochemistry and immunohistofluorescence
ISH was performed on pancreatic cancer samples using an ISH miR‐31‐5p detection kit (MK10180, Boster Biological Technology Co., Ltd., China). The process was conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, paraffin‐embedded tissue samples were cut into 5 μm thick sections, which were dewaxed stepwise with xylene, ethanol and water. Then, 3% H2O2 was utilized to remove endogenic peroxidase and pepsin was utilized to expose the nucleic acids. Next, sections were treated with an miR‐31‐5p‐digoxin probe and incubated at 40°C overnight. Afterwards, the slides were hydrated with saline sodium citrate solution and incubated in blocking buffer. Then, the slides were successively treated with a biotin‐labelled antibody against digoxin and streptavidin–biotin enzyme complex. Finally, Diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining solution was used to evaluate the relative level of miR‐31‐5p expression. IHC and immunohistofluorescence was performed according to a previously described protocol (Qin et al., 2023). The antibodies used were 0.4 μg/mL anti‐SPARC (1:1000, 15274‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.4 μg/mL anti‐cleaved caspase‐3 (1:100, 9664, Cell Signaling Technology, Massachusetts, USA), 0.2 μg/mL anti‐Ki67 (1:2000, 27309‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), and 4 μg/mL anti‐LATS2 (1:100, 20276‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 3.5 μg/mL anti‐SP1(1:200, 21962‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.5 μg/mL anti‐αSMA (1:1000, 67735‐1‐Ig, Proteintech, China), CoraLite488‐conjugated Goat Anti‐Mouse IgG (1:100, SA00013‐1, Proteintech, China) and CoraLite594‐conjugated Goat Anti‐Rabbit IgG (1:100, SA00013‐4, Proteintech, China).
2.4. Cell lines and culture conditions
The PANC‐1, BxPC‐3, PATU8988T, AsPC‐1 and MIA PaCa‐2 pancreatic cancer cell lines, and an immortalized pancreatic ductal cell line (HPNE) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, USA). The Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells (HPaSteC) line, thus PSC, was purchased from ScienCell Research Laboratories (California, USA). The cells were cultured in DMEM (HyClone, Utah, USA) and RPMI‐1640 (HyClone, Utah, USA) media with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS, Biological Industries, Israel) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Biological Industries, Israel) and were grown in a cell incubator (37°C with 5% CO2).
2.5. Transfection assay and stable cell line construction
When the seeded cells reached 70% confluence, they were infected with an SP1‐overexpression plasmid (SP1 OE), a LATS2‐overexpression plasmid (LATS2 OE), a SPARC‐overexpression plasmid (SPARC OE) or a negative control (Vector) (Shanghai Genechem, China). SP1 cDNA, LATS2 cDNA, or SPARC cDNA was subcloned into a pcDNA3.1(+) vector. Small interfering RNAs (siSP1, siRUNX1, siYY1, siLATS2, siSPARC) and scrambled siRNA (negative control, NC) were purchased from RiboBio (Guangzhou, China) and Tsingke (Beijing, China) to construct knockdown cells. Additionally, the miRNA mimic library, the miR‐31‐5p mimic and inhibitor and the respective negative controls (mimic NC and inhibitor NC) were purchased from RiboBio (Guangzhou, China) to control cellular miR‐31‐5p expression. The transfection process was conducted with Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen, Lithuania) according to the manufacturer's instructions. To construct stable cell lines, miR‐31‐5p mimic or inhibitor sequences or RAB27a siRNA sequences were cloned into Ubi‐MCS‐3FLAG‐SV40‐Puro lentiviral vectors (Shanghai Genechem, China). To knock out the hsa‐miR‐31 gene using the CRISPR–Cas9 genomic editing system, two guide RNAs (targeted sequences: TGCTGGCATAGCTGTTGAAC and TGGCAATATGTTGGCATAGC) were synthesized in DNA form and cloned into MCS‐EF1a‐Cas9‐FLAG‐P2A‐puro vectors (Shanghai Genechem, China). The lentiviral vectors were utilized to package viral particles. PANC1 and MIA PaCa‐2 cells were infected with the lentivirus for over 24 h. Then, puromycin (1 μg/mL, Sigma‒Aldrich, Missouri, USA) was added to the medium to remove uninfected cells.
2.6. Conditional culture
A coculture system was constructed as described previously (Hergenreider et al., 2012). Briefly, recipient cells were seeded in 6‐well plates (3 × 105 cells per well), and donor cells were seeded into well inserts with 0.4 μm pores (3 × 105 cells per insert, Corning Transwell 3450). After cell adherence, the inserts were placed in 6‐well plates to construct a coculture system. To avoid the influence of FBS containing EVs, we used exosome‐depleted FBS (C3801, Biological Industries, Israel) after conditional culture. To inhibit EVs release from the donor cells, 10 μM GW4869 (HY‐19363, MedChemExpress, USA), a neutral sphingomyelinase inhibitor, was added to the upper compartment of the coculture system for 48 h. In addition to the coculture system, some other treatments were used for the cells. To test the ability of EVs to affect downstream pathways in recipient cells, we treated cells with PANC‐1 derived EVs, miR‐31‐5p mimic EVs, or miR‐31‐5p knockout EVs (5 μg/mL) for 48 h. To exclude endogenous miR‐31‐5p effects in PSCs, 10 μM 5,6‐Dichlorobenzimidazole riboside (DRB) (HY‐14392, MedChemExpress, USA), an RNA biogenesis inhibitor, was employed to accompany with EVs treatment. To test the role of PSC‐secreted SPARC in pancreatic cancer cells, we added 3 μg/mL recombinant human SPARC (120‐36‐50G, PeproTech, USA) to the cell medium and tested the cell phenotype in terms of proliferation and chemoresistance.
2.7. EV purification and characterization
Cell‐derived EVs were purified from the cell culture medium by a previously described protocol (Hergenreider et al., 2012). Briefly, conditioned medium was collected from cultured cells grown in EV‐free medium for 24 h. The medium was centrifuged at 500 × g for 15 min at 4°C and then filtered through a 0.22 μm filter (SLGP033RB, Millipore, USA) to eliminate cells and debris. EVs were pelleted by ultracentrifugation at 110,000 × g for 70 min and washed with PBS at 110,000 × g for 70 min at 4°C. Finally, 100 μL of PBS was used to suspend the EV pellet for various experiments. Plasma‐derived EVs were extracted with a Size‐Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Kit (Exosupur, Echo Biotech, China). The process was conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 1 mL of plasma was added to the column bed, and relevant fractions were collected and concentrated with a 100 kDa centrifugal concentrator (UFC8100, Millipore, USA). Freeze‒thaw cycles were avoided for the fractions. EVs were characterized by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA, ZetaView, Particle Metrix, Germany) and transmission electron microscopy (JEOL, Japan) for particle morphology and Western blotting for EV protein marker detection. For NTA, the EVs samples were comprehensively tested in 3 cycles by 11 cameras in different positions. For comparing the EVs release from pancreatic cancer cells with lentivirus NC and lentivirus siRAB27A, same cell numbers were seeded on the culture dish with same volume of EV‐free medium. Conditional medium was collected after 24 h, and the EVs were purified via abovementioned method. The EV numbers were calculated by NTA as well.
2.8. PKH67 staining and EVs transfer tracking
Twenty micrograms of EVs derived from MIA PaCa‐2 cells were labelled with a PKH67 Green Fluorescent Cell Linker Kit (MINI67, Sigma, USA). The process was conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions. EVs in PBS and PKH67 were diluted in Diluent C and mixed for 5 min. Then, 3% BSA (ST2249, Beyotime, China) was employed to end the staining reaction. Then, EVs labelled with PKH67 were isolated with an SEC Kit (Exosupur, Echo Biotech, China). EVs labelled with PKH67 were added to PSC culture medium. After 24 h, the PSC cells were stained with Hoechst and washed with PBS three times. Fluorescence results for EV absorption were obtained from images captured via confocal microscopy (AX, Nikon). For further tracking the transfer of miR‐31‐5p from cancer cells to PSCs, we transfected pancreatic cancer cells with FAM (6‐carboxy‐fluorescein) labelled miR‐31‐5p. After 6 h, we cocultured transfected pancreatic cancer cells with PSCs by abovementioned coculture system for 24 h. The Fluorescence results were recorded by confocal microscopy (AX, Nikon).
2.9. RNA isolation and qRT‒PCR
We extracted total RNA with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, California, USA). A NanoDrop ND‐1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, USA) was utilized to monitor the quantity of extracted RNA. A reverse transcription kit (Thermo Fisher, Lithuania) and SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Lithuania) were employed to synthesize complementary DNA and conduct quantitative PCR (qRT‒PCR). To detect miR‐31‐5p levels, reverse transcription and qRT‒PCR were performed with All‐in‐One miRNA qRT‒PCR Detection Kit 2.0 (QP116, GeneCopoeia, USA). β‐Actin and U6 primers were used as internal controls for cellular mRNA and miRNA, respectively (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). For EV miR‐31‐5p detection, the synthetic miRNA cel‐miR‐39‐3p (5 fmol/μL, Sequence: 5′‐UCACCGGGUGUAAAUCAGCUUG‐3′, RiboBio, China) was added to samples as an exogenous control. For comparing the miR‐31‐5p levels between cell lysate and EVs, the RNA concentration measured by NanoDrop ND‐1000 spectrophotometer were utilized as control. Relative expression was calculated via the 2−ΔΔCT method. The sequences of the primers used in this study are listed in Table S1.
2.10. Western blotting
RIPA lysis buffer with protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Beyotime, China) was utilized to extract total cellular protein. Cytoplasmic‐Nuclear protein separation kit (AQ805, Analysis Quiz, China) was used to extract cytoplasmic and nuclear protein according to manufacturer's instructions. The concentrations of protein samples and EVs samples were quantified by a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime, China) (LABLEAD, China). Western blotting was performed according to the same protocol reported in our previously published article (Qin et al., 2023). The primary antibodies used in this study were 0.35 μg/mL anti‐SP1 (21962‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.4 μg/mL anti‐LATS2 (20276‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.375 μg/mL anti‐YAP1 (3584‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.4 μg/mL anti‐SPARC (15274‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.24 μg/mL anti‐phospho‐YAP1 (ab76252, Abcam, UK), anti‐vinculin (66305‐1‐Ig, Proteintech, China), 0.2 μg/mL anti‐β actin (81115‐1‐RR, Proteintech, China), 0.2 μg/mL anti‐α tubulin (11224‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.502 μg/mL anti‐phospho‐ERK1/2 (4370, Cell Signaling Technology, Massachusetts, USA), 0.25 μg/mL and anti‐ERK1/2 (11257‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China). The secondary antibodies used were 0.08 μg/mL goat anti‐rabbit IgG (ZSGB‐BIO, ZB‐2301, China) and 0.08 μg/mL goat anti‐mouse IgG (ZSGB‐BIO, ZB‐2305, China). 0.6 μg/mL Anti‐ GM130 (11308‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.6 μg/mL Anti‐VDAC1 (55259‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 1 μg/mL Anti‐CD81 (66866‐1‐Ig, Proteintech, China), 0.8 μg/mL Anti‐CD63 (25682‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.6 μg/mL Anti‐CD9 (20597‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China), 0.2 μg/mL anti‐TSG101 (ab125011, Abcam, UK), 1 μg/mL anti‐Calnexin (ab22595, Abcam, UK), 0.4 μg/mL anti‐Alix (12422‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China) and 0.25 μg/mL anti‐Histone H3 (17168‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China) antibodies were also used.
2.11. Immunofluorescence assay
After transfection, cells were seeded in cell culture slides (Solarbio, China). After 24 h of culture, 4% paraformaldehyde was added for 10 min. Then, the cells were permeabilized with 1% Triton X‐100 for 5 min. Blocking was performed with 3% BSA, and the samples were then incubated with anti‐YAP1 (3584‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China) at 4°C overnight. Then, the slides were incubated with fluorophore‐conjugated secondary antibodies (SA00013‐2, Proteintech, China) for 1.5 h at room temperature in the dark. Finally, the cell culture slides were mounted with fluorescent mounting medium containing DAPI (ZSGB‐BIO, ZB‐2301, China). Images were acquired by confocal microscopy (AX, Nikon). The distribution of YAP1 in the nucleus or cytoplasm was analysed via ImageJ V1.53. Briefly, DAPI and YAP1 signal for the same field were imported into the ImageJ. DAPI positive area was regarded as cell nucleus. Nuclear fluorescence is equal to the YAP1 signal within the nuclear area. Cytoplasmic fluorescence = total YAP1 fluorescence—nuclear fluorescence.
2.12. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay
A Pierce Magnetic ChIP Kit (26157, Thermo Scientific, USA) was employed to test the interaction of SP1 and the miR‐31‐5p gene promoter. The process was conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, the cells were collected after being fixed with 4% formaldehyde. Then, the cells were lysed, and the nucleic acids were degraded with micrococcal nuclease (MNase). Sonication at 4°C was performed to break the chromatin into fragments. Five micrograms of anti‐IgG or anti‐SP1 (21962‐1‐AP, Proteintech, China) was incubated with the chromatin–protein complex. We finally purified the DNA with protein A/G magnetic beads. The results were further analysed by qRT‒PCR.
