Abstract
Among a variety of deep muscle trigger points, the piriform muscle trigger point is selected for individual scrutiny. This seems fully justified by the great potential for confusing this entity with discogenic disease and consequently having unnecessary surgical procedures carried out.
The diagnosis can be made from findings on simple physical diagnostic tests and an appropriate history. Low back and hip pain with pain radiating down the back of the leg should suggest piriform syndrome as part of the differential diagnosis. This is especially true if a female patient has complaint of dyspareunia.
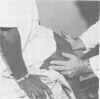
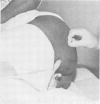
Pain and weakness on resisted abduction-external rotation of the thigh is a sign of piriform syndrome. This is confirmed by tenderness and reproduction of the patient's complaints by digital pressure over the belly of the piriform muscle, completing the diagnostic criteria.
Local injection of the muscle belly is curative. There are no laboratory or x-ray findings leading to a diagnosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awad E. A. Interstitial myofibrositis: hypothesis of the mechanism. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1973 Oct;54(10):449–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENDSTRUP P., JESPERSEN K., ASBOE-HANSEN Morphological and chemical connective tissue changes in fibrositic muscles. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Dec;16(4):438–440. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonica J. J. Management of intractable pain in general practice. GP. 1966 Jan;33(1):107–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. B. Commonly overlooked pain syndromes responsive to simple therapy. Postgrad Med. 1975 Oct;58(4):107–113. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1975.11714172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. B. Psychophysiology of pain: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. J Fam Pract. 1974 May;1(1):9–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]