Abstract
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), in contrast to both chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), its 7 alpha-epimer, and lithocholic acid, enhanced receptor-dependent low-density lipoprotein (LDL) uptake and degradation in isolated hamster hepatocytes. The increase in cell-associated LDL was time- and concentration-dependent, with a maximum effect observed at approx. 60 min with 1 mM-UDCA. This increase was not associated with a detergent effect of UDCA, as no significant modifications were observed either in the cellular release of lactate dehydrogenase or in Trypan Blue exclusion. The effect of UDCA was not due to a modification of the LDL particle, but rather was receptor-related. UDCA (1 mM) maximally increased the number of 125I-LDL-binding sites (Bmax.) by 35%, from 176 to 240 ng/mg of protein, without a significant modification of the binding affinity. Furthermore, following proteolytic degradation of the LDL receptor with Pronase, specific LDL binding decreased to the level of non-specific binding, and the effect of UDCA was abolished. Conversely, the trihydroxy 7 beta-hydroxy bile acid ursocholic acid and its 7 alpha-epimer, cholic acid, induced a significant decrease in LDL binding by approx. 15%. The C23 analogue of UDCA (nor-UDCA) and CDCA did not affect LDL binding. On the other hand, UDCA conjugated with either glycine (GUDCA) or taurine (TUDCA), increased LDL binding to the same extent as did the free bile acid. The half maximum time (t1/2) to reach the full effect was 1-2 min for UDCA and TUDCA, while GUDCA had a much slower t1/2 of 8.3 min. Ketoconazole (50 microM), an antifungal agent, increased LDL binding, but this effect was not additive when tested in the presence of 0.7 mM-UDCA. The results of the studies indicate that, in isolated hamster hepatocytes, the UDCA-induced increase in receptor-dependent LDL binding and uptake represents a direct effect of this bile acid. The action of the bile acid is closely related to its specific structural conformation, since UDCA and its conjugates are the only bile acids shown to express this ability thus far. However, certain agents other than bile acids, such as ketoconazole, have a similar effect. Finally, the studies suggest that the recruitment of LDL receptors from a latent pool in the hepatocellular membrane may be the mechanism by which UDCA exerts its direct effect.
Full text
PDF

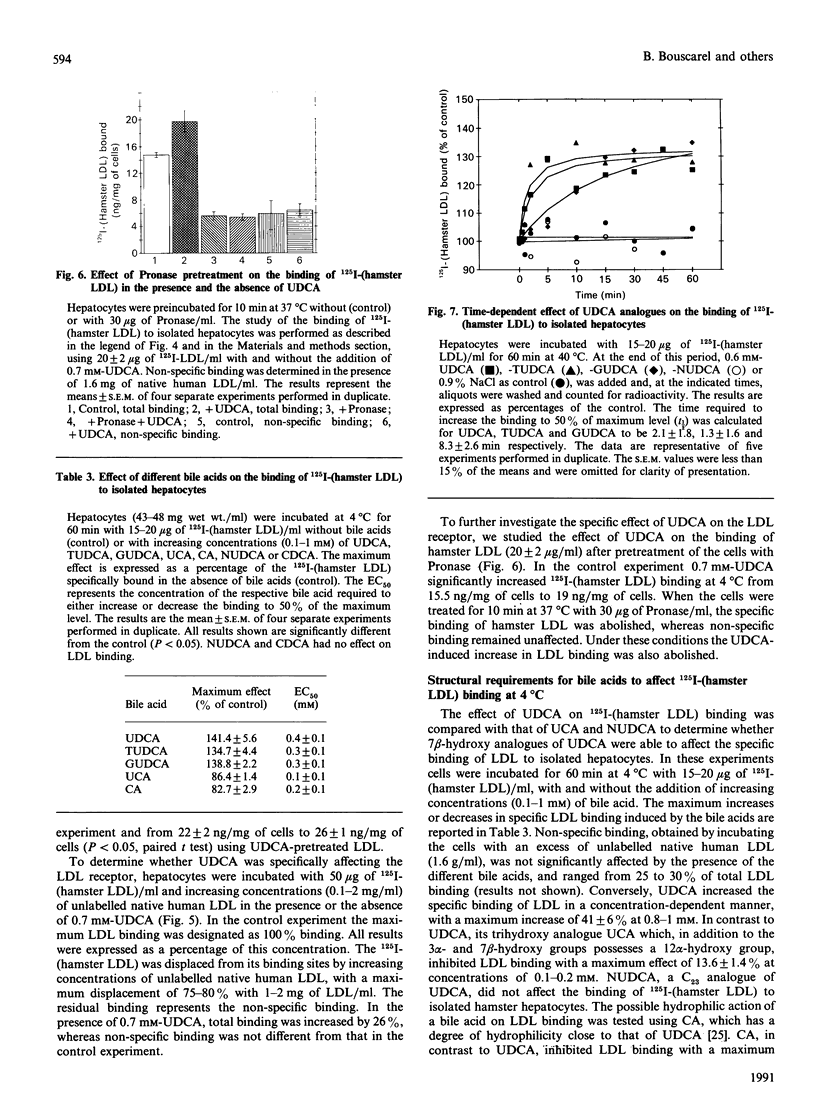




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelin B., Raviola C. A., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Regulation of hepatic lipoprotein receptors in the dog. Rapid regulation of apolipoprotein B,E receptors, but not of apolipoprotein E receptors, by intestinal lipoproteins and bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):816–831. doi: 10.1172/JCI110835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwer M. S., Engelking L. R., Nolan K., Sullivan D., Zimniak P., Lester R. Hepatotoxic bile acids increase cytosolic Ca++ activity of isolated rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):887–891. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bihain B. E., Deckelbaum R. J., Yen F. T., Gleeson A. M., Carpentier Y. A., Witte L. D. Unesterified fatty acids inhibit the binding of low density lipoproteins to the human fibroblast low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17316–17321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Watanabe Y., Kita T. Impaired receptor-mediated catabolism of low density lipoprotein in the WHHL rabbit, an animal model of familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3305–3309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouscarel B., Augert G., Taylor S. J., Exton J. H. Alterations in vasopressin and angiotensin II receptors and responses during culture of rat liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Dec 10;1055(3):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90042-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouscarel B., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of the angiotensin II receptor in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Evidence that a single population is coupled to two different responses. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14913–14919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouscarel B., Meurer K., Decker C., Exton J. H. The role of protein kinase C in the inactivation of hepatic glycogen synthase by calcium-mobilizing agonists. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):47–53. doi: 10.1042/bj2510047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouscarel B., Wilson P. B., Blackmore P. F., Lynch C. J., Exton J. H. Agonist-induced down-regulation of the angiotensin II receptor in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14920–14924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Dana S. E., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-dependent hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters contained in plasma low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2925–2929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein receptors in the liver. Control signals for plasma cholesterol traffic. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):743–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Kovanen P. T., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated uptake of lipoprotein-cholesterol and its utilization for steroid synthesis in the adrenal cortex. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1979;35:215–257. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571135-7.50009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corin R. E., Donner D. B. Up-regulation of insulin receptors in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11413–11416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dave J. R., Knazek R. A., Liu S. C. Arachidonic acid, bradykinin and phospholipase A2 modify both prolactin binding capacity and fluidity of mouse hepatic membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Kollmer M. E., Glickman R. M. Apolipoprotein B synthesis in rat small intestine: regulation by dietary triglyceride and biliary lipid. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jan;27(1):30–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H. Gallstone dissolution therapy with ursodiol. Patient selection. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Dec;34(12 Suppl):36S–38S. doi: 10.1007/BF01536660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Roat J. W., Gonzalez V., Sarva R. P., Farivar S. Comparative efficacy and side effects of ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acids in dissolving gallstones. A double-blind controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1257–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Föllmann W., Petzinger E., Kinne R. K. Alterations of bile acid and bumetanide uptake during culturing of rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):C700–C712. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.4.C700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle P. R., Theilmann L., Raedsch R., Otto G., Stiehl A. Ursodeoxycholate reduces hepatotoxicity of bile salts in primary human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 1):486–491. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The LDL pathway in human fibroblasts: a receptor-mediated mechanism for the regulation of cholesterol metabolism. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:147–181. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. K., Sexton R. C., Rudney H. Differential regulation of low density lipoprotein suppression of HMG-CoA reductase activity in cultured cells by inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 1990 Feb;31(2):203–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H. M., Kolhatkar A. A., Marino M. W., Manchester K. M., Donner D. B. Identification, characterization, and homologous up-regulation of latent (cryptic) receptors for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18590–18594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Role of the liver in lipoprotein catabolism. Methods Enzymol. 1986;129:591–612. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)29093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Müller P., Portenier M., Staehelin M. Determination of the desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors by [3H]CGP-12177. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2160669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Hylemon P. B., Vlahcevic Z. R. Regulation of bile acid synthesis. III. Correlation between biliary bile salt hydrophobicity index and the activities of enzymes regulating cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1989 Aug;30(8):1161–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeg J. M., Demosky S. J., Jr, Schaefer E. J., Starzl T. E., Brewer H. B., Jr Characterization of hepatic low density lipoprotein binding and cholesterol metabolism in normal and homozygous familial hypercholesterolemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):429–436. doi: 10.1172/JCI111229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeg J. M., Maher M. B., Zech L. A., Bailey K. R., Gregg R. E., Lackner K. J., Fojo S. S., Anchors M. A., Bojanovski M., Sprecher D. L. Effectiveness of mevinolin on plasma lipoprotein concentrations in type II hyperlipoproteinemia. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Apr 15;57(11):933–939. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90733-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishac E. J., Kunos G. An arachidonate metabolite is involved in the conversion from alpha 1- to beta-adrenergic glycogenolysis in isolated rat liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):53–57. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Okajima F., Ui M. Conversion of adrenergic mechanism from an alpha- to a beta-type during primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Accompanying decreases in the function of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory component of adenylate cyclase identified as the substrate of islet-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15464–15473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempen H. J., van Son K., Cohen L. H., Griffioen M., Verboom H., Havekes L. Effect of ketoconazole on cholesterol synthesis and on HMG-CoA reductase and LDL-receptor activities in Hep G2 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 15;36(8):1245–1249. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Rodwell V. W. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by reversible phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. J Lipid Res. 1985 Aug;26(8):903–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume N., Kita T., Mikami A., Yokode M., Ishii K., Nagano Y., Kawai C. Induction of mRNA for low-density lipoprotein receptors in heterozygous Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits treated with CS-514 (Pravastatin) and cholestyramine. Circulation. 1989 May;79(5):1084–1090. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.5.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiss O., von Bergmann K., Streicher U., Strotkoetter H. Effect of three different dihydroxy bile acids on intestinal cholesterol absorption in normal volunteers. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):144–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Fischer H., Kurtz W., Güldütuna S., Hübner K., Hellstern A., Gatzen M., Leuschner M. Ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis: results of a controlled double-blind trial. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1268–1274. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Leuschner M., Sieratzki J., Kurtz W., Hübner K. Gallstone dissolution with ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with chronic active hepatitis and two years follow-up. A pilot study. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Jul;30(7):642–649. doi: 10.1007/BF01308413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Kan P. B., Hirst M. A., Marcus R. A., Feldman D. Ketoconazole blocks adrenal steroidogenesis by inhibiting cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1172/JCI110903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P. T., Gil G., Südhof T. C., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Mevinolin, an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, induces mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in livers of hamsters and rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8370–8374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. H. Two independent lipoprotein receptors on hepatic membranes of dog, swine, and man. Apo-B,E and apo-E receptors. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1197–1206. doi: 10.1172/JCI110365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavolti M., Fromm H., Ceryak S., Roberts I. M. Modulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity by bile acids: differential effects of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids in the hamster. J Lipid Res. 1987 Nov;28(11):1281–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavolti M., Fromm H., Ceryak S., Shehan K. L. Interaction of potentially toxic bile acids with human plasma proteins: binding of lithocholic (3 alpha-hydroxy-5 beta-cholan-24-oic) acid to lipoproteins and albumin. Lipids. 1989 Jul;24(7):673–676. doi: 10.1007/BF02535089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myant N. B., Mitropoulos K. A. Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):135–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsell K., Angelin B., Leijd B., Einarsson K. Comparative effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on bile acid kinetics and biliary lipid secretion in humans. Evidence for different modes of action on bile acid synthesis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1248–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. Conversion of adrenergic regulation of glycogen phosphorylase and synthase from an alpha to a beta type during primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):658–668. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petzinger E., Frimmer M. Comparative investigations on the uptake of phallotoxins, bile acids, bovine lactoperoxidase and horseradish peroxidase into rat hepatocytes in suspension and in cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 13;937(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G., Roberts D. C., West C. E. Separation of plasma lipoproteins by density-gradient ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90488-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennert H., Fischer R. T., Alvarez J. G., Trzaskos J. M., Strauss J. F., 3rd Generation of regulatory oxysterols: 26-hydroxylation of cholesterol by ovarian mitochondria. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):738–746. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Grigolo B., Pellicciari R., Natalini B. Structure-activity relationship studies on natural and synthetic bile acid analogs. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Dec;34(12 Suppl):24S–35S. doi: 10.1007/BF01536659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M. J., Peterson C. O. LDL receptors in bovine tissues assayed as the heparin-sensitive binding of 125I-labeled LDL in homogenates: relation between liver LDL receptors and serum cholesterol in the fetus and post term. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 22;836(1):96–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M. J., Reihnér E., Einarsson K., Ewerth S., Angelin B. Low density lipoprotein receptor-binding activity in human tissues: quantitative importance of hepatic receptors and evidence for regulation of their expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3469–3473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter A. M., Bugaut M., Saxton J., Fisher S. C., Brindley D. N. Effects of preincubation of primary monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes with low- and high-density lipoproteins on the subsequent binding and metabolism of human low-density lipoprotein. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):79–84. doi: 10.1042/bj2470079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter A. M., Saxton J., Brindley D. N. Characterization of the binding of human low-density lipoprotein to primary monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj2400549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A., Merritt S., Turkewitz A. Antibody-induced receptor loss. Different fates for asialoglycoproteins and the asialoglycoprotein receptor in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15225–15232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedwick K. E., Aller L. H. Spectrophotometry of H II regions in the spiral galaxy M101. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):1994–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Packard C. J., Grundy S. M., Yeshurun D., Gotto A. M., Jr, Taunton O. D. Effects of saturated and polyunsaturated fat diets on the chemical composition and metabolism of low density lipoproteins in man. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jan;21(1):91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal A. K., Finver-Sadowsky J., McSherry C. K., Mosbach E. H. Effect of cholesterol and bile acids on the regulation of cholesterol metabolism in hamster. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 12;752(2):214–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Dietschy J. M. Dietary saturated triacylglycerols suppress hepatic low density lipoprotein receptor activity in the hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4526–4530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Rates of low density lipoprotein uptake and cholesterol synthesis are regulated independently in the liver. J Lipid Res. 1985 Apr;26(4):465–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange R. C. Hepatic bile flow. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1055–1102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel T. J., Kruijt J. K., Van Gent T., Van Tol A. Saturable high affinity binding, uptake and degradation of rat plasma lipoproteins by isolated parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;665(1):22–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bossche H., Ruysschaert J. M., Defrise-Quertain F., Willemsens G., Cornelissen F., Marichal P., Cools W., Van Cutsem J. The interaction of miconazole and ketoconazole with lipids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 15;31(16):2609–2617. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90707-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega G. L., Grundy S. M. Mechanisms of primary hypercholesterolemia in humans. Am Heart J. 1987 Feb;113(2 Pt 2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y. Serial inbreeding of rabbits with hereditary hyperlipidemia (WHHL-rabbit). Atherosclerosis. 1980 Jun;36(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]