2.13. DNA agarose gel electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis was conducted as previously reported (Mukai et al., 2020). One percent agarose gels were made (Sigma‒Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) and stained with Ultra GelRed (Vazyme, Jiangsu, China). After adding the DNA sample, the gel was run for 50 min at a 110 V constant voltage in 1× Tris‐Borate‐EDTA (TBE) buffer (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). The gels were finally scanned with a gel imaging system.
2.14. Dual‑luciferase reporter assay
A dual‐luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the direct interaction between miR‐31‐5p and the 3′UTR (Untranslated Region) of LATS2 mRNA. The control sequence and the wild‐type and mutant 3′UTR sequences of LATS2 mRNA were cloned into the SV40 vector containing the luciferase sequence to construct reporter plasmids (Shanghai GeneChem, China). The cells were transfected with miR‐31‐5p mimic (or inhibitor) and luciferase reporter plasmids. In addition, the binding of SP1 and the miR‐31‐5p gene promoter region was also confirmed by a dual‐luciferase reporter assay. The control sequence, wild‐type 2000 bp, wild‐type 500 bp, and mutant 500 bp miR‐31‐5p gene promoter region sequence were cloned into the GV238 vector containing the luciferase sequence (Shanghai GeneChem, China). The cells were transfected with SP1 siRNA (or SP1 overexpression plasmids) and promoter region luciferase reporter plasmids. After 48 h of transfection, we lysed the cells and conducted experiments with a Dual Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay Kit (11402ES60, Yeasen Biotechnology, China). A multifunctional microplate reader (Synergy H1, Biotek, USA) was utilized to obtain the bioluminescence results.
2.15. Cell proliferation, colony formation assays and growth inhibition assays
Twenty‐four hours after transfection, MIA PaCa‐2 or PANC‐1 cells were seeded in 96‐well plates (3000 cells per well). Then, a sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay (Sigma‒Aldrich, Missouri, USA) was used to measure cell viability at different times (Hergenreider et al., 2012). A multifunctional microplate reader (Synergy H1, Biotek, USA) was utilized to determine the optical density at 564 nm (OD564). For the colony formation assay, we seeded the transfected cells into 6‐well plates (1000 cells per well). After 2 weeks, 0.4% crystal violet (Sigma‒Aldrich, Missouri, USA) in methanol was used to stain the cells, which were then photographed. For growth inhibition assays, 24 h after transfection, MIA PaCa‐2 or PANC‐1 cells were seeded into 96‐well plates (3000 cells per well). Upon cell adherence, each well was treated with control medium (0 gemcitabine concentration) and gradient gemcitabine (Vianex S.A.‐Plant C, Greece) concentrations (from 1 nM to 1 mM for MIA PaCa‐2; from 10 nM to 10 mM for PANC‐1). After 48 h of incubation, the SRB assay was performed to evaluate cell viability and the inhibition rate. Cell viability (%) = OD564 under gradient gemcitabine concentrations / OD564 under control medium × 100%; Inhibition rate (%) = 100%—Cell viability (%).
2.16. Apoptosis assay
Pancreatic cancer cells were seeded into 6‐well plates. At 24 h after treatment (with mimic, inhibitor or rhSPARC), the cells were treated with gemcitabine (1 μM for MIA PaCa‐2; 10 μM for PANC1, Vianex S.A.‐Plant C, Greece). All cells in one well were collected in binding buffer at 48 h after treatment. Next, propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin V‐FITC were used to stain the cells according to the manufacturer's instructions (Yishan Biotechnology, China). Analysis of the results was performed with FlowJo V10.8.1. Because it is hard to distinguish late apoptosis and necrosis in the second quadrant (PI+/Annexin V‐FITC+, the second quadrant, Q2). Therefore, only the early apoptotic cells (PI‐/Annexin V‐FITC+, Q3) were calculated.
2.17. ELISA
The Human SPARC Quantikine Enzyme‐Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Kit (#DSP00, R&D Systems) was utilized to perform ELISA. Conditioned medium from PSCs (in 10% FBS) was collected and diluted 8‐fold in Calibrator Diluent RD6‐59. Standard samples were prepared, and the procedure was conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions. Additionally, to eliminate the influence of FBS‐containing SPARC, the SPARC concentration in whole medium with 10% FBS was also tested, which was subtracted in the subsequent data analysis as background. A multifunctional microplate reader (Synergy H1, Biotek, USA) was utilized to determine the optical density at 450 nm.
2.18. Animal experiments
In this study, animal experiments were conducted under the inspection of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in Peking Union Medical College Hospital (XHDW‐2023‐036, XHDW‐2022‐105, XHDW‐2023‐081). Pancreatic cancer cells were constructed with the aforementioned lentivirus. Pancreatic cancer cells were suspended and subcutaneously injected into the dorsal region of 8‐week‐old BALB/c nude mice (Chinese Academy of Sciences, China) (5 × 106 cells in 300 μL of PBS per mouse). For coinjected tumours, equal numbers of two cell types (2.5 × 106 pancreatic cancer cells and 2.5 × 106 PSCs) were concurrently injected into the backs of nude mice. For orthotopic xenograft models, 2.5 × 106 pancreatic cancer cells and 2.5 × 106 PSCs (or 2.5 × 106 pancreatic cancer cells only) in 40 μL diluted Matrigel Matrix (354234, CORNING, USA) (1:1 diluted with PBS) were concurrently injected into the pancreas of 8‐week‐old nude mice (Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology, China). According to previous publications, 5–6 mice (5–6 technical repetitions) were determined to be the minimum number for each group. The person who assessed the tumour size was blinded to the treatment and group distribution. Subcutaneous tumour size was measured as the tumour volume (mm3 = 1/2 × length × width2). To test the ability of miR‐31‐5p to enhance chemoresistance in vivo, gemcitabine was used to treat mice via intraperitoneal injection (25 mg/kg, twice weekly). To test the ability of EV miR‐31‐5p to enhance chemoresistance in vivo, intraperitoneal injection gemcitabine (25 mg/kg) and tail vein injection EVs (20 μg in 100 μL PBS per mouse) were simultaneously provided twice weekly. For orthotopic models, same frequency (twice weekly) and doses of gemcitabine (25 mg/kg) and EVs (20 μg in 100 μL PBS per mouse, mimic NC EVs or miR‐31‐5p mimic EVs) were administrated two days after the coinjection for 2 weeks. The involved mice with subcutaneous xenografts were sacrificed 34 days after administration or when the xenograft major axis approached 2000 mm in length (Ethical restriction), and all xenografts were resected for subsequent experiments.
2.19. Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 9 Software was utilized to generate graphs and statistical results. ANOVA, unpaired Student's t test or paired Student's t test was used to compare differences among groups. Overall survival (OS) curves were generated via the Kaplan‒Meier method. All the experiments were repeated at least three times. Differences were determined to be significant when the p‐value was lower than 0.05 (two‐sided).
3. RESULTS
3.1. miR‐31‐5p promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer
In our previous publication, we found many chemoresistance‐related miRNAs in pancreatic cancer cells with an miRNA microarray (Wang et al., 2016). To further investigate the ability of these miRNAs to promote pancreatic cancer chemoresistance, we constructed an miRNA mimic library containing the top 19 chemoresistance‐related miRNAs. Gemcitabine‐based chemotherapy, one of the first‐line chemotherapeutics for pancreatic cancer patients, was employed to acquire IC50 values via a chemosensitivity assay in three pancreatic cancer cell lines after transfection of the miRNA mimic library. Under gradient gemcitabine treatment, the majority of chemoresistance‐related miRNAs increased IC50 values in pancreatic cancer cells, thus promoting chemoresistance (Figure 1a–c). To explore which one is most meaningful among these miRNAs, five different miRNAs with top IC50 values in three pancreatic cancer cell lines were intersected, only miR‐31‐5p could obviously elevated IC50 values in all three cell lines (Figure 1d). The role of miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer was subsequently analysed. In the TCGA database, high miR‐31‐5p expression was obviously related to poor prognosis (Figure 1e). The basal miR‐31‐5p expression levels in pancreatic cancer cell lines were compared (Figure 1f). MIA PaCa‐2 cells were utilized for miR‐31‐5p upregulation by the mimic, and PANC‐1 cells were employed for miR‐31‐5p downregulation by the inhibitor. The miR‐31‐5p mimic significantly increased cell proliferation and gemcitabine resistance (Figure 1g–i). The miR‐31‐5p inhibitor significantly decreased cell proliferation and increased gemcitabine sensitivity (Figure 1j‒l). Additionally, miR‐31‐5p inhibitor significantly promoted cell apoptosis under gemcitabine treatment (Figure 1m), while miR‐31‐5p mimic repressed cell apoptosis (Figure 1n). Therefore, miR‐31‐5p might contribute to chemoresistance.
FIGURE 1.
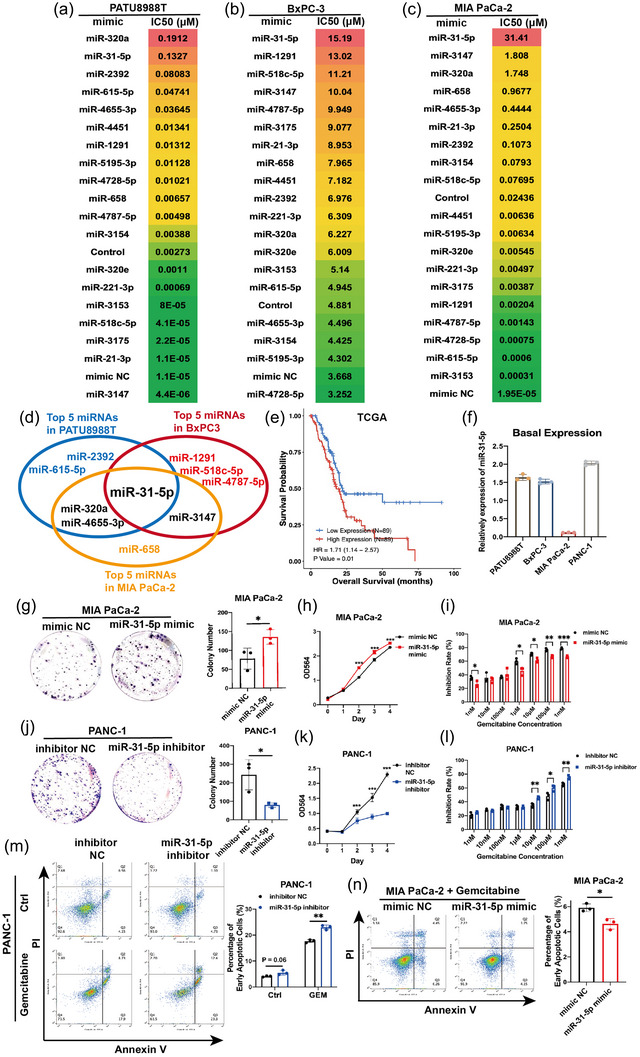
miR‐31‐5p promotes pancreatic cancer cell chemoresistance and proliferation and reduces apoptosis. (a)–(c) IC50 results from the growth inhibition assay in PATU8988T, BxPC‐3 and MIA PaCa‐2 cells treated with gradient gemcitabine after transfection of the miRNA mimic library. Control treatment represents that cells were only treated with transfection agents without any exogenous RNA. (d) The intersection of top five miRNA mimics in three Individual pancreatic cancer cell lines. The miR‐31‐5p mimic showed an obvious ability to promote gemcitabine chemoresistance in both cell lines. (e) High miR‐31‐5p expression was related to shorter survival in the TCGA database. (f) Basal expression of miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cell lines. (g)–(l) miR‐31‐5p promoted proliferation and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa‐2 and PANC‐1 cells. (m), (n) miR‐31‐5p reduced apoptosis in PANC‐1 and MIA PaCa‐2 cells under gemcitabine treatment. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
3.2. SP1 transcribes miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells
To identify the upstream regulator of miR‐31‐5p, a widely used transcription factor database TransmiR2.0 was searched (Tong et al., 2019). TransmiR2.0 collected miRNA genome information, public chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP‐seq) data from high‐throughput experiments and transcription factor binding motifs information. It could infer possible transcription factors by coordinating the ChIP‐seq data and transcription factor binding motifs information with the transcription start sites of miRNA in genome (Tong et al., 2019). Therefore, TransmiR2.0 was utilized to infer possible transcription factors of miR‐31‐5p based on ChIP‐seq and motif sequence information (Table S2 and S3). The results showed that Specificity protein 1 (SP1), runt‐related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) and YIN YANG 1(YY1) are three potential transcription factors of miR‐31‐5p (Figure 2a). However, RUNX1 and YY1 downregulation failed to affect miR‐31‐5p expression (Figure 2b,c). SP1 downregulation decreased miR‐31‐5p expression (Figure 2d), and SP1 overexpression promoted miR‐31‐5p expression (Figure 2e). To clarify that SP1 could directly transcribe miR‐31‐5p, the fine mechanism was further studied in detail. There are two conventinal kinds of possible transcription start sites of miRNA (Tong et al., 2019) (Liu et al., 2018). First, miR‐31‐5p shares the promoter with its host gene, thus MIR31HG (lncRNA). Second, miR‐31‐5p has its own promoter just before its 5′‐end (Tables S2 and S3). Previous study showed that miR‐31‐5p levels were stable after MIR31HG downregulation and overexpression in pancreatic caner cells, which indicated that MIR31HG and miR‐31‐5p expression are relatively independent (Yang et al., 2016). Similarly, miR‐31‐5p and MIR31HG levels were detected in pancreatic cancer cells after downregulating SP1, miR‐31‐5p levels were decreased with unchanged MIR31HG expression (Figure S1). Therefore, in pancreatic cancer cells, miR‐31‐5p might be controlled by SP1 through its own promoter. According to the JASPAR database (Castro‐Mondragon et al., 2022), there are three motif sequences in the promoter region of miR‐31‐5p, which could be named locations a, b and c. Location c has the highest prediction score among those three locations (Figure 2f,g). To clarify the transcriptional role of SP1 in vivo, we constructed full‐length wild‐type, shortened wild‐type and mutant luciferase reporter gene plasmids (Figure 2h). The dual‐luciferase reporter system also confirmed that SP1 could bind location c and miR‐31‐5p transcript in vivo in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure 2i,j). We designed primers to further confirm the binding site and thus location c. The ChIP‐PCR results showed that SP1 could bind to the DNA fragment containing location c (Figure 2k,l); thus, SP1 could bind to the miR‐31‐5p promoter region. The ChIP‒qPCR results further indicated binding between SP1 and the miR‐31‐5p promoter region (Figure 2m,n). Thus, SP1 transcribes miR‐31‐5p by directly binding its promoter region. The rescue experiments showed that miR‐31‐5p could significantly reverse the effects of SP1 on pancreatic cancer proliferation (Figure 2o,p) and chemosensitivity (Figure 2q,r). Thus, SP1 promoted pancreatic cancer progression through miR‐31‐5p transcription.
