Abstract
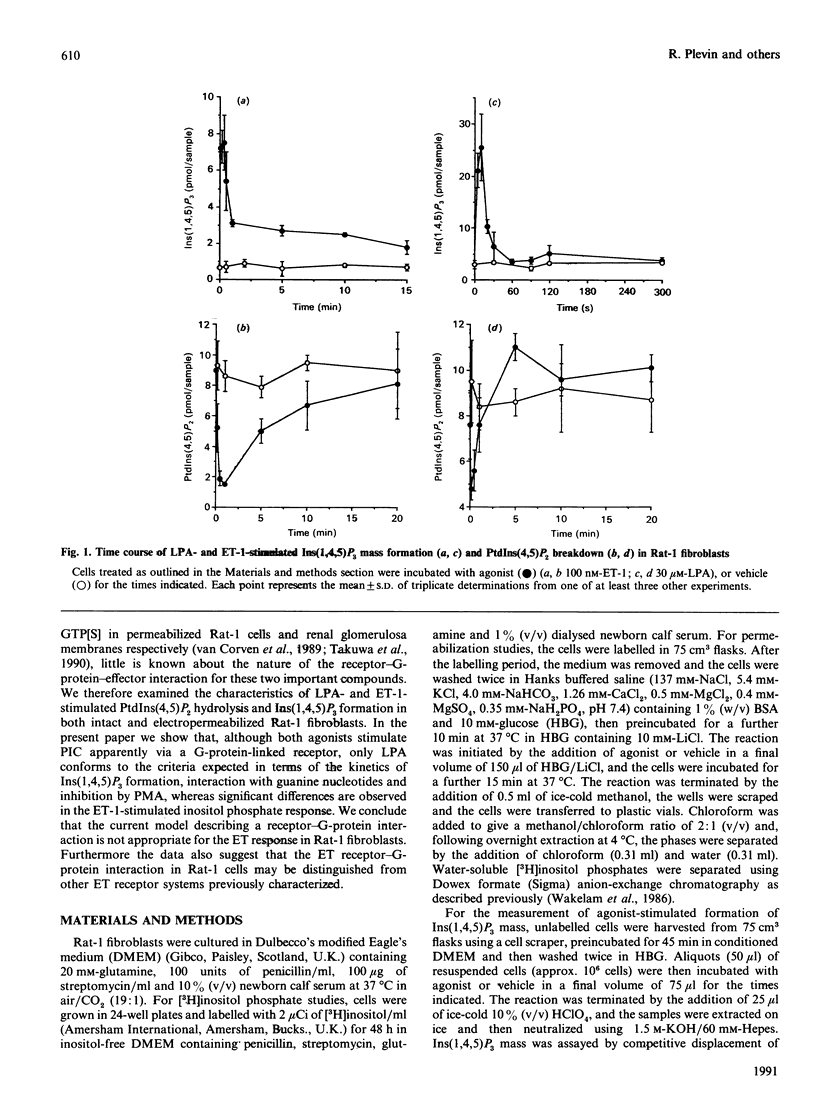
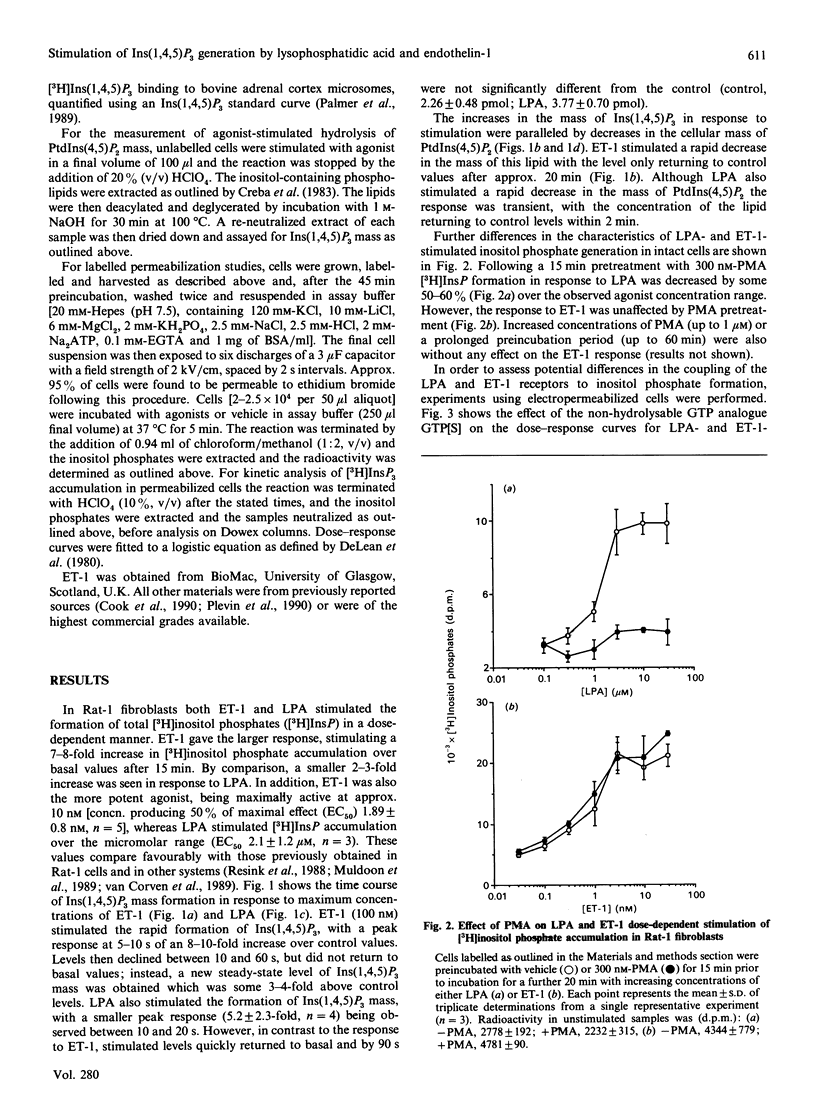
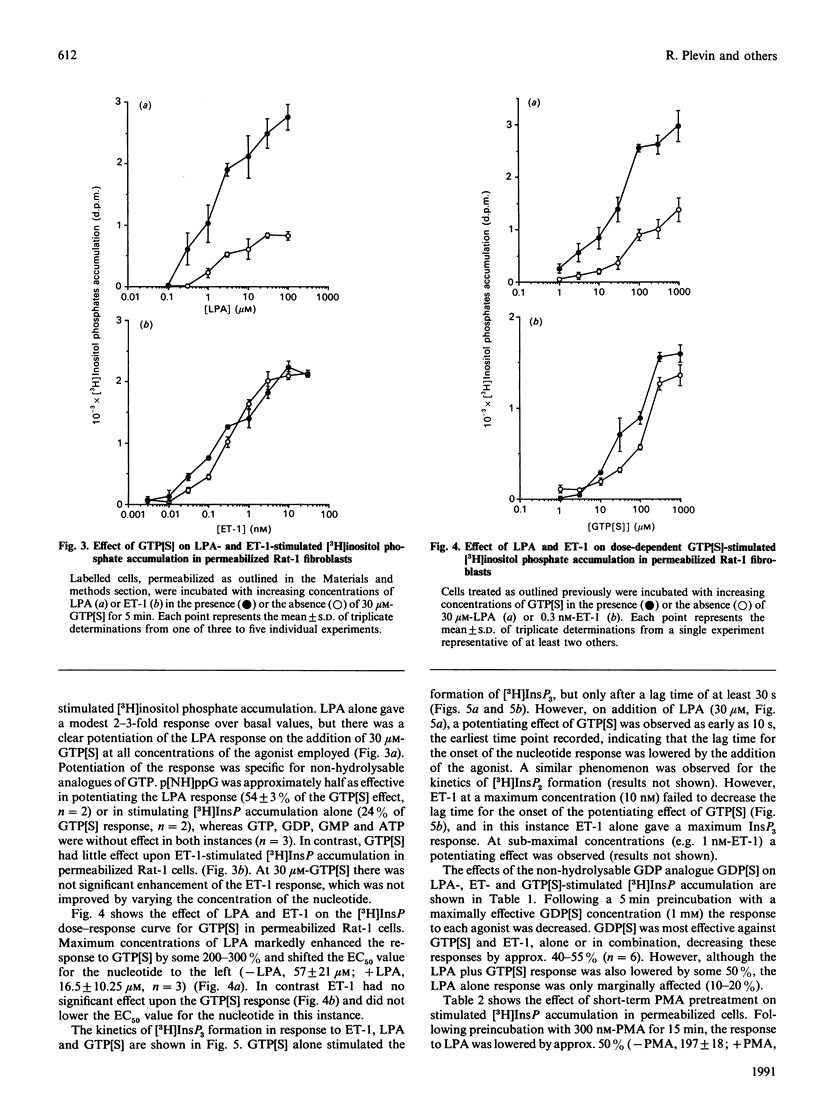
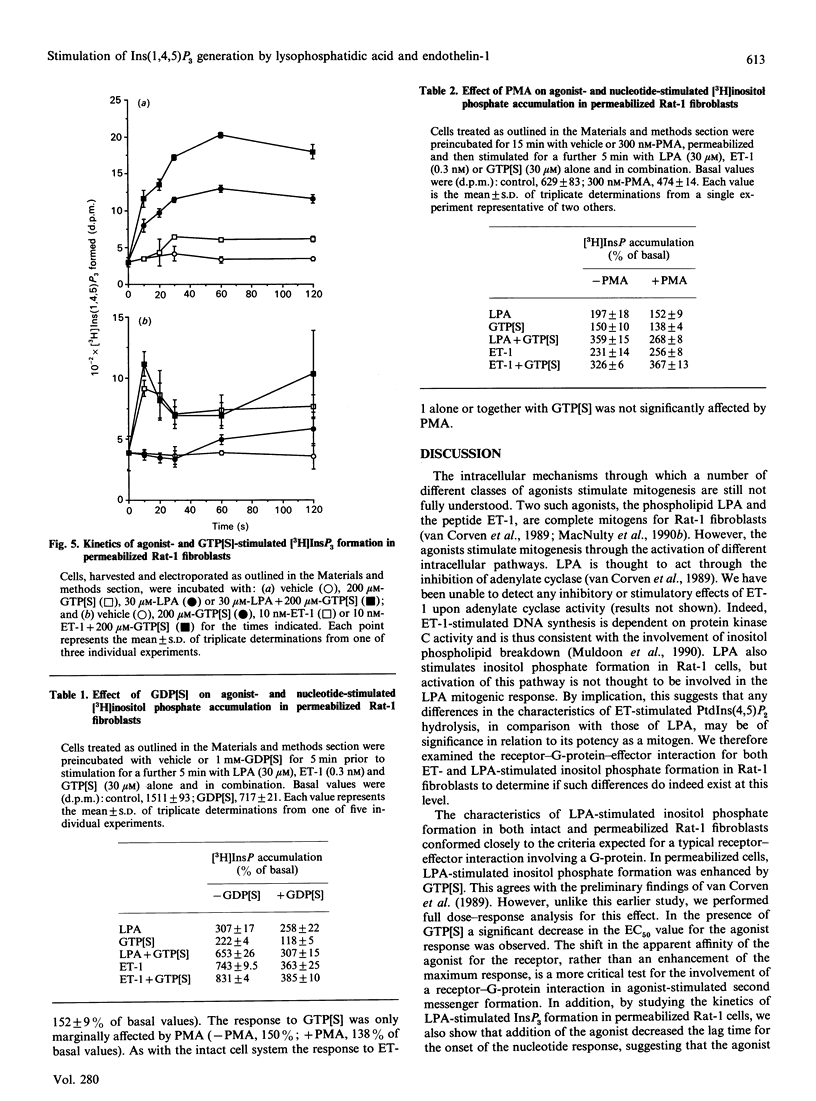
Endothelin-1 (ET-1)- and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-stimulated PtdIns(4,5)P2 hydrolysis has been studied in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Although both agonists caused the dose-dependent accumulation of inositol phosphates, a number of differences were observed. LPA induced a transient increase in Ins(1,4,5)P3 mass which returned to basal levels within 90 s, whereas the response to ET-1 did not desensitize, with levels remaining at 3-4 times basal values for up to 15 min. Stimulated decreases in mass levels of PtdIns(4,5)P2 mirrored Ins(1,4,5)P3 formation for both agonists. Experiments with electropermeabilized cells demonstrated that the effects of both agonists are stimulated by a phospholipase C controlled by a guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory protein; however, there are differences in the nature of these interactions. The inositol phosphate response to ET-1 is poorly potentiated by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) and markedly inhibited by guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate (GDP[S]), whereas that to LPA is potentiated by GTP[S] but is relatively insensitive to GDP[S]. In addition, LPA decreased the lag time for the onset of GTP[S]-stimulated [3H]InsP3 accumulation, whereas ET-1 was without effect. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate treatment of the cells inhibited LPA-stimulated, but not ET-1-stimulated, inositol phosphate formation in both intact and permeabilized cells, suggesting that the site of protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation may be blocked in ET-1-stimulated Rat-1 cells. The results indicate that the receptor-G-protein-phospholipase C interaction for the two agonists may not conform to the same model.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambar I., Kloog Y., Schvartz I., Hazum E., Sokolovsky M. Competitive interaction between endothelin and sarafotoxin: Binding and phosphoinositides hydrolysis in rat atria and brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki S., Kawahara Y., Kariya K., Sunako M., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Stimulation of phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphoinositides by endothelin in cultured rabbit aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1072–1079. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley D. M., Corps A. N., Brown K. D. Bombesin and platelet-derived growth factor stimulate formation of inositol phosphates and Ca2+ mobilization in Swiss 3T3 cells by different mechanisms. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):177–185. doi: 10.1042/bj2580177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Kinetics of activation of phospholipase C by P2Y purinergic receptor agonists and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Hepler J. R., Harden T. K. Hormone and growth factor receptor-mediated regulation of phospholipase C activity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blakeley D. M., Hamon M. H., Laurie M. S., Corps A. N. Protein kinase C-mediated negative-feedback inhibition of unstimulated and bombesin-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):631–639. doi: 10.1042/bj2450631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Littlewood C. J. Endothelin stimulates DNA synthesis in Swiss 3T3 cells. Synergy with polypeptide growth factors. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):977–980. doi: 10.1042/bj2630977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. F., Hauser G. Effects of bradykinin, GTP gamma S, R59022 and N-ethylmaleimide on inositol phosphate production in NG108-15 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro E., Garcia A., Picatoste F. Carbachol and histamine stimulation of guanine-nucleotide-dependent phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):29–35. doi: 10.1042/bj2610029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Palmer S., Plevin R., Wakelam M. J. Mass measurement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and sn-1,2-diacylglycerol in bombesin-stimulated Swiss 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2650617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T., Okano Y., Nozawa Y. Bradykinin-induced generation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in fibroblasts and neuroblastoma cells: effect of pertussis toxin, extracellular calcium, and down-regulation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1429–1435. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geny B., Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Phorbol ester inhibits polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase activity stimulated by either Ca2+, fluoride or GTP analogue in HL60 membranes and in permeabilized HL60 cells. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Boyer J. L., Downes C. P. Phosphoinositide hydrolysis by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-activated phospholipase C of turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):583–593. doi: 10.1042/bj2520583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNulty E. E., Plevin R., Wakelam M. J. Endothelin stimulates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis in Rat-1 cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Jun;18(3):482–483. doi: 10.1042/bst0180482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNulty E. E., Plevin R., Wakelam M. J. Stimulation of the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylcholine by endothelin, a complete mitogen for Rat-1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):761–766. doi: 10.1042/bj2720761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousli M., Bueb J. L., Bronner C., Rouot B., Landry Y. G protein activation: a receptor-independent mode of action for cationic amphiphilic neuropeptides and venom peptides. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Sep;11(9):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90179-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon L. L., Pribnow D., Rodland K. D., Magun B. E. Endothelin-1 stimulates DNA synthesis and anchorage-independent growth of Rat-1 fibroblasts through a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. Cell Regul. 1990 Mar;1(4):379–390. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.4.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon L. L., Rodland K. D., Forsythe M. L., Magun B. E. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis, diacylglycerol release, and gene expression in response to endothelin, a potent new agonist for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8529–8536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakayama M., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Endothelin-mediated stimulation of DNA synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):880–883. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92804-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsako S., Deguchi T. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid of calcium influx and cyclic GMP synthesis in neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10945–10948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Guanosine 5'-O-(thiotriphosphate)-dependent inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes is inhibited by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1638–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Hughes K. T., Lee D. Y., Wakelam M. J. Development of a novel, Ins(1,4,5)P3-specific binding assay. Its use to determine the intracellular concentration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in unstimulated and vasopressin-stimulated rat hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Different effects of phorbol ester on angiotensin II- and stable GTP analogue-induced activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in membranes isolated from rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):209–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2480209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Palmer S., Gardner S. D., Wakelam M. J. Regulation of bombesin-stimulated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate generation in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts by a guanine-nucleotide-binding protein. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):605–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2680605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Scott-Burden T., Bühler F. R. Endothelin stimulates phospholipase C in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1360–1368. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Scott-Burden T., Weber E., Bühler F. R. Phorbol ester promotes a sustained down-regulation of endothelin receptors and cellular responses to endothelin in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1213–1219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90995-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubert P., Gillard V., Plas P., Guillon J. M., Chabrier P. E., Braquet P. Angiotensin II and phorbol-esters potently down-regulate endothelin (ET-1) binding sites in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):809–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Kahan C., Hartmann T., Pouyssegur J. Strong and persistent activation of inositol lipid breakdown induces early mitogenic events but not Go to S phase progression in hamster fibroblasts. Comparison of thrombin and carbachol action in cells expressing M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22292–22299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S., Wann S., Mené P., Dubyak G. R., Kester M., Nakazato Y., Sedor J. R., Dunn M. J. Endothelin stimulates phospholipase C, Na+/H+ exchange, c-fos expression, and mitogenesis in rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):708–712. doi: 10.1172/JCI113935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa N., Takuwa Y., Yanagisawa M., Yamashita K., Masaki T. A novel vasoactive peptide endothelin stimulates mitogenesis through inositol lipid turnover in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7856–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa Y., Kasuya Y., Takuwa N., Kudo M., Yanagisawa M., Goto K., Masaki T., Yamashita K. Endothelin receptor is coupled to phospholipase C via a pertussis toxin-insensitive guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):653–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI114488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., van Paridon P. A., Verlaan I., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Epidermal-growth-factor-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human A431 cells. Differences from the effect of bradykinin. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2520857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Renterghem C., Vigne P., Barhanin J., Schmid-Alliana A., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Molecular mechanism of action of the vasoconstrictor peptide endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):977–985. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Marsault R., Breittmayer J. P., Frelin C. Endothelin stimulates phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and DNA synthesis in brain capillary endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):415–420. doi: 10.1042/bj2660415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin, a novel endothelium-derived peptide. Pharmacological activities, regulation and possible roles in cardiovascular control. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 15;38(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


