Abstract
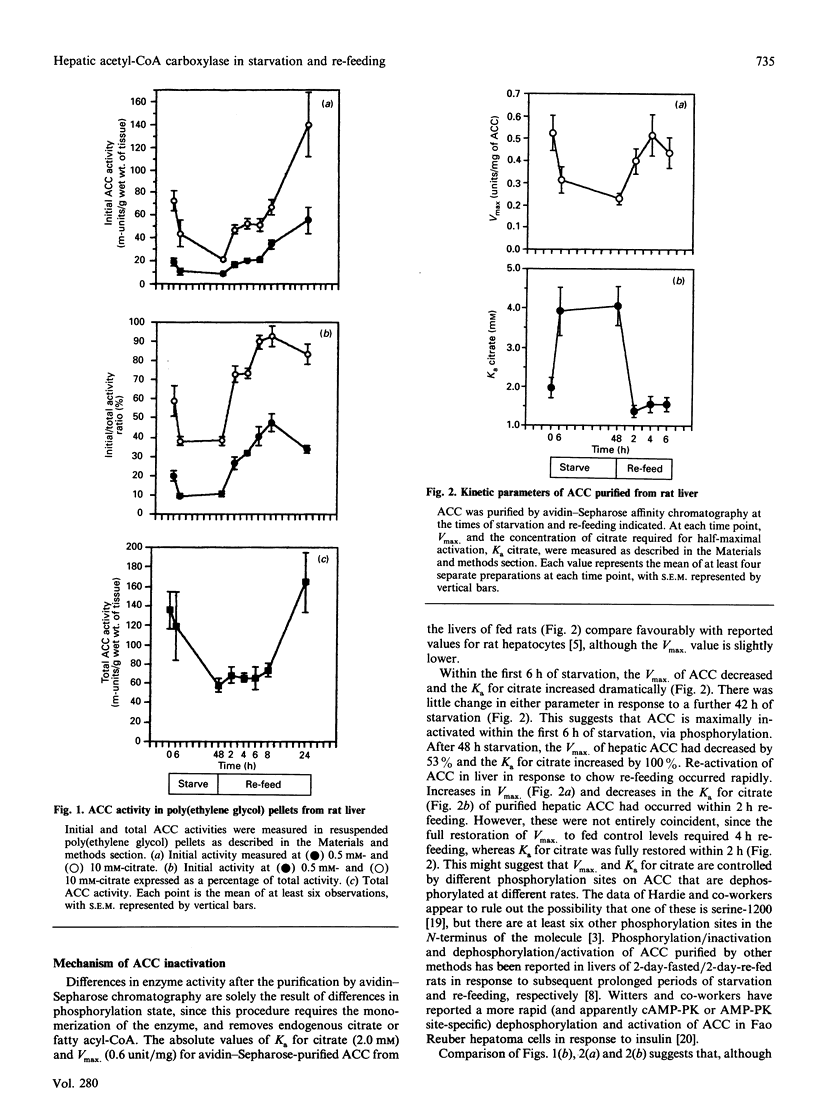
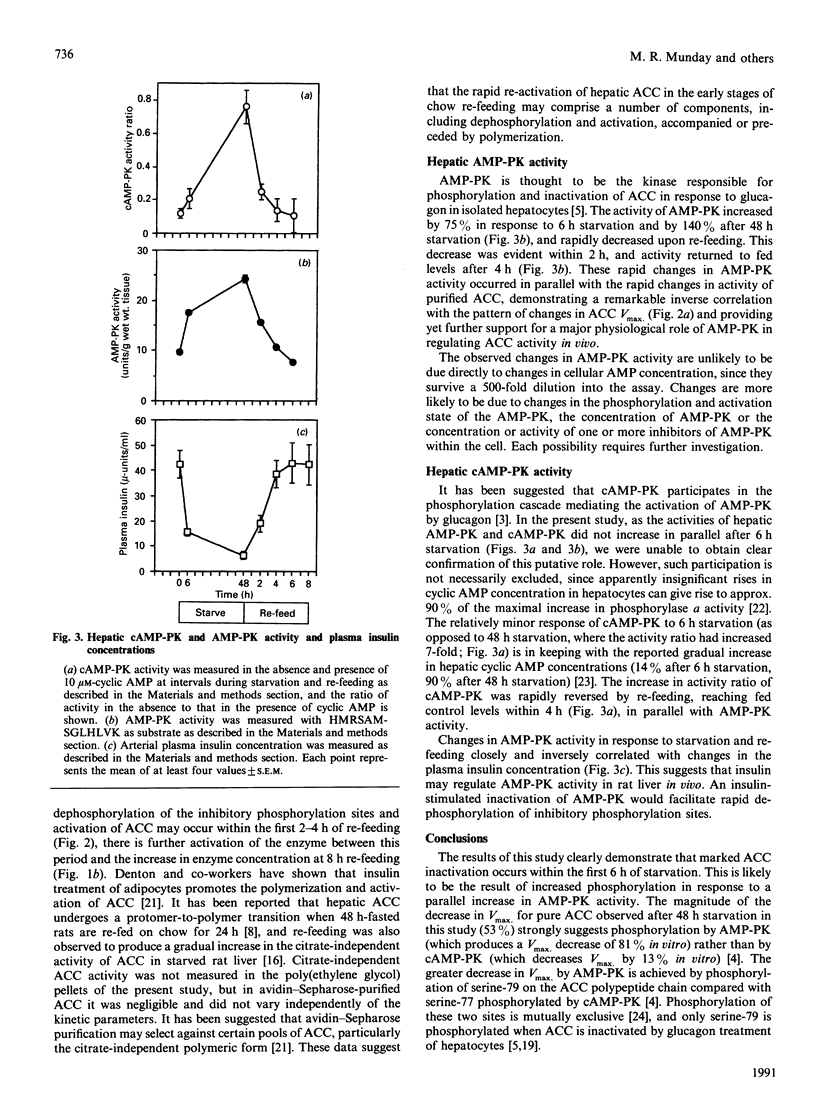
Rapid inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity in rat liver in response to 6 h starvation and rapid re-activation in response to 2-6 h of re-feeding chow were shown to be due to changes in the expressed activity of existing enzyme. Decreases and increases in ACC concentration occurred at later stages of the transitions, i.e. 6-48 h starvation and 8-24 h re-feeding respectively. The decrease in expressed activity of ACC was due primarily to changes in its phosphorylation state, demonstrated by a significantly decreased Vmax. and significantly increased Ka for citrate of enzyme purified by avidin-Sepharose chromatography from 6 h- or 48 h-starved rats. These effects were totally reversed within 2-4 h of chow re-feeding. Changes in the activity of purified ACC closely correlated with reciprocal changes in the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMP-PK) over the fed to starved to re-fed transition. Increases in the activity ratio of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in response to starvation lagged behind the increase in AMP-PK and the decrease in ACC activity. Changes in AMP-PK and ACC activities of rat liver closely correlated with changes in plasma insulin concentration in response to time courses of starvation and re-feeding.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick A. C., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Use of rapid gel-permeation chromatography to explore the inter-relationships between polymerization, phosphorylation and activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Effects of insulin and phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):773–782. doi: 10.1042/bj2410773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carling D., Zammit V. A., Hardie D. G. A common bicyclic protein kinase cascade inactivates the regulatory enzymes of fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. P., Sim A. T., Hardie D. G. Location and function of three sites phosphorylated on rat acetyl-CoA carboxylase by the AMP-activated protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen M. J., Hindriks G. A. Studies on the substrate for hepatic lipogenesis in the rat. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80558-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G., Back D. W., Wilson S. B., Goldman M. J. Regulation of genes for enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:46–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G. Regulation of fatty acid synthesis via phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Prog Lipid Res. 1989;28(2):117–146. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(89)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Moore F., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Roles of the AMP-activated and cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinases in the adrenaline-induced inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat adipocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness M. J., MacLennan P. A., Palmer T. N., Sugden M. C. The disposition of carbohydrate between glycogenesis, lipogenesis and oxidation in liver during the starved-to-fed transition. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):325–330. doi: 10.1042/bj2520325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness M. J., Sugden M. C. Hepatic carbon flux after re-feeding. Hyperthyroidism blocks glycogen synthesis and the suppression of glucose output observed in response to carbohydrate re-feeding. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):627–634. doi: 10.1042/bj2470627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Kilburn E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. The roles of synthesis and degradation in regulation of enzyme levels in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6254–6262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. M., Zammit V. A. Changes in the properties of cytosolic acetyl-CoA carboxylase studied in cold-clamped liver samples from fed, starved and starved-refed rats. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):511–517. doi: 10.1042/bj2720511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday M. R., Campbell D. G., Carling D., Hardie D. G. Identification by amino acid sequencing of three major regulatory phosphorylation sites on rat acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):331–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday M. R., Carling D., Hardie D. G. Negative interactions between phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by the cyclic AMP-dependent and AMP-activated protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday M. R., Hardie D. G. The role of acetyl-CoA carboxylase phosphorylation in the control of mammary gland fatty acid synthesis during the starvation and re-feeding of lactating rats. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):85–91. doi: 10.1042/bj2370085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikori K., Iritani N., Numa S. Levels of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase and its effectors in rat liver after short-term fat-free refeeding. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 15;32(1):19–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80725-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Hemmings B. A., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. Characterisation of a reconstituted Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):455–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman-Lopez C. R., Shriver B. J., Joseph C. R., Allred J. B. Mitochondrial acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Time course of mobilization/activation in liver of refed rats. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):927–930. doi: 10.1042/bj2600927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:3–6. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz H. J., Müller M. J., Krone W., Tarnowski W. Coordinate control of intermediary metabolism in rat liver by the insulin/glucagon ratio during starvation and after glucose refeeding. Regulatory significance of long-chain acyl-CoA and cyclic AMP. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Oct;183(2):647–663. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim A. T., Hardie D. G. The low activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in basal and glucagon-stimulated hepatocytes is due to phosphorylation by the AMP-activated protein kinase and not cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jun 20;233(2):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Liu Y. L., Holness M. J. Glucose utilization and disposal in cardiothoracic and skeletal muscles during the starved-to-fed transition in the rat. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 15;272(1):133–137. doi: 10.1042/bj2720133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thampy K. G., Wakil S. J. Regulation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. II. Effect of fasting and refeeding on the activity, phosphate content, and aggregation state of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6454–6458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Watts T. D., Daniels D. L., Evans J. L. Insulin stimulates the dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5473–5477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