FIGURE 2.
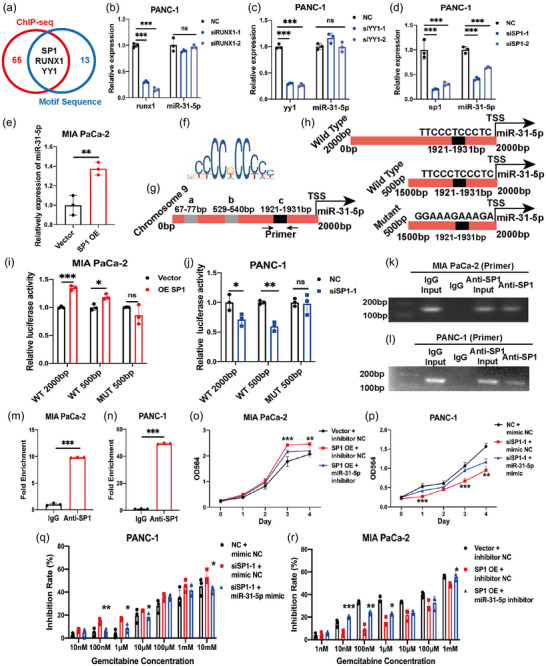
SP1 transcribes miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells. (a) Predicting upstream transcription factors with the TransmiR2.0 website, which is based on public ChIP‐seq results and motif sequences. (b), (c) RUNX1 and YY1 downregulation failed to downregulate miR‐31‐5p expression. (d) SP1 downregulation could decrease miR‐31‐5p expression. (e) SP1 overexpression increased miR‐31‐5p expression. (f) The motif model of SP1. (g) The three potential binding regions (a, b and c) predicted by the JASPAR database in the promoter region of miR‐31‐5p. (h) Luciferase reporter gene plasmid design. (i), (j) SP1 activated the activity of luciferase reporter gene plasmids with wild‐type sequences. (k)–(n) ChIP‐PCR and ChIP‒qPCR showed that SP1 could bind to the promoter region of miR‐31‐5p. (o), (p) miR‐31‐5p partially rescued the effects of SP1 on cell proliferation. (q), (r) miR‐31‐5p partially rescued the effects of SP1 on chemoresistance. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. ChIP, chromatin‐‑immunoprecipitation.
3.3. miR‐31‐5p represses LATS2 and regulates the Hippo pathway in pancreatic cancer cells
To clarify the downstream target of miR‐31‐5p, we integrated three databases, TargetScan, miRDB and Targetminer, to predict the binding between miRNA and mRNA (Figure 3a). Among the investigated pairs, miR‐31‐5p and the LATS2 transcript showed a high probability of binding (8 mer seed match) (Figure 3b). Additionally, it has been reported that miR‐31‐5p could target the LATS2 transcript in many other cancer types with conservative properties (Cheng et al., 2022) (Hsu et al., 2019; Yuan et al., 2021). Therefore, miR‐31‐5p and LATS2 were further explored. miR‐31‐5p inhibited LATS2 expression at the RNA level (Figure 3c), while the miR‐31‐5p inhibitor upregulated LATS2 expression (Figure 3d). Additionally, overexpressing and downregulating SP1 expression also respectively changed LATS2 expression levels (Figure 3e,f), further indicating SP1/miR‐31‐5p/LATS2 pathway. LATS2 is a key regulator in the Hippo pathway that can phosphorylate Yes1‐associated transcriptional regulator (YAP1) and restrict its nuclear localization, thus inhibiting downstream pathways of YAP1 (Fu et al., 2022). Consistently, miR‐31‐5p overexpression repressed LATS2 expression and phosphorylated YAP1 at the protein level (Figure 3g). miR‐31‐5p downregulation increased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels (Figure 3h). Given that SP1 could transcribe miR‐31‐5p, the pathway from SP1 to the Hippo pathway was further verified. SP1 overexpression decreased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels (Figure 3i). SP1 downregulation increased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels (Figure 3j). Moreover, rescue experiments were performed. In the context of SP1 overexpression, miR‐31‐5p downregulation increased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels (Figure 3k). In the context of SP1 downregulation, miR‐31‐5p overexpression increased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels (Figure 3l).
FIGURE 3.
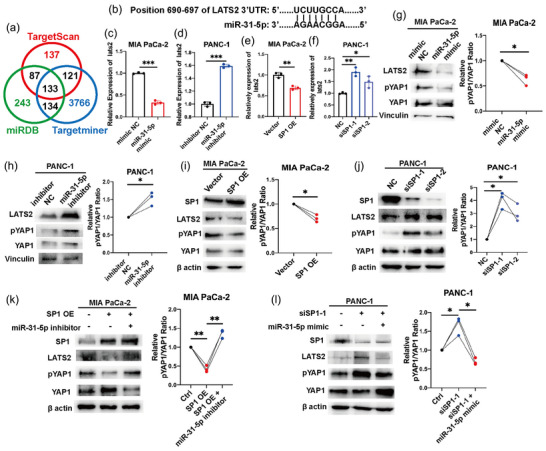
miR‐31‐5p regulates LATS2 expression in pancreatic cancer cells. (a) Prediction of the downstream mRNA of miR‐31‐5p on the basis of three public databases. (b) miR‐31‐5p has a strong ability to bind the 3′UTR region of LATS2 (8‐mer). (c), (d) miR‐31‐5p regulated LATS2 expression at the mRNA level. (e), (f) miR‐31‐5p regulated LATS2 expression at the mRNA level. (g), (h) miR‐31‐5p regulated LATS2 expression and the downstream Hippo pathway at the protein level. (i), (j) SP1 regulated LATS2 and the downstream Hippo pathway at the protein level. (k), (l) The effects of SP1 on the LATS2 and Hippo pathways were rescued by miR‐31‐5p. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
To confirm the direct binding between miR‐31‐5p and the 3′UTR of LATS2 mRNA, wild‐type and mutant luciferase reporter gene plasmids were constructed to clarify the direct interaction between miR‐31‐5p and LATS2 mRNA (Figure 4a). The dual‐luciferase reporter system confirmed that miR‐31‐5p could bind to the mRNA of LATS2 in vivo in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure 4b,c). To clarify the ability of miR‐31‐5p to inhibit the Hippo pathway, immunofluorescence was performed to detect the location of YAP1 in pancreatic cancer cells. miR‐31‐5p overexpression significantly promoted the nuclear translocation of YAP1, while miR‐31‐5p downregulation reduced nuclear YAP1 levels (Figure 4d–h). Rescue experiments focusing on the miR‐31‐5p/LATS2 pathway at the protein level showed that LATS2 could reverse the effects of miR‐31‐5p on the Hippo pathway and its downstream targets, such as BIRC5 (Hao et al., 2019) (Figure 4i,j). Additionally, rescue experiments focusing on proliferation and chemosensitivity phenotypes were performed. LATS2 significantly reversed the effect of miR‐31‐5p on cell proliferation and chemoresistance (Figure 4k–n). Considering that nuclear YAP1 can transcribe oncogenes, including CYR61, CTGF, BIRC5, and ANKRD1 (Li et al., 2022; Pu et al., 2019; Saikawa et al., 2018), the downstream targets of the Hippo pathway were also evaluated in RNA levels. miR‐31‐5p obviously enhanced their expression (Figure S2A,B), which further supported the role of the miR‐31‐5p/Hippo pathway in pancreatic cancer progression and chemoresistance.
FIGURE 4.
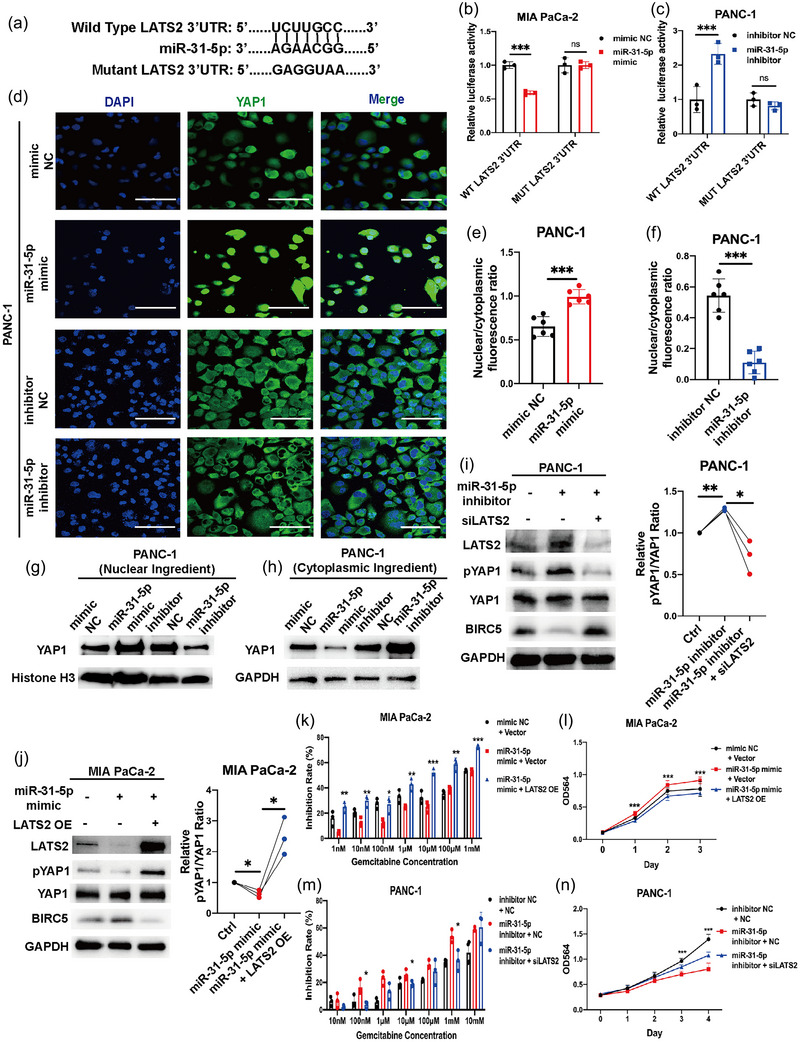
miR‐31‐5p directly repressed LATS2 mRNA expression and promoted chemoresistance and proliferation by regulating LATS2. (a) Model of luciferase reporter plasmids for LATS2 with wild‐type and mutant 3′UTRs. (b), (c) Luciferase activity in pancreatic cancer cells after transfection with miR‐31‐5p mimic/inhibitor and luciferase reporter plasmids. miR‐31‐5p could target LATS2 3′UTR. (d)–(f) miR‐31‐5p increased the nuclear localization of YAP1 in pancreatic cancer cells. (g), (h) The YAP1 protein levels in the nuclear and cytoplasmic ingredients. (i), (j) miR‐31‐5p regulated YAP1 phosphorylation (phospho‐Ser127) and downstream target, BIRC5, via LATS2 at the protein level. (k)–(n) LATS2 rescued the ability of miR‐31‐5p to promote chemoresistance and proliferation. Scale bars equal 50 μm. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
3.4. Pancreatic cancer cells regulate the Hippo pathway and promote SPARC expression in PSCs via miR‐31‐5p in EVs
The basal expression of miR‐31‐5p was significantly lower in PSCs than in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure 5a). The miR‐31‐5p levels were significantly upregulated in PSCs cocultured with pancreatic cancer cells (Figure 5b). However, under treatment with GW4869 (an exosome biogenesis inhibitor) (Cao et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2023; Xie et al., 2022), PSCs were resistant to the increase in miR‐31‐5p expression (Figure 5b). EVs components from PANC‐1 cell culture medium obviously increased the miR‐31‐5p levels of PSCs when compared with the supernatant components treatment (Figure 5c). Moreover, at the protein level, PSCs cocultured with pancreatic cancer cells showed decreased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels, while GW4869 treatment recovered these effects (Figure 5d), which indicated the possibility that pancreatic cancer cells transmitted EV miR‐31‐5p to regulate the Hippo pathway in PSCs. Additionally, in the coculture system, miR‐31‐5p overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells decreased LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels in PSCs (Figure 5e). To exclude that pancreatic cancer cells might also transmit EVs SP1 protein to PSCs and induce downstream Hippo pathway, we further detected SP1 levels in PSCs after coculturing with PANC‐1. SP1 protein levels were stable between control and coculture system (Figure S3A), indicating there is no obvious transfer of SP1 protein between cancer cells and PSCs. We extracted EVs from the cell medium of pancreatic cancer cell lines. The quality of the EVs was assessed by protein markers, NTA and morphology analysis (Figure S4A–F). SP1 protein was also negative in pancreatic cancer cell EVs (Figure S4A). EV miR‐31‐5p levels were also assessed among pancreatic cancer cell lines and normal pancreatic ductal cells. miR‐31‐5p levels were relatively higher in the EVs derived from pancreatic cancer cells (Figure S4G,H). Similarly, both coculturing with pancreatic cancer cells and EVs from pancreatic cancer cells could decrease LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels in PSCs (Figure 5f). To further exclude the endogenous miR‐31‐5p in PSCs, the RNA biogenesis inhibitor, 5,6‐Dichlorobenzimidazole riboside, thus DRB, was utilized (Cao et al., 2022). PANC‐1 EVs elevated miR‐31‐5p levels of recipient PSCs even under DRB treatment, further supporting the transfer of EV miR‐31‐5p (Figure 5g). To acquire sufficient miR‐31‐5p mimic EVs, we employed lentiviral transfection to stably overexpress miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure 5h). miR‐31‐5p in EVs effectively increased miR‐31‐5p levels in the recipient PSCs (Figure 5i). Similarly, to acquire miR‐31‐5p knockout (KO) EVs, we employed the CRISPR‒Cas9 system to stably knock out miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure S4I). The respective EVs were collected from the cell culture medium. After labelling EVs with PKH67, the treated PSCs (recipient cells) showed green spots (Figure 5j), which indicated that the PSCs could accept EVs derived from pancreatic cancer cells. Moreover, the protein levels of LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 were also decreased under EV miR‐31‐5p treatment (Figure 5k). Consistently, EV miR‐31‐5p failed to change the SP1 protein levels in PSCs (Figure S3B). To further confirm the role of miR‐31‐5p in PSCs, miR‐31‐5p mimic or inhibitor was transfected into PSCs. miR‐31‐5p overexpression and downregulation obviously altered LATS2 and phosphorylated YAP1 levels in PSCs (Figure 5l). Immunofluorescence was further performed to evaluate the ability of miR‐31‐5p to regulate the Hippo pathway. Similarly, miR‐31‐5p effectively promoted the nuclear translocation of YAP1 (Figure 5m,n); thus, the Hippo pathway was inhibited.
