Abstract
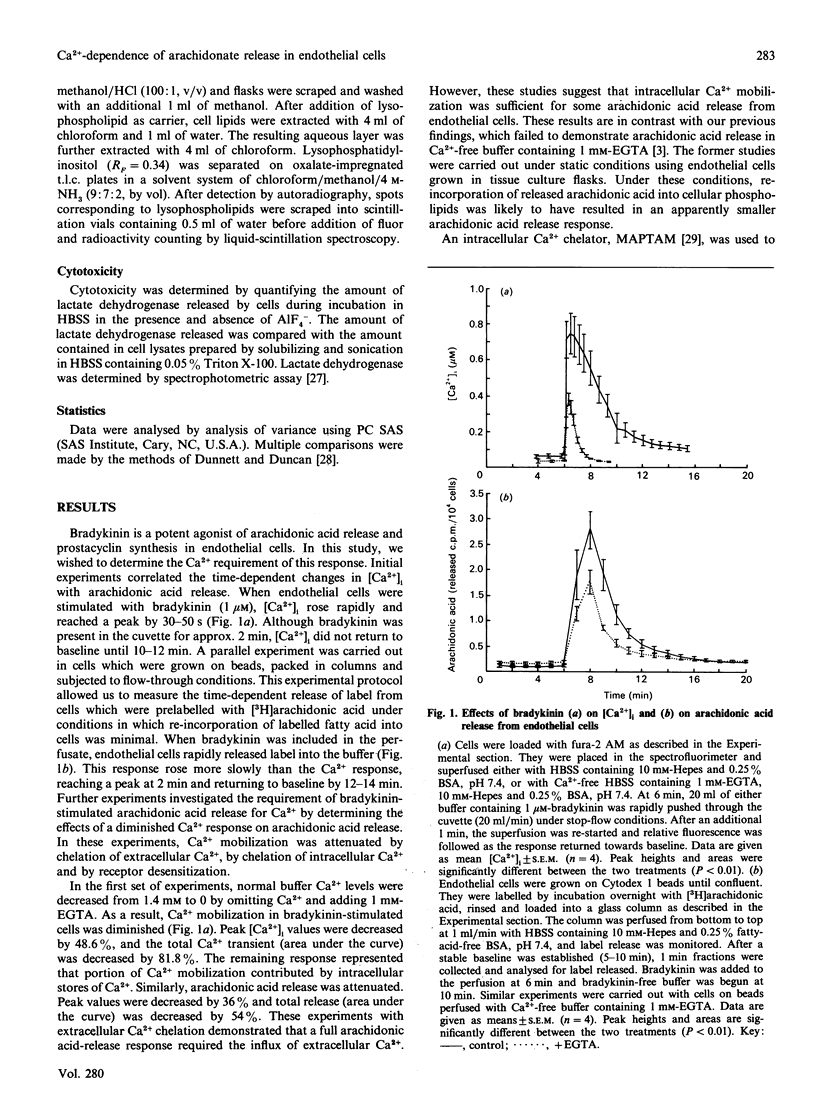
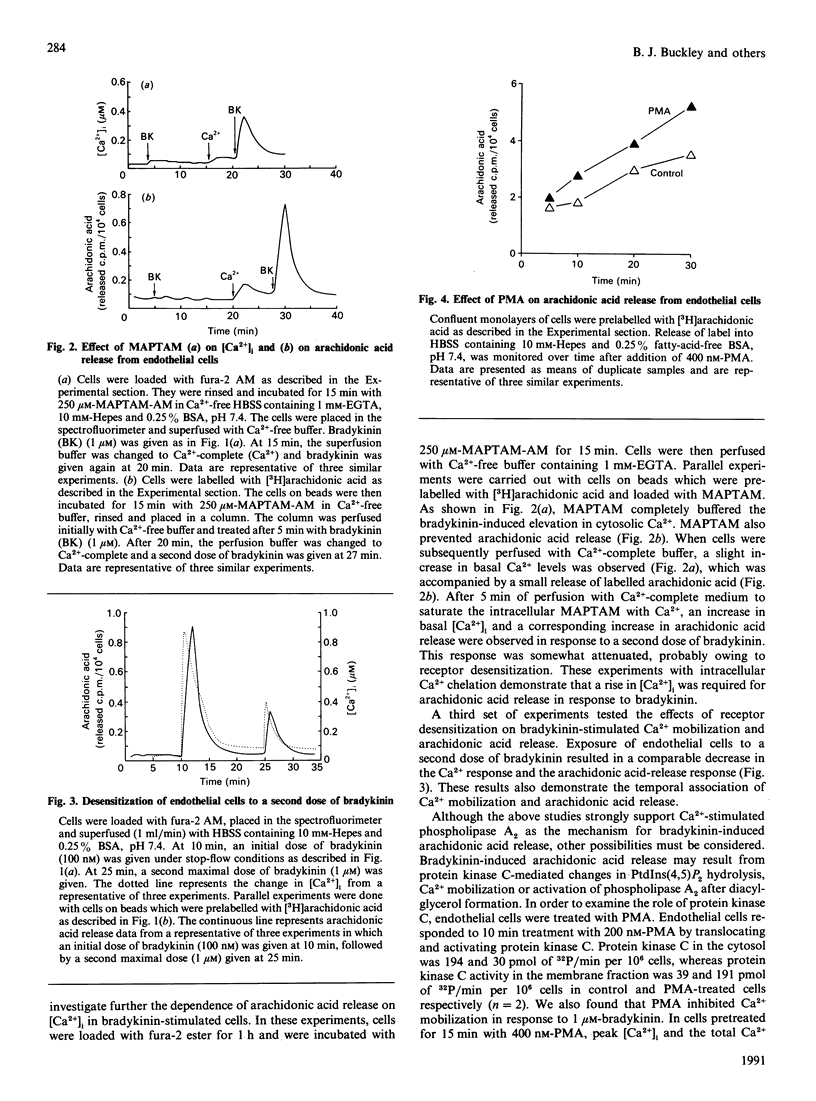
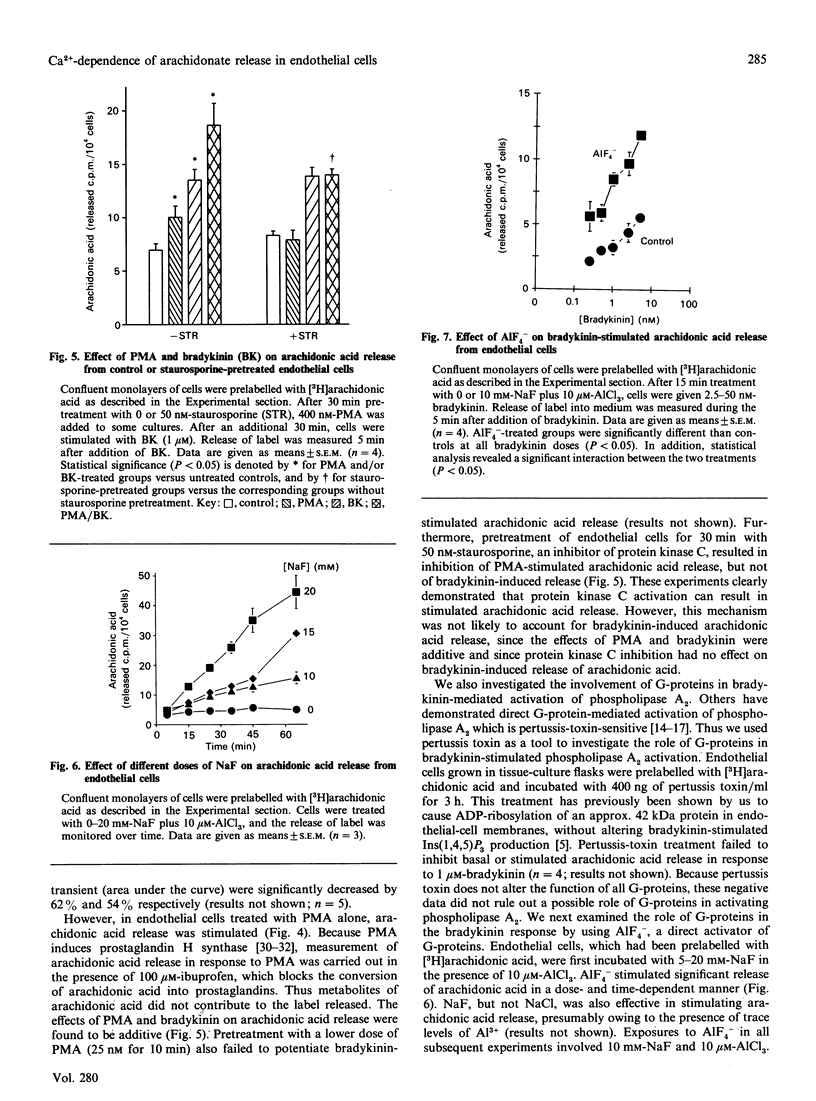
Ca2+ metabolism and its relationship to arachidonic acid release were studied in cultured pig aortic endothelial cells. When cells were treated with bradykinin, a rapid rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) occurred. Arachidonic acid release from cells prelabelled with [3H]arachidonic acid and subjected to flow-through conditions closely followed the changes in [Ca2+]i. Attenuation of the Ca2+ response by chelating extracellular and intracellular Ca2+ or by desensitization of receptors led to comparable attenuation of arachidonate release. Activation of protein kinase C inhibited Ca2+ mobilization in response to bradykinin and stimulated arachidonic acid release. Inhibition of protein kinase C had no effect on bradykinin-stimulated arachidonic acid release, suggesting that protein kinase C does not mediate the bradykinin response. The role of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G-proteins) in mediating the bradykinin response was also investigated. Bradykinin-stimulated arachidonic acid release was not diminished by preincubation with pertussis toxin. Treatment with the G-protein activator AlF4- resulted in the release of a large pool of arachidonic acid and the formation of lysophospholipids. Combined treatment with AlF4- and bradykinin resulted in a greater than additive effect on arachidonic acid release. In contrast with bradykinin, AlF(4-)-stimulated arachidonic acid release was not dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca2+ or the mobilization of intracellular Ca2+. These results demonstrate Ca(2+)-dependent (bradykinin) and Ca(2+)-independent (AlF4-) pathways of phospholipase A2 activation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Capasso E. L. GTP gamma S increases thrombin-mediated inositol trisphosphate accumulation in permeabilized human endothelial cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1121–1125. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Dennis P. A., Griendling K. K., Diehl T. S., Davies P. F. GTP gamma S loading of endothelial cells stimulates phospholipase C and uncouples ATP receptors. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):C667–C673. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.5.C667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. C., McCarthy K. D., Lapetina E. G., Morell P. Receptor-stimulated phospholipase A2 activation is coupled to influx of external calcium and not to mobilization of intracellular calcium in C62B glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20147–20153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Luini A., Axelrod J. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C are activated by distinct GTP-binding proteins in response to alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7201–7205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. D., Hallam T. J., Pearson J. D. Protein kinase C activation alters the sensitivity of agonist-stimulated endothelial-cell prostacyclin production to intracellular Ca2+. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):431–437. doi: 10.1042/bj2620431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. D., Newton J. S., Jacob R., Pearson J. D. Homologous desensitization of ATP-mediated elevations in cytoplasmic calcium and prostacyclin release in human endothelial cells does not involve protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 15;272(1):217–221. doi: 10.1042/bj2720217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing D. J., Sabouni M. H., Brown G. L., Mustafa S. J. Fluoride produces endothelium-dependent relaxation and endothelium-independent contraction in coronary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jul;254(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Beaudry G. A., King L., Waite M. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Comparison of A23187 and 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 17;792(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derian C. K., Moskowitz M. A. Polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in endothelial cells and carotid artery segments. Bradykinin-2 receptor stimulation is calcium-independent. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3831–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Pertussis toxin inhibits endothelium-dependent relaxations evoked by fluoride. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 13;178(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94803-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Painter R. G., Fenton J. W., 2nd, English D., Callahan K. S. Thrombin-induced prostacyclin biosynthesis in human endothelium: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in stimulus/coupling responses. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jan;142(1):186–193. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerig M., Habenicht A. J., Heitz R., Zeh W., Katus H., Kommerell B., Ziegler R., Glomset J. A. sn-1,2-Diacylglycerols and phorbol diesters stimulate thromboxane synthesis by de novo synthesis of prostaglandin H synthase in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):903–911. doi: 10.1172/JCI112900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S. Secretory function of vascular endothelium. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1987;17A:397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Klein D. C. Activation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors, protein kinase C, or treatment with intracellular free Ca2+ elevating agents increases pineal phospholipase A2 activity. Evidence that protein kinase C may participate in Ca2+-dependent alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of pineal phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11764–11770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Deykin D. Activation of phospholipases A2 and C in pig aortic endothelial cells synthesizing prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7151–7154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Fishman P. H., Rebois R. V. Differential activation of the stimulatory and inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding proteins by fluoroaluminate in cells and in membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10645–10651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipase A2 activity in bovine rod outer segments by the beta gamma subunits of transducin and its inhibition by the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L. Light activation of phospholipase A2 in rod outer segments of bovine retina and its modulation by GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya H., Patton G. M., Hong S. L. Bradykinin-induced activation of phospholipase A2 is independent of the activation of polyphosphoinositide-hydrolyzing phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4972–4977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert T. L., Kent R. S., Whorton A. R. Bradykinin stimulation of inositol polyphosphate production in porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15288–15293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Siess W. Measurement of inositol phospholipid turnover in platelets. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:176–192. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnússon M. K., Halldórsson H., Kjeld M., Thorgeirsson G. Endothelial inositol phosphate generation and prostacyclin production in response to G-protein activation by AlF4-. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):703–711. doi: 10.1042/bj2640703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan-Boyd R., Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J., Hassid A. Effects of bradykinin and angiotensin II on intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C588–C598. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullane K. M., Pinto A. Endothelium, arachidonic acid, and coronary vascular tone. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):54–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan V., Holowka D., Baird B. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein participates in IgE receptor-mediated activation of endogenous and reconstituted phospholipase A2 in a permeabilized cell system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1459–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J., Daniel L. W., Waite M. Evidence of protein kinase C involvement in phorbol diester-stimulated arachidonic acid release and prostaglandin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5385–5393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotton S., Erneux C., Boeynaems J. M. Dual role of GTP-binding proteins in the control of endothelial prostacyclin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1113–1120. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M. S., Doherty P. J., Gottesman M. M. The tumor promoter phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate induces a program of altered gene expression similar to that induced by platelet-derived growth factor and transforming oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):357–360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier W. T. Activation of high levels of endogenous phospholipase A2 in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):195–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka S. R., Insel P. A. Phorbol ester and neomycin dissociate bradykinin receptor-mediated arachidonic acid release and polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Evidence that bradykinin mediates noninterdependent activation of phospholipases A2 and C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14640–14647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum I. The epidermal growth factor receptor is coupled to a phospholipase A2-specific pertussis toxin-inhibitable guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in cultured rat inner medullary collecting tubule cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4218–4222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. P., Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Hormone- and tumor promoter-induced activation or membrane association of protein kinase C in intact cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:399–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):527–528. doi: 10.1038/290527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorton A. R., Sweetman B. J., Oates J. A. Application of high performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to analysis of prostaglandin E1 in biological media. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorton A. R., Willis C. E., Kent R. S., Young S. L. The role of calcium in the regulation of prostacyclin synthesis by porcine aortic endothelial cells. Lipids. 1984 Jan;19(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF02534603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K., Hatzakis H., Lo S. S., Seong D. C., Sanduja S. K., Tai H. H. Stimulation of de novo synthesis of prostaglandin G/H synthase in human endothelial cells by phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19043–19047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xuan Y. T., Watkins W. D., Whorton A. R. Regulation of endothelin-mediated calcium mobilization in vascular smooth muscle cells by isoproterenol. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C492–C502. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