FIGURE 5.
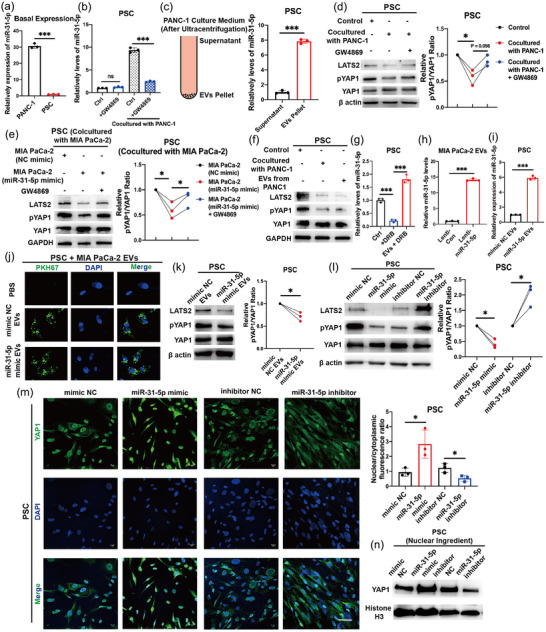
Pancreatic cancer cells transferred EV miR‐31‐5p to PSCs. (a) The basal expression of miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs. Pancreatic cancer cells expressed higher miR‐31‐5p than PSCs. (b) The expression of miR‐31‐5p in PSCs in the control and cocultures subjected to PANC‐1. GW4869 treatment repressed the elevated miR‐31‐5p in PSCs under coculture. (c) After treating with EVs Pellet from pancreatic cancer cells culture medium, the miR‐31‐5p levels in PSCs was significantly increased. (d) The levels of LATS2 and pYAP1 (phospho‐Ser127) in PSCs in the control and cocultures subjected to PANC1 or GW4869 treatment. GW4869 treatment reversed LATS2 expression and Hippo pathway. (e) The levels of LATS2 and pYAP1 (phospho‐Ser127) in PSCs cocultured with pancreatic cancer cells. GW4869 treatment reversed LATS2 expression and Hippo pathway in PSCs, which is driven by miR‐31‐5p mimic in pancreatic cancer cells. (f) Both cocultures subjected to PANC‐1 and its EVs inhibited the levels of LATS2 and pYAP1 (phospho‐Ser127) in PSCs. (g) PANC‐1 EVs upregulated miR‐31‐5p levels in PSCs even under DRB treatment. (h) Higher amounts of miR‐31‐5p in EVs extracted from stable miR‐31‐5p‐overexpressing cells. (i) EV miR‐31‐5p increased the levels of miR‐31‐5p in the recipient PSCs. (j) PSCs absorbed PKH67‐labelled EVs from pancreatic cancer cells. (k) EV miR‐31‐5p decreased LATS2 and pYAP1 (phospho‐Ser127) levels in the recipient PSCs. (l) miR‐31‐5p inhibited LATS2 and pYAP1 (phospho‐Ser127) expression in PSCs. (m) miR‐31‐5p enhanced YAP1 nuclear localization in PSCs. (n) miR‐31‐5p increased the YAP1 protein levels in the nuclear ingredient of PSCs. Scale bars equal 25 μm. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. EV, extracellular vesicle; PSC, pancreatic stellate cell.
In PSCs, SPARC can be transcribed by YAP1 (Xiao et al., 2019), promoting adjacent pancreatic cancer cell growth upon secretion (Munasinghe et al., 2020). In the TCGA database, pancreatic cancer showed an obviously positive correlation between SP1 and SPARC expression at the protein level (Figure S5A). To clarify the significance of intracellular SP1/miR‐31‐5p in the tumour microenvironment, we employed public single‐cell data for pancreatic cancer to evaluate the expression of SP1 and SPARC in the tumour microenvironment (Peng et al., 2019). SP1 is expressed at higher levels in epithelial cells, while SPARC is expressed at higher levels in stromal cells, including PSCs and fibroblasts (Figure S5B–E). Additionally, compared with pancreatic cancer cell lines, PSCs had lower SP1 expression and higher SPARC protein expression (Figure 6a,b). Consistently, a previous report also showed that the SPARC gene is hypermethylated in pancreatic cancer cells, which leads to SPARC silencing (Vaz et al., 2015). Therefore, SP1/miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells could exploit PSCs via EVs. Whether the expression of SPARC in PSCs was regulated by EV miR‐31‐5p was further confirmed. In the pancreatic cancer cell and PSC coculture system, miR‐31‐5p overexpression in cancer cells induced SPARC expression, but GW4869 treatment abrogated this effect (Figure 6c). Additionally, considering that YAP1 can transcribe SPARC in PSCs (Xiao et al., 2019), the mRNA level of SPARC in PSCs was tested after adding miR‐31‐5p mimic EVs, which repressed LATS2 and increased SPARC (Figure 6d). Rescue experiments were also performed for EV miR‐31‐5p and LATS2 in PSCs. After adding miR‐31‐5p mimic EVs, LATS2 overexpression reversed the upregulation of SPARC (Figure 6e). After adding miR‐31‐5p KO EVs, LATS2 inhibition reversed the downregulation of SPARC (Figure 6f). In addition to EVs, the role of miR‐31‐5p in inducing SPARC was confirmed by mimic and inhibitor transfection. miR‐31‐5p overexpression increased the mRNA level of SPARC in PSCs (Figure 6g). Furthermore, the rescue experiments also suggested that miR‐31‐5p upregulated SPARC by targeting LATS2 in PSCs (Figure 6h,i). Given that SPARC is a secreted protein, the SPARC concentration in the cell medium was detected by ELISA. miR‐31‐5p overexpression increased SPARC secretion, while miR‐31‐5p inhibition decreased SPARC secretion (Figure 6j). Moreover, miR‐31‐5p mimic EV treatment also obviously increased the SPARC concentration in the cell medium of PSCs (Figure 6k). Thus, miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells could promote the secretion of SPARC from PSCs via EVs.
FIGURE 6.
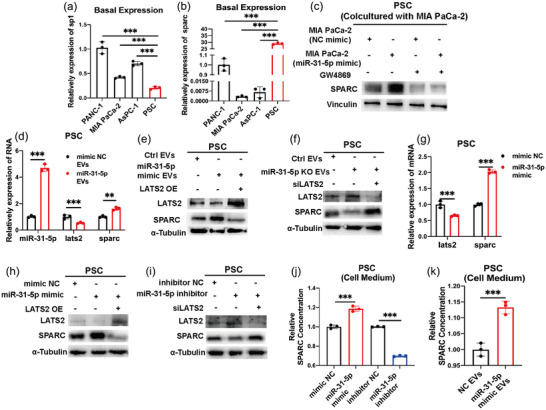
EV miR‐31‐5p improved SPARC expression in PSCs. (a), (b) The basal expression of SP1 and SPARC in pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs. (c) The expression levels of SPARC in PSCs after coculture with MIA PaCa‐2 cells. miR‐31‐5p mimic pancreatic cancer cells increased SPARC expression in PSCs. (d) The increased RNA expression levels of miR‐31‐5p, LATS2 and SPARC in PSCs after EV miR‐31‐5p treatment. (e), (f) LATS2 rescued the expression of SPARC in PSCs after EV miR‐31‐5p treatment. (g) The expression levels of LATS2 and SPARC at the RNA level in PSCs after miR‐31‐5p mimic transfection. (h), (i) LATS2 rescued the expression of SPARC in PSCs after miR‐31‐5p mimic or inhibitor transfection. (j) miR‐31‐5p increased SPARC secretion from PSCs. (k) EV miR‐31‐5p increased SPARC secretion from PSCs. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. EV, extracellular vesicle; PSC, pancreatic stellate cell; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich.
3.5. SPARC increases pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance by activating ERK signalling
Previous reports showed that SPARC could activate the ERK signalling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma and bronchial epithelial cells (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). To confirm that SPARC could stimulate the ERK signalling pathway and promote pancreatic cancer progression, we detected phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels under coculture treatment. First, the efficiency of siRNAs and overexpression plasmids in regulating SPARC expression was tested (Figure 7a,b). After downregulation of SPARC in PSCs and coculture of PSCs with pancreatic cancer cells, the phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels in cancer cells were reduced (Figure 7c,d). Similarly, SPARC overexpression in PSCs upregulated phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels in cocultured cancer cells (Figure 7e,f). Then, we added recombinant human SPARC (rhSPARC) to pancreatic cancer cells, which promoted the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (Figure 7g,h). In addition, the chemosensitivity phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells was clarified after coculture with PSCs. Compared with the control groups, PSCs subjected to SPARC downregulation increased the chemosensitivity of cancer cells (Figure 7i), while SPARC overexpression in PSCs decreased chemosensitivity (Figure 7j–k). These chemosensitivity and cell proliferation results were also verified under rhSPARC treatment. Consistently, rhSPARC enhanced chemoresistance and cell growth (Figure 7l–o). Importantly, under gemcitabine treatment, cell apoptosis could be obviously restricted by rhSPARC (Figure 7p), which suggested that PSC‐derived SPARC could promote the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells.
FIGURE 7.
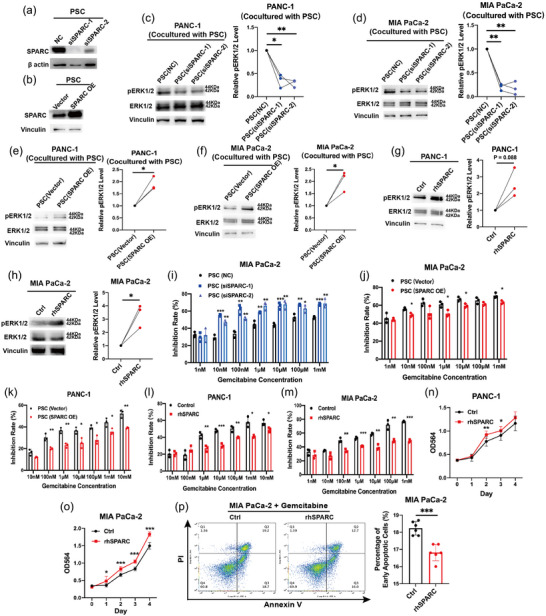
SPARC stimulated the ERK signalling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. (a) siRNA effectively repressed SPARC expression in PSCs. (b) Plasmid effectively overexpressed SPARC expression in PSCs. (c)–(F) Increased phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels in pancreatic cancer cells after coculture with PSCs. (g), (h) Increased phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels in pancreatic cancer cells after treatment with recombinant human SPARC. (i)–(k) The chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells after coculture with PSCs. SPARC in PSCs promoted the chemoresistance. (l)–(o) The chemoresistance and proliferation ability of pancreatic cancer cells were increased after recombinant human SPARC treatment. (p) The decreased early cell apoptosis rate of pancreatic cancer cells after recombinant human SPARC treatment. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. PSC, pancreatic stellate cell; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich.
3.6. miR‐31‐5p promotes pancreatic cancer chemoresistance in vivo
To validate the ability of miR‐31‐5p to increase chemoresistance in vivo, in addition to stable miR‐31‐5p overexpression cells, stable miR‐31‐5p inhibition cells were also constructed with a lentivirus carrying an miR‐31‐5p inhibitor. We employed nude mice, stable miR‐31‐5p overexpression/inhibition cells, and PSCs to construct subcutaneous xenografts. After the mice were injected with PBS (Control groups) or gemcitabine, the tumour volumes were measured every three days. miR‐31‐5p overexpression significantly accelerated tumour growth even under gemcitabine treatment, thus upregulating chemoresistance in vivo (Figure 8a–c) (Table S4). miR‐31‐5p inhibition repressed chemoresistance (Figure 8d–f) (Table S5). LATS2 expression, cell proliferation and apoptosis were confirmed by IHC. After miR‐31‐5p overexpression, LATS2 expression was repressed (Figure 8g), Ki67+ proliferative cells were increased, and the abundance of cleaved caspase3+ apoptotic cells was decreased (Figure 8g,h). Consistently, miR‐31‐5p inhibition increased LATS2 expression and apoptotic cells and decreased the abundance of proliferative cells (Figure 8i,j). To test whether miR‐31‐5p in cancer cells promoted tumour chemoresistance in a PSC‐dependent manner, we constructed mixed subcutaneous xenografts by coinjecting equal numbers of cancer cells and PSCs. miR‐31‐5p overexpression in cancer cells obviously increased the chemoresistance of the coinjected xenografts (Figure 8k‒m) (Table S6). A dense stroma and miR‐31‐5p expression could be seen in the subcutaneous tumour after histological analysis (Figure 8n). Furthermore, RAB27A was employed to inhibit EV secretion from cancer cells (Cao et al., 2022; Ostrowski et al., 2010). The efficiency of stable RAB27A‐downregulation cell lines was first confirmed (Figure S6A). RAB27A‐downregulation could effectively repress EVs release (Figure S6B,C). The transfer of miR‐31‐5p from pancreatic cancer cells to PSCs in vitro was further confirmed by stable RAB27A‐downregulation cell lines and fluorescent labelled miR‐31‐5p mimic (miR‐31‐5p mimic 5′FAM). This transfer was repressed by RAB27A downregulation, thus EVs release restriction, in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure S7A). The RAB27A‐downregulation cells were then utilized to verify the key role of EV release from pancreatic cancer cells in miR‐31‐5p‐mediated chemoresistance. After inhibiting EV release, chemosensitivity was increased. miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells subjected to RAB27A downregulation failed to significantly induce chemoresistance in subcutaneous tumours (Figure 8o–q) (Table S7). Additionally, the IHC results showed that the miR‐31‐5p/Hippo/SPARC pathway was involved in these effects in vivo (Figure 8r).
FIGURE 8.
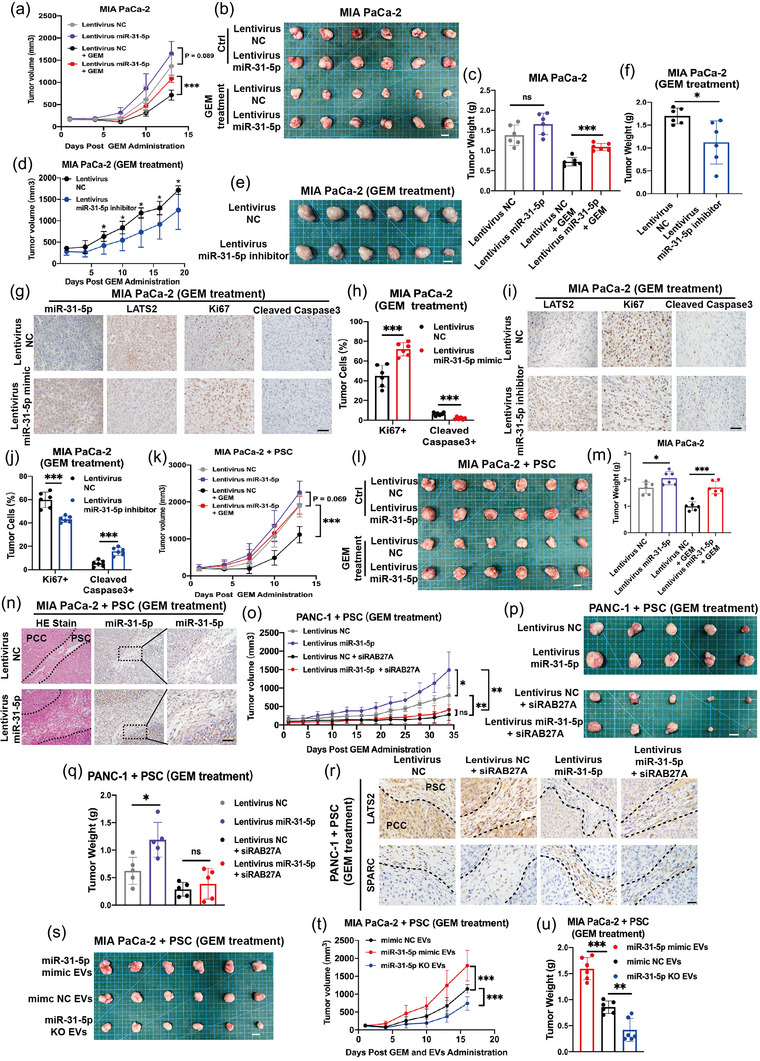
miR‐31‐5p promoted pancreatic cancer chemoresistance in animal experiments. (a)–(c) Pancreatic cancer cell lines with stable miR‐31‐5p overexpression showed higher growth ability in vivo, especially under gemcitabine treatment, thus higher chemoresistance. Scale bar equals 1 cm. (d)–(f) Pancreatic cancer cell lines with stable miR‐31‐5p inhibition showed lower chemoresistance in vivo. Scale bar equals 1 cm. (g), (h) miR‐31‐5p overexpression inhibited LATS2 expression and cell apoptosis and increased cell proliferation. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (i), (j) miR‐31‐5p inhibition upregulated LATS2 expression and cell apoptosis and inhibited cell proliferation. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (k)‒(m) miR‐31‐5p overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells obviously improved the chemoresistance of cancer cell‐PSC coinjected xenografts. Scale bar equals 1 cm. (n) miR‐31‐5p overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells promoted stroma formation and increased miR‐31‐5p levels in stromal cells and thus PSCs. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (o)–(q) RAB27A downregulation in pancreatic cancer cells restricted the ability of miR‐31‐5p to promote chemoresistance in the coinjected xenografts. Scale bar equals 1 cm. (r) miR‐31‐5p overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells inhibited LATS2 expression in both cancer cells and PSCs and upregulated SPARC expression in PSCs. RAB27A downregulation in pancreatic cancer cells rescued LATS2 inhibition and SPARC upregulation in PSCs. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (s)–(u) miR‐31‐5p EVs increased the chemoresistance of the mixed subcutaneous xenografts comprised by cancer cells and PSCs. Scale bar equals 1 cm. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. EV, extracellular vesicle; GEM, gemcitabine; PSC, pancreatic stellate cell; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich.
To further confirm the role of EVs in inducing chemoresistance in tumour microenvironment, we coinjected equal numbers of cancer cells and PSCs to constructed subcutaneous xenografts. Then, the mice were simultaneously received intraperitoneal injection gemcitabine and tail vein injection of different EVs twice a week. miR‐31‐5p EVs could significantly increase the chemoresistance of the tumour microenvironment containing cancer cells and PSCs (Figure 8s–u) (Table S8). The orthotopic mice models with equal numbers of cancer cells and PSCs were also performed. Two days after the coinjection, gemcitabine and EVs were administrated to mice. After 2 weeks, orthotopic tumours in pancreas were taken out to be measured and weighted. Besides subcutaneous xenografts, miR‐31‐5p EVs could also upregulate the chemoresistance of orthotopic tumours with pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs (Figure S7B). miR‐31‐5p EVs increased the miR‐31‐5p levels and decreased the LATS2 expression in PSCs within orthotopic xenografts (Figure S7C,D).
3.7. miR‐31‐5p expression is related to poor prognosis and low LATS2 expression in pancreatic cancer patients
To further clarify the clinical significance of miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer, we detected miR‐31‐5p expression in clinical samples. A TMA containing paired pancreatic cancer tissue and adjacent normal tissue of 70 cases was subjected to ISH for miR‐31‐5p. The results showed that pancreatic cancer tissue expressed higher miR‐31‐5p levels than paired normal tissue (Figure 9a,b). miR‐31‐5p was highly expressed in patients with higher T stages (Table S9). Moreover, the miR‐31‐5p‐positive signal was preferably located surrounding the malignant epithelium in pancreatic tissue (Figure 9a), which is consistent with the role of EV miR‐31‐5p. Importantly, compared to the low miR‐31‐5p group, high miR‐31‐5p expression was related to shorter survival (Figure 9c). Additionally, the quality of the EVs from human plasma was also assessed (Figure S4J–L). The relationships among SP1, miR‐31‐5p, LATS2, and SPARC expression were further compared in TMA (Figure 9d). SP1 expression positively correlated with miR‐31‐5p expression (Figure 9e). Additionally, there was also a significantly negative relationship between miR‐31‐5p and LATS2 expression and an obviously positive relationship between miR‐31‐5p and SPARC expression in the stroma (Figure 9f,g). Compared to those from the healthy controls, EVs from pancreatic patients had higher plasma miR‐31‐5p levels (Figure 9h). Pairing plasma EVs miR‐31‐5p levels with 36 months’ follow‐up information, higher plasma EVs miR‐31‐5p levels before operation potentially related to shorter relapse‐free survival after operation, which remains further verification via larger clinical cohorts (Figure 9i). In conclusion, miR‐31‐5p in cancer cells and EV miR‐31‐5p are vital for pancreatic cancer chemoresistance (Figure 9j).
FIGURE 9.
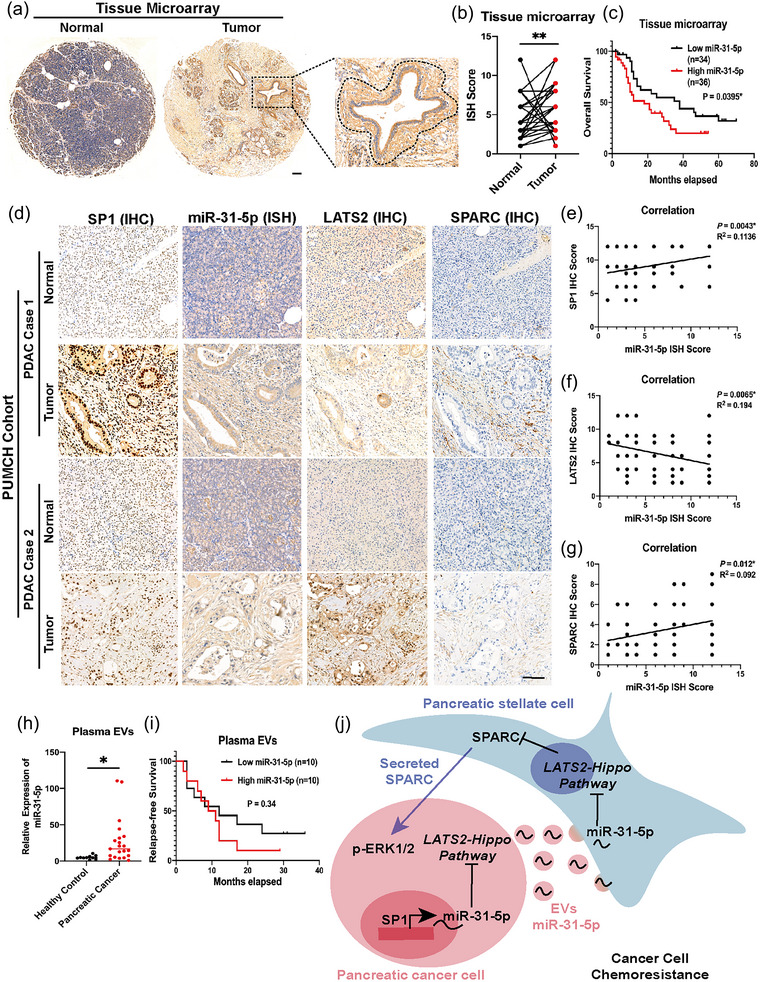
miR‐31‐5p expression is related to poor prognosis, lower LATS2 expression, and higher SPARC expression in pancreatic cancer patients. (a), (b) miR‐31‐5p expression was relatively higher in tumour tissue in the TMA with 70 paired normal and tumour tissues. In some cases, the positive signal of miR‐31‐5p is preferentially near malignant cells. Scale bar equals 100 μm. (c) High miR‐31‐5p expression was related to poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients. (d)–(g) miR‐31‐5p expression was negatively related to LATS2 but positively related to SP1 and SPARC expression. Scale bar equals 100 μm. (h) Pancreatic cancer patients have higher plasma EV miR‐31‐5p levels than healthy people. (i) The correlation between preoperative plasma EV miR‐31‐5p levels and postoperative relapse‐free survival. (j) The model of EV miR‐31‐5p‐ and SPARC‐mediated communication between pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. EV, extracellular vesicle; PSC, pancreatic stellate cell; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich; TMA, tissue microarray.
4. DISCUSSION
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal malignances in the world. Chemotherapy is an important strategy to treat pancreatic cancer. Effective chemotherapy not only prolongs the survival of patients with advanced disease but also transforms unresectable or borderline resectable tumours into resectable tumours, thus making a cure possible (van Dam et al., 2022). Therefore, chemotherapy has been one of the key elements of basic research on pancreatic cancer to improve the efficacy of chemotherapy and reduce the occurrence of chemotherapy resistance (Zeng et al., 2019). At present, the first‐line chemotherapy regimens for pancreatic cancer are mainly divided into three categories. One category includes gemcitabine‐based combination chemotherapy regimens (e.g., gemcitabine combined with nab‐paclitaxel), another includes 5‐fluorouracil (5‐FU) or 5‐FU derivative‐based chemotherapy regimens (e.g., FOLFIRINOX regimen), and the third includes platinum‐containing regimens applied in patients with BRCA mutations (e.g., the FOLFOX regimen) (Burris et al., 1997). Numerous clinical trials have attempted to combine targeted drugs with gemcitabine or improve combination chemotherapy regimens. However, no improvements have been reported thus far. Therefore, an in‐depth study of the mechanism of gemcitabine resistance and the discovery of targeted therapies that enhance sensitivity to gemcitabine are urgently needed. Recently, many studies have shown the important role of exosomes in inducing pancreatic cancer chemoresistance (Pan et al., 2022). In this study, we identified the key role of miR‐31‐5p in promoting gemcitabine chemoresistance not only in pancreatic cancer cells but also in the pancreatic cancer tumour microenvironment, which might be a key reason for the short survival of pancreatic cancer patients.
The Hippo/YAP1 pathway is a well‐known signalling pathway that accelerates cancer progression. YAP1 has been extensively studied and identified as a potent oncogene (Moroishi et al., 2015). LATS2 is one of the core components of the Hippo pathway and can directly phosphorylate YAP1. Phosphorylated YAP1 is sequestered by binding with 14‐3‐3 in the cytoplasm and is ultimately degraded by ubiquitination and the proteasome (Mao et al., 2021). Some reports have shown a key role of the Hippo/YAP1 pathway in promoting chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer (Yuan et al., 2016). In addition to transcribing key survival genes, YAP1 was shown in a recent study to support stemness and iron metabolism in pancreatic cancer cells, enhancing chemoresistance (Zhou et al., 2023). YAP1 can also bind with BRD4 at its enhancer region, regulating a wide variety of downstream genes and promoting pancreatic cancer progression (Yamazaki et al., 2023). In this study, miR‐31‐5p was shown to regulate YAP1 levels by targeting LATS2 in both pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs via EVs, providing a novel way to intervene in the Hippo/YAP1 pathway and pancreatic cancer progression.
The tumour microenvironment is complex and heterogeneous. Considering that cancer cells can live well in their niches, the cooperation between cancer cells and stromal components warrants further research. PSCs are key stromal cell types in the pancreatic cancer tumour microenvironment. In recent years, several studies have suggested that pancreatic cancer cell‐PSC interactions may play important roles in the development of chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Leukocyte inhibitory factor secreted by PSCs activates the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway in pancreatic cancer cells while downregulating the expression of Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter (ENTs), Concentrative Nucleoside Transporter (CNTs) and the key enzyme Deoxycytidine Kinase (DCK), ultimately leading to gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer (Shi et al., 2019). Another study showed that the chemokine CXCL12 secreted by PSCs acts on pancreatic cancer cells, while E26 transformation specific Homologous Factor (EHF) in cancer cells induces chemoresistance by inhibiting the transcription of CXCR4, the receptor of CXCL12, as well as the transcription of stemness genes such as SOX9 and OCT4 (Zhou et al., 2022). Until now, most studies have focused only on the unidirectional relationship between pancreatic cancer and PSCs, and the complicated interaction between pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs remains to be further studied. Our study revealed the bidirectional relationship between pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs, which deepens our understanding of the tumour microenvironment in the context of chemoresistance. A previous study showed that SPARC could promote pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration through autocrine secretion (Pan et al., 2021). In fact, SPARC is silenced in pancreatic cancer cells but highly expressed in stromal cells (Vaz et al., 2015). Ying Xiao et al. showed that YAP1 upregulated SPARC expression in PSCs, but SPARC inhibited pancreatic cancer cell proliferation (Xiao et al., 2019). Later, another study showed that fibronectin could act as a molecular switch to determine SPARC function. SPARC could promote pancreatic cancer cell proliferation with fibronectin treatment but inhibit proliferation without fibronectin treatment, which revealed the oncogenic role of SPARC in vivo (Munasinghe et al., 2020). However, the detailed mechanism by which SPARC promotes pancreatic cancer cells was not very clear at that time. SPARC is an ectogenic factor, and previous reports in other cancer cells showed that the ERK pathway was activated upon SPARC treatment (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020). Consistent with this, we found that SPARC could stimulate the ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer cells, which further upregulated chemoresistance as a positive feedback mechanism mediated by EV miR‐31‐5p. However, although the transfer of EV miR‐31‐5p from pancreatic cancer cells to PSCs has been confirmed in vitro and in vivo, the function of endogenous miR‐31‐5p in PSCs under real pathophysiologic conditions should not be neglected. Considering the ubiquitous Hippo pathway in both pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs, it is worth to further explore the role of miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs by genetically engineered mice (miR‐31‐5p KO specially in cancer cells or PSCs) and high‐throughput sequencing methods such as single‐cell analysis in the future.
In addition to mediating cell‒cell communication, EVs perform many other functions that warrant further study. Many studies have shown that EVs containing nucleic acids, proteins and metabolites promote cancer progression. Therefore, restricting EV secretion within the pancreatic cancer tumour microenvironment is a novel way to treat pancreatic cancer (Qin et al., 2023). Given that both normal and malignant cells communicate with other cells via EVs, the classical pathway of EV secretion is shared by nearly all cells (Ostrowski et al., 2010). Exploring the specific mechanism underlying EV secretion from cancer cells might lead to the development of a novel targeted therapy against pancreatic cancer (Wu et al., 2023). Additionally, detecting circulating EVs via liquid biopsy is also promising in clinical applications. Benefitting from the protection of the lipid bilayer, EVs secreted from cancer cells that carry special information related to malignancy could be extracted from plasma and realize cancer diagnosis and disease monitoring (Nakamura et al., 2022). Therefore, we will perform follow‐up in our clinical cohort to confirm the relationship between plasma EV miR‐31‐5p levels and the response to chemotherapy, which might be a possible predictor of chemoresistance. Pancreatic cancer shows not only increased EV secretion but also a strong ability to absorb EVs (Qin et al., 2023), which might be mediated by receptor‐ligand binding (Lau & Yam, 2023). In addition, the biological features of EVs enable them to be stable in the circulatory system. Their biocompatibility also makes it easy for them to enter the dense tumour microenvironment (Liang et al., 2021). Therefore, EVs provide a potential platform for loading anticancer drugs to realize targeted therapy, and exosomes loaded with miR‐31‐5p inhibitors have the potential to increase the clinical efficiency of gemcitabine.
5. CONCLUSION
In summary, SP1 transcribes miR‐31‐5p in pancreatic cancer cells, which inhibits the LATS2 and Hippo pathways, ultimately inducing the expression of many survival genes. Additionally, miR‐31‐5p in cancer cells could be packaged into EVs, which could be transmitted to adjacent activated PSCs and thus CAFs, inhibiting the LAST2 and Hippo pathways in those recipient cells. In addition, SPARC expression in PSCs was elevated, stimulating the ERK1/2 pathway in pancreatic cancer cells, thus further promoting chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Therefore, we found a novel mechanism by which miRNAs promote cancer progression at the levels of both cells and the tumour microenvironment (Figure 9i).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Cheng Qin: Conceptualization (equal); data curation (equal); formal analysis (equal); funding acquisition (supporting); investigation (equal); methodology (equal); project administration (equal); software (equal); validation (equal); visualization (equal); writing—original draft (lead). Bangbo Zhao: Conceptualization (equal); data curation (equal); formal analysis (equal); investigation (equal); methodology (equal); project administration (equal); resources (equal); software (equal); visualization (equal); writing—review and editing (lead). Yuanyang Wang: Data curation (supporting); validation (supporting); writing—review and editing (supporting). Zeru Li: Data curation (supporting); validation (supporting). Tianyu Li: Validation (supporting); writing—review and editing (supporting). Yutong Zhao: Validation (supporting). Weibin Wang: Conceptualization (equal); funding acquisition (equal); project administration (equal); supervision (equal); writing—review and editing (equal). Yupei Zhao: Conceptualization (equal); funding acquisition (lead); project administration (equal); supervision (equal); writing—review and editing (equal).
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting information
Supplemental Figure 1. SP1 downregulation repressed miR‐31‐5p expression but failed to inhibit MIR31HG expression in PANC‐1. Three primers for MIR31HG were referenced from 3 previous publications (Yan et al., 2018) (Montes et al., 2021) (Montes et al., 2015).***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 2. miR‐31‐5p regulated downstream targets of the Hippo pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. (A) The miR‐31‐5p mimic upregulated the expression of downstream targets of the Hippo pathway in pancreatic cancer, including CYR61, CTGF, BIRC5, and ANKRD1. (B) The miR‐31‐5p inhibitor downregulated the expression of downstream targets of the Hippo pathway. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 3. EV miR‐31‐5p failed to change SP1 in PSCs. (A) SP1 levels were unchanged in PSCs when coculturing with PANC‐1. (B) EVs from pancreatic cancer cells failed to change SP1 levels in PSCs.
Supplemental Figure 4. Quality control of EV extraction. (A, B) Compared with cell lysates, EVs from pancreatic cancer cells had higher levels of EV markers (CD63, CD81, CD9, TSG101, and Alix) and lower levels of a cell markers (GM130, VDAC1, Calnexin). Moreover, SP1 protein was minimal in the EVs from pancreatic cancer cells. (C, D) NTA showed that the diameter of the majority of EVs derived from pancreatic cancer cell line was less than 200 nm. (E, F) Transmission electron microscopy revealed the EV structure. Scale bar equals 200 nm. (G) miR‐31‐5p was higher in pancreatic cancer cells EVs than HPNE EVs. (H) miR‐31‐5p was relatively enriched in EVs than cell lysate. (I) miR‐31‐5p was effectively repressed by CRISPR‐Cas9 system in pancreatic cancer cells.(J) Compared with cell lysates, EVs from plasma had higher levels of EV markers (CD63, CD81, and Alix) and lower levels of a cell markers (Calnexin). (K) NTA showed that the diameter of the majority of EVs derived from plasma was also less than 200 nm. (L) Transmission electron microscopy revealed the EV structure from plasma. Scale bar equals 200 nm. (I) *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 5. The expression of SP1 and SPARC in the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic cancer. (A) Positive correlation between sp1 and sparc expression at the RNA level in pancreatic cancer based on the TCGA database. (B‐E) The single‐cell database showed that pancreatic cancer cells had higher SP1 expression, and SPARC tended to be expressed in stromal cells.
Supplemental Figure 6. The efficiency of siRAB27A lentivirus. (A) The lentivirus with the siRNA sequence targeting RAB27A inhibited RAB27A expression in pancreatic cancer cells. (B, C) Nanoparticle tracking analysis showed that RAB27A downregulation effectively reduced the EVs release from the host cells. ***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 7. Fluorescent miR‐31‐5p transfer and orthotopic models. (A) Fluorescent miR‐31‐5p (miR‐31‐5p mimic 5′FAM) was transferred from pancreatic cancer cells to PSCs, which could be inhibited by RAB27A downregulation in pancreatic cancer cells. Scale bar equals 10 μm. (B) miR‐31‐5p obviously improved the chemoresistance of orthotopic mice models for pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs. (C) PSCs in orthotopic xenografts preferred to absorb EVs miR‐31‐5p. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (D) EVs miR‐31‐5p repressed LATS2 expression in PSCs. Scale bar equals 25 μm. **P < 0.01.
Supplemental Table 1: Primers sequences
Supplemental Table 2: Possible transcription factors based on ChIP‐seq
Supplemental Table 3: Possible transcription factors based on motif sequence
Supplemental Table 4: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 A‐C
Supplemental Table 5: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 D‐F
Supplemental Table 6: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 K‐M
Supplemental Table 7: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 O‐Q
Supplemental Table 8: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 S‐U
Supplemental Table 9: Correlations of miR31‐5p expression levels with clinical and pathologic parameters
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the support from the National Multidisciplinary Cooperative Diagnosis and Treatment Capacity Building Project for Major Diseases. Weibin Wang received the support from Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7232127), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82173074), the National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (No. 2022‐PUMCH‐B‐004), the Capital's Funds for Health Improvement and Research, CFH (2024‐2‐4017). Yupei Zhao received National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (No. 2022‐PUMCH‐D‐001), the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (No. 2021‐I2M‐1‐002), and the Nonprofit Central Research Institute Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2018PT32014).Cheng Qin received support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3332022114).
Qin, C. , Zhao, B. , Wang, Y. , Li, Z. , Li, T. , Zhao, Y. , Wang, W. , & Zhao, Y. (2024). Extracellular Vesicles miR‐31‐5p Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Chemoresistance via Regulating LATS2‐Hippo Pathway and Promoting SPARC Secretion from Pancreatic Stellate Cells. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 13, e12488. 10.1002/jev2.12488
Cheng Qin and Bangbo Zhao contributed equally to this study.
Contributor Information
Weibin Wang, Email: wwb_xh@163.com.
Yupei Zhao, Email: zhao8028@263.net.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Not applicable.
REFERENCES
- Burris, H. A., 3rd , Moore, M. J. , Andersen, J. , Green, M. R. , Rothenberg, M. L. , Modiano, M. R. , Cripps, M. C. , Portenoy, R. K. , Storniolo, A. M. , Tarassoff, P. , Nelson, R. , Dorr, F. A. , Stephens, C. D. , & Von Hoff, D. D. (1997). Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first‐line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology : Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 15(6), 2403–2413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bynigeri, R. R. , Jakkampudi, A. , Jangala, R. , Subramanyam, C. , Sasikala, M. , Rao, G. V. , Reddy, D. N. , & Talukdar, R. (2017). Pancreatic stellate cell: Pandora's box for pancreatic disease biology. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 23(3), 382–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M. , Isaac, R. , Yan, W. , Ruan, X. , Jiang, L. , Wan, Y. , Wang, J. , Wang, E. , Caron, C. , Neben, S. , Drygin, D. , Pizzo, D. P. , Wu, X. , Liu, X. , Chin, A. R. , Fong, M. Y. , Gao, Z. , Guo, K. , Fadare, O. , … Wang, S. E. (2022). Cancer‐cell‐secreted extracellular vesicles suppress insulin secretion through miR‐122 to impair systemic glucose homeostasis and contribute to tumour growth. Nature Cell Biology, 24(6), 954–967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro‐Mondragon, J. A. , Riudavets‐Puig, R. , Rauluseviciute, I. , Lemma, R. B. , Turchi, L. , Blanc‐Mathieu, R. , Lucas, J. , Boddie, P. , Khan, A. , Manosalva Pérez, N. , Fornes, O. , Leung, T. Y. , Aguirre, A. , Hammal, F. , Schmelter, D. , Baranasic, D. , Ballester, B. , Sandelin, A. , Lenhard, B. , … Mathelier, A. (2022). JASPAR 2022: The 9th release of the open‐access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Research, 50(D1), D165–D173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X. , Sha, M. , Jiang, W. , Chen, L. , & Song, M. (2022). LINC00174 suppresses non‐small cell lung cancer progression by up‐regulating LATS2 via sponging miR‐31‐5p. Cell Journal, 24(3), 140–147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoud, A. Z. , Mulholland, E. J. , Cole, G. , & McCarthy, H. O. (2019). MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer: Biomarkers, prognostic, and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer, 19(1), 1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M. , Hu, Y. , Lan, T. , Guan, K. L. , Luo, T. , & Luo, M. (2022). The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 7(1), 376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F. , Xu, Q. , Wang, J. , Yu, S. , Chang, H. H. , Sinnett‐Smith, J. , Eibl, G. , & Rozengurt, E. (2019). Lipophilic statins inhibit YAP nuclear localization, co‐activator activity and colony formation in pancreatic cancer cells and prevent the initial stages of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in KrasG12D mice. PLoS ONE, 14(5), e0216603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms, E. J. , Berry, M. W. , Chaw, R. C. , DuFort, C. C. , Sun, D. , Onate, M. K. , Oon, C. , Bhattacharyya, S. , Sanford‐Crane, H. , Horton, W. , Finan, J. M. , Sattler, A. , Makar, R. , Dawson, D. W. , Xia, Z. , Hingorani, S. R. , & Sherman, M. H. (2022). Mesenchymal lineage heterogeneity underlies nonredundant functions of pancreatic cancer‐associated fibroblasts. Cancer Discovery, 12(2), 484–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hergenreider, E. , Heydt, S. , Tréguer, K. , Boettger, T. , Horrevoets, A. J. , Zeiher, A. M. , Scheffer, M. P. , Frangakis, A. S. , Yin, X. , Mayr, M. , Braun, T. , Urbich, C. , Boon, R. A. , & Dimmeler, S. (2012). Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nature Cell Biology, 14(3), 249–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hergenreider, E. , Heydt, S. , Tréguer, K. , Boettger, T. , Horrevoets, A. J. , Zeiher, A. M. , Scheffer, M. P. , Frangakis, A. S. , Yin, X. , Mayr, M. , Braun, T. , Urbich, C. , Boon, R. A. , & Dimmeler, S. (2012). Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nature Cell Biology, 14(3), 249–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hergenreider, E. , Heydt, S. , Tréguer, K. , Boettger, T. , Horrevoets, A. J. , Zeiher, A. M. , Scheffer, M. P. , Frangakis, A. S. , Yin, X. , Mayr, M. , Braun, T. , Urbich, C. , Boon, R. A. , & Dimmeler, S. (2012). Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nature Cell Biology, 14(3), 249–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho, W. J. , Jaffee, E. M. , & Zheng, L. (2020). The tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer—Clinical challenges and opportunities. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 17(9), 527–540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H. H. , Kuo, W. W. , Shih, H. N. , Cheng, S. F. , Yang, C. K. , Chen, M. C. , Tu, C. C. , Viswanadha, V. P. , Liao, P. H. , & Huang, C. Y. (2019). FOXC1 regulation of miR‐31‐5p confers oxaliplatin resistance by targeting LATS2 in colorectal cancer. Cancers, 11(10), 1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. , Wang, Z. , Zhang, Y. , Pradhan, R. N. , Ganguly, D. , Chandra, R. , Murimwa, G. , Wright, S. , Gu, X. , Maddipati, R. , Müller, S. , Turley, S. J. , & Brekken, R. A. (2022). Mesothelial cell‐derived antigen‐presenting cancer‐associated fibroblasts induce expansion of regulatory T cells in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell, 40(6), 656–673.e7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau, N. C. H. , & Yam, J. W. P. (2023). From exosome biogenesis to absorption: Key takeaways for cancer research. Cancers, 15(7), 1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. , Tang, Z. , Zhang, W. , Ye, Z. , & Liu, F. (2021). GEPIA2021: Integrating multiple deconvolution‐based analysis into GEPIA. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(W1), W242–W246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. , Guo, H. , Wang, Q. , Chen, K. , Marko, K. , Tian, X. , & Yang, Y. (2020). Pancreatic stellate cells derived exosomal miR‐5703 promotes pancreatic cancer by downregulating CMTM4 and activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Letters, 490, 20–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, R. , Qu, H. , Wang, S. , Chater, J. M. , Wang, X. , Cui, Y. , Yu, L. , Zhou, R. , Jia, Q. , Traband, R. , Wang, M. , Xie, W. , Yuan, D. , Zhu, J. , Zhong, W. D. , & Jia, Z. (2022). CancerMIRNome: An interactive analysis and visualization database for miRNome profiles of human cancer. Nucleic Acids Research, 50(D1), D1139–D1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. , Fan, Y. , Xu, J. , Huo, L. , Scott, A. W. , Jin, J. , Yang, B. , Shao, S. , Ma, L. , Wang, Y. , Yao, X. , Pool Pizzi, M. , Sewastjanow Da Silva, M. , Zhang, G. , Zhuo, L. , Cho, E. J. , Dalby, K. N. , Shanbhag, N. D. , Wang, Z. , … Ajani, J. A. (2022). GRK3 is a poor prognosticator and serves as a therapeutic target in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR, 41(1), 257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y. , Duan, L. , Lu, J. , & Xia, J. (2021). Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics, 11(7), 3183–3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. , Shyr, Y. , Cai, J. , & Liu, Q. (2018). Interplay between miRNAs and host genes and their role in cancer. Briefings in Functional Genomics, 18(4), 255–266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. , Feng, Y. , Wang, X. , Yang, X. , Hu, Y. , Li, Y. , Zhang, Q. , Huang, Y. , Shi, K. , Ran, C. , Hou, J. , Jiang, L. , Li, J. , & Wang, X. (2020). SPARC negatively correlates with prognosis after transarterial chemoembolization and facilitates proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ERK/MMP signaling pathways. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y. , Zhao, L. , Mao, J. , Liu, W. , Ma, W. , & Zhao, B. (2023). Rab27a‐mediated extracellular vesicle secretion contributes to osteogenesis in periodontal ligament‐bone niche communication. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 8479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q. , Wu, H. , Xiao, Y. , Liang, Z. , & Liu, T. (2020). Upregulation of exosomal microRNA21 in pancreatic stellate cells promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration and enhances Ras/ERK pathway activity. International Journal of Oncology, 56(4), 1025–1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W. , Mai, J. , Peng, H. , Wan, J. , & Sun, T. (2021). YAP in pancreatic cancer: Oncogenic role and therapeutic strategy. Theranostics, 11(4), 1753–1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes, M. , Lubas, M. , Arendrup, F. S. , Mentz, B. , Rohatgi, N. , Tumas, S. , Harder, L. M. , Skanderup, A. J. , Andersen, J. S. , & Lund, A. H. (2021). The long non‐coding RNA MIR31HG regulates the senescence associated secretory phenotype. Nature Communications, 12(1), 2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes, M. , Nielsen, M. M. , Maglieri, G. , Jacobsen, A. , Højfeldt, J. , Agrawal‐Singh, S. , Hansen, K. , Helin, K. , van de Werken, H. J. G. , Pedersen, J. S. , & Lund, A. H. (2015). The lncRNA MIR31HG regulates p16(INK4A) expression to modulate senescence. Nature Communications, 6, 6967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroishi, T. , Hansen, C. G. , & Guan, K. L. (2015). The emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 15(2), 73–79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, T. , Yoneji, T. , Yamada, K. , Fujita, H. , Nara, S. , & Su'etsugu, M. (2020). Overcoming the challenges of megabase‐sized plasmid construction in Escherichia coli . ACS Synthetic Biology, 9(6), 1315–1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe, A. , Malik, K. , Mohamedi, F. , Moaraf, S. , Kocher, H. , Jones, L. , & Hill, N. J. (2020). Fibronectin acts as a molecular switch to determine SPARC function in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Letters, 477, 88–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K. , Zhu, Z. , Roy, S. , Jun, E. , Han, H. , Munoz, R. M. , Nishiwada, S. , Sharma, G. , Cridebring, D. , Zenhausern, F. , Kim, S. , Roe, D. J. , Darabi, S. , Han, I. W. , Evans, D. B. , Yamada, S. , Demeure, M. J. , Becerra, C. , Celinski, S. A. , … Goel, A. (2022). An exosome‐based transcriptomic signature for noninvasive, early detection of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A multicenter cohort study. Gastroenterology, 163(5), 1252–1266.e2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Öhlund, D. , Handly‐Santana, A. , Biffi, G. , Elyada, E. , Almeida, A. S. , Ponz‐Sarvise, M. , Corbo, V. , Oni, T. E. , Hearn, S. A. , Lee, E. J. , Chio, I. I. , Hwang, C. I. , Tiriac, H. , Baker, L. A. , Engle, D. D. , Feig, C. , Kultti, A. , Egeblad, M. , Fearon, D. T. , … Tuveson, D. A. (2017). Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 214(3), 579–596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski, M. , Carmo, N. B. , Krumeich, S. , Fanget, I. , Raposo, G. , Savina, A. , Moita, C. F. , Schauer, K. , Hume, A. N. , Freitas, R. P. , Goud, B. , Benaroch, P. , Hacohen, N. , Fukuda, M. , Desnos, C. , Seabra, M. C. , Darchen, F. , Amigorena, S. , Moita, L. F. , & Thery, C. (2010). Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nature Cell Biology, 12(1), 19–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan, K. , Huang, X. , & Jia, X. (2021). SPARC promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration through autocrine secretion into the extracellular milieu. Oncology Letters, 21(6), 485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y. , Tang, H. , Li, Q. , Chen, G. , & Li, D. (2022). Exosomes and their roles in the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Medicine, 11(24), 4979–4988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel, G. K. , Khan, M. A. , Bhardwaj, A. , Srivastava, S. K. , Zubair, H. , Patton, M. C. , Singh, S. , Khushman, M. , & Singh, A. P. (2017). Exosomes confer chemoresistance to pancreatic cancer cells by promoting ROS detoxification and miR‐155‐mediated suppression of key gemcitabine‐metabolising enzyme, DCK. British Journal of Cancer, 116(5), 609–619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J. , Sun, B. F. , Chen, C. Y. , Zhou, J. Y. , Chen, Y. S. , Chen, H. , Liu, L. , Huang, D. , Jiang, J. , Cui, G. S. , Yang, Y. , Wang, W. , Guo, D. , Dai, M. , Guo, J. , Zhang, T. , Liao, Q. , Liu, Y. , Zhao, Y. L. , … Wu, W. (2019). Single‐cell RNA‐seq highlights intra‐tumoral heterogeneity and malignant progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Research, 29(9), 725–738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu, N. , Gao, S. , Yin, H. , Li, J. A. , Wu, W. , Fang, Y. , Zhang, L. , Rong, Y. , Xu, X. , Wang, D. , Kuang, T. , Jin, D. , Yu, J. , & Lou, W. (2019). Cell‐intrinsic PD‐1 promotes proliferation in pancreatic cancer by targeting CYR61/CTGF via the Hippo pathway. Cancer Letters, 460, 42–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C. , Wang, Y. , Zhao, B. , Li, Z. , Li, T. , Yang, X. , Zhao, Y. , & Wang, W. (2023). STOML2 restricts mitophagy and increases chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer through stabilizing PARL‐induced PINK1 degradation. Cell Death & Disease, 14(3), 191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C. , Zhao, B. , Wang, Y. , Li, T. , Li, Z. , Li, T. , Zhao, Y. , & Wang, W. (2023). Exosome‐mediated cell–cell communication within pancreatic cancer tumor microenvironment: A narrative review. Journal of Pancreatology, 6(1), 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saikawa, S. , Kaji, K. , Nishimura, N. , Seki, K. , Sato, S. , Nakanishi, K. , Kitagawa, K. , Kawaratani, H. , Kitade, M. , Moriya, K. , Namisaki, T. , Mitoro, A. , & Yoshiji, H. (2018). Angiotensin receptor blockade attenuates cholangiocarcinoma cell growth by inhibiting the oncogenic activity of Yes‐associated protein. Cancer Letters, 434, 120–129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y. , Gao, W. , Lytle, N. K. , Huang, P. , Yuan, X. , Dann, A. M. , Ridinger‐Saison, M. , DelGiorno, K. E. , Antal, C. E. , Liang, G. , Atkins, A. R. , Erikson, G. , Sun, H. , Meisenhelder, J. , Terenziani, E. , Woo, G. , Fang, L. , Santisakultarm, T. P. , Manor, U. , … Hunter, T. (2019). Targeting LIF‐mediated paracrine interaction for pancreatic cancer therapy and monitoring. Nature, 569(7754), 131–135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R. L. , Miller, K. D. , Wagle, N. S. , & Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 73(1), 17–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D. , Wang, J. , Han, Y. , Dong, X. , Ge, J. , Zheng, R. , Shi, X. , Wang, B. , Li, Z. , Ren, P. , Sun, L. , Yan, Y. , Zhang, P. , Zhang, F. , Li, T. , & Wang, C. (2021). TISCH: A comprehensive web resource enabling interactive single‐cell transcriptome visualization of tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(D1), D1420–D1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z. , Cui, Q. , Wang, J. , & Zhou, Y. (2019). TransmiR v2.0: An updated transcription factor‐microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(D1), D253–D258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam, J. L. , Janssen, Q. P. , Besselink, M. G. , Homs, M. Y. V. , van Santvoort, H. C. , van Tienhoven, G. , de Wilde, R. F. , Wilmink, J. W. , van Eijck, C. H. J. , & Groot Koerkamp, B. , & Dutch Pancreatic Cancer Group . (2022). Neoadjuvant therapy or upfront surgery for resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: A meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. European Journal of Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990), 160, 140–149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz, J. , Ansari, D. , Sasor, A. , & Andersson, R. (2015). SPARC: A potential prognostic and therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas, 44(7), 1024–1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. , Zhao, L. , Wei, X. , Wang, L. , Liu, S. , Yang, Y. , Wang, F. , Sun, G. , Zhang, J. , Ma, Y. , Zhao, Y. , & Yu, J. (2016). MicroRNA‐320a promotes 5‐FU resistance in human pancreatic cancer cells. Scientific Reports, 6, 27641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B. , Liu, D. A. , Guan, L. , Myint, P. K. , Chin, L. , Dang, H. , Xu, Y. , Ren, J. , Li, T. , Yu, Z. , Jabban, S. , Mills, G. B. , Nukpezah, J. , Chen, Y. H. , Furth, E. E. , Gimotty, P. A. , Wells, R. G. , Weaver, V. M. , Radhakrishnan, R. , … Guo, W. (2023). Stiff matrix induces exosome secretion to promote tumour growth. Nature Cell Biology, 25(3), 415–424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y. , Zhang, H. , Ma, Q. , Huang, R. , Lu, J. , Liang, X. , Liu, X. , Zhang, Z. , Yu, L. , Pang, J. , Zhou, L. , Liu, T. , Wu, H. , & Liang, Z. (2019). YAP1‐mediated pancreatic stellate cell activation inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Letters, 462, 51–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L. , Li, J. , Wang, G. , Sang, W. , Xu, M. , Li, W. , Yan, J. , Li, B. , Zhang, Z. , Zhao, Q. , Yuan, Z. , Fan, Q. , & Dai, Y. (2022). Phototheranostic metal‐phenolic networks with antiexosomal PD‐L1 enhanced ferroptosis for synergistic immunotherapy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 144(2), 787–797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, G. , Huang, H. , Feng, M. , Yang, G. , Zheng, S. , You, L. , Zheng, L. , Hu, Y. , Zhang, T. , & Zhao, Y. (2018). MiR‐10a‐5p targets TFAP2C to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR, 37(1), 76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, M. , Hino, S. , Usuki, S. , Miyazaki, Y. , Oda, T. , Nakao, M. , Ito, T. , & Yamagata, K. (2023). YAP/BRD4‐controlled ROR1 promotes tumor‐initiating cells and hyperproliferation in pancreatic cancer. The EMBO Journal, 42(14), e112614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S. , Tang, Z. , Chen, K. , Liu, Y. , Yu, G. , Chen, Q. , Dang, H. , Chen, F. , Ling, J. , Zhu, L. , Huang, A. , & Tang, H. (2018). Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by sponging microRNA‐575 to modulate ST7L expression. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research: CR, 37(1), 214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W. , Wu, X. , Zhou, W. , Fong, M. Y. , Cao, M. , Liu, J. , Liu, X. , Chen, C. H. , Fadare, O. , Pizzo, D. P. , Wu, J. , Liu, L. , Liu, X. , Chin, A. R. , Ren, X. , Chen, Y. , Locasale, J. W. , & Wang, S. E. (2018). Cancer‐cell‐secreted exosomal miR‐105 promotes tumour growth through the MYC‐dependent metabolic reprogramming of stromal cells. Nature Cell Biology, 20(5), 597–609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. , Liu, P. , Zhang, J. , Peng, X. , Lu, Z. , Yu, S. , Meng, Y. , Tong, W. M. , & Chen, J. (2016). Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG exhibits oncogenic property in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and is negatively regulated by miR‐193b. Oncogene, 35(28), 3647–3657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. , Chen, J. , Wang, J. , Ma, S. , Feng, W. , Wu, Z. , Guo, Y. , Zhou, H. , Mi, W. , Chen, W. , Yin, B. , & Lin, Y. (2022). Very‐low‐density lipoprotein receptor‐enhanced lipid metabolism in pancreatic stellate cells promotes pancreatic fibrosis. Immunity, 55(7), 1185–1199.e8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y. , Li, D. , Li, H. , Wang, L. , Tian, G. , & Dong, Y. (2016). YAP overexpression promotes the epithelial‐mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Molecular Medicine Reports, 13(1), 237–242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y. , Wang, Z. , Chen, M. , Jing, Y. , Shu, W. , Xie, Z. , Li, Z. , Xu, J. , He, F. , Jiao, P. , Wang, J. , Xu, J. , Xia, Y. , Liu, S. , Du, H. , Li, H. , Dai, L. , Dai, Y. , & Zhang, Y. (2021). Macrophage‐derived exosomal miR‐31‐5p promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumourigenesis through the large tumor suppressor 2‐mediated Hippo signalling pathway. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 17(5), 822–837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S. , Pöttler, M. , Lan, B. , Grützmann, R. , Pilarsky, C. , & Yang, H. (2019). Chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. , Zhang, Y. , Da, J. , Jia, Z. , Wu, H. , & Gu, K. (2020). Downregulation of SPARC expression decreases cell migration and invasion involving epithelial‐mesenchymal transition through the p‐FAK/p‐ERK pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Cancer, 11(2), 414–420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. , Li, S. , Li, L. , Li, M. , Guo, C. , Yao, J. , & Mi, S. (2015). Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 13(1), 17–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. , Xie, J. , Sun, H. , Wei, Q. , & Nong, G. (2021). miR29a3p regulates the epithelialmesenchymal transition via the SPARC/ERK signaling pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 48(3), 171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T. , Liu, J. , Xie, Y. , Yuan, S. , Guo, Y. , Bai, W. , Zhao, K. , Jiang, W. , Wang, H. , Wang, H. , Zhao, T. , Huang, C. , Gao, S. , Wang, X. , Yang, S. , & Hao, J. (2022). ESE3/EHF, a promising target of rosiglitazone, suppresses pancreatic cancer stemness by downregulating CXCR4. Gut, 71(2), 357–371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T. , Xie, Y. , Hou, X. , Bai, W. , Li, X. , Liu, Z. , Man, Q. , Sun, J. , Fu, D. , Yan, J. , Zhang, Z. , Wang, Y. , Wang, H. , Jiang, W. , Gao, S. , Zhao, T. , Chang, A. , Wang, X. , Sun, H. , … Liu, J. (2023). Irbesartan overcomes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer by suppressing stemness and iron metabolism via inhibition of the Hippo/YAP1/c‐Jun axis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR, 42(1), 111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Figure 1. SP1 downregulation repressed miR‐31‐5p expression but failed to inhibit MIR31HG expression in PANC‐1. Three primers for MIR31HG were referenced from 3 previous publications (Yan et al., 2018) (Montes et al., 2021) (Montes et al., 2015).***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 2. miR‐31‐5p regulated downstream targets of the Hippo pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. (A) The miR‐31‐5p mimic upregulated the expression of downstream targets of the Hippo pathway in pancreatic cancer, including CYR61, CTGF, BIRC5, and ANKRD1. (B) The miR‐31‐5p inhibitor downregulated the expression of downstream targets of the Hippo pathway. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 3. EV miR‐31‐5p failed to change SP1 in PSCs. (A) SP1 levels were unchanged in PSCs when coculturing with PANC‐1. (B) EVs from pancreatic cancer cells failed to change SP1 levels in PSCs.
Supplemental Figure 4. Quality control of EV extraction. (A, B) Compared with cell lysates, EVs from pancreatic cancer cells had higher levels of EV markers (CD63, CD81, CD9, TSG101, and Alix) and lower levels of a cell markers (GM130, VDAC1, Calnexin). Moreover, SP1 protein was minimal in the EVs from pancreatic cancer cells. (C, D) NTA showed that the diameter of the majority of EVs derived from pancreatic cancer cell line was less than 200 nm. (E, F) Transmission electron microscopy revealed the EV structure. Scale bar equals 200 nm. (G) miR‐31‐5p was higher in pancreatic cancer cells EVs than HPNE EVs. (H) miR‐31‐5p was relatively enriched in EVs than cell lysate. (I) miR‐31‐5p was effectively repressed by CRISPR‐Cas9 system in pancreatic cancer cells.(J) Compared with cell lysates, EVs from plasma had higher levels of EV markers (CD63, CD81, and Alix) and lower levels of a cell markers (Calnexin). (K) NTA showed that the diameter of the majority of EVs derived from plasma was also less than 200 nm. (L) Transmission electron microscopy revealed the EV structure from plasma. Scale bar equals 200 nm. (I) *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 5. The expression of SP1 and SPARC in the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic cancer. (A) Positive correlation between sp1 and sparc expression at the RNA level in pancreatic cancer based on the TCGA database. (B‐E) The single‐cell database showed that pancreatic cancer cells had higher SP1 expression, and SPARC tended to be expressed in stromal cells.
Supplemental Figure 6. The efficiency of siRAB27A lentivirus. (A) The lentivirus with the siRNA sequence targeting RAB27A inhibited RAB27A expression in pancreatic cancer cells. (B, C) Nanoparticle tracking analysis showed that RAB27A downregulation effectively reduced the EVs release from the host cells. ***P < 0.001.
Supplemental Figure 7. Fluorescent miR‐31‐5p transfer and orthotopic models. (A) Fluorescent miR‐31‐5p (miR‐31‐5p mimic 5′FAM) was transferred from pancreatic cancer cells to PSCs, which could be inhibited by RAB27A downregulation in pancreatic cancer cells. Scale bar equals 10 μm. (B) miR‐31‐5p obviously improved the chemoresistance of orthotopic mice models for pancreatic cancer cells and PSCs. (C) PSCs in orthotopic xenografts preferred to absorb EVs miR‐31‐5p. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (D) EVs miR‐31‐5p repressed LATS2 expression in PSCs. Scale bar equals 25 μm. **P < 0.01.
Supplemental Table 1: Primers sequences
Supplemental Table 2: Possible transcription factors based on ChIP‐seq
Supplemental Table 3: Possible transcription factors based on motif sequence
Supplemental Table 4: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 A‐C
Supplemental Table 5: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 D‐F
Supplemental Table 6: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 K‐M
Supplemental Table 7: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 O‐Q
Supplemental Table 8: Tumor volume and mice body weight in figure 8 S‐U
Supplemental Table 9: Correlations of miR31‐5p expression levels with clinical and pathologic parameters
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.


