Abstract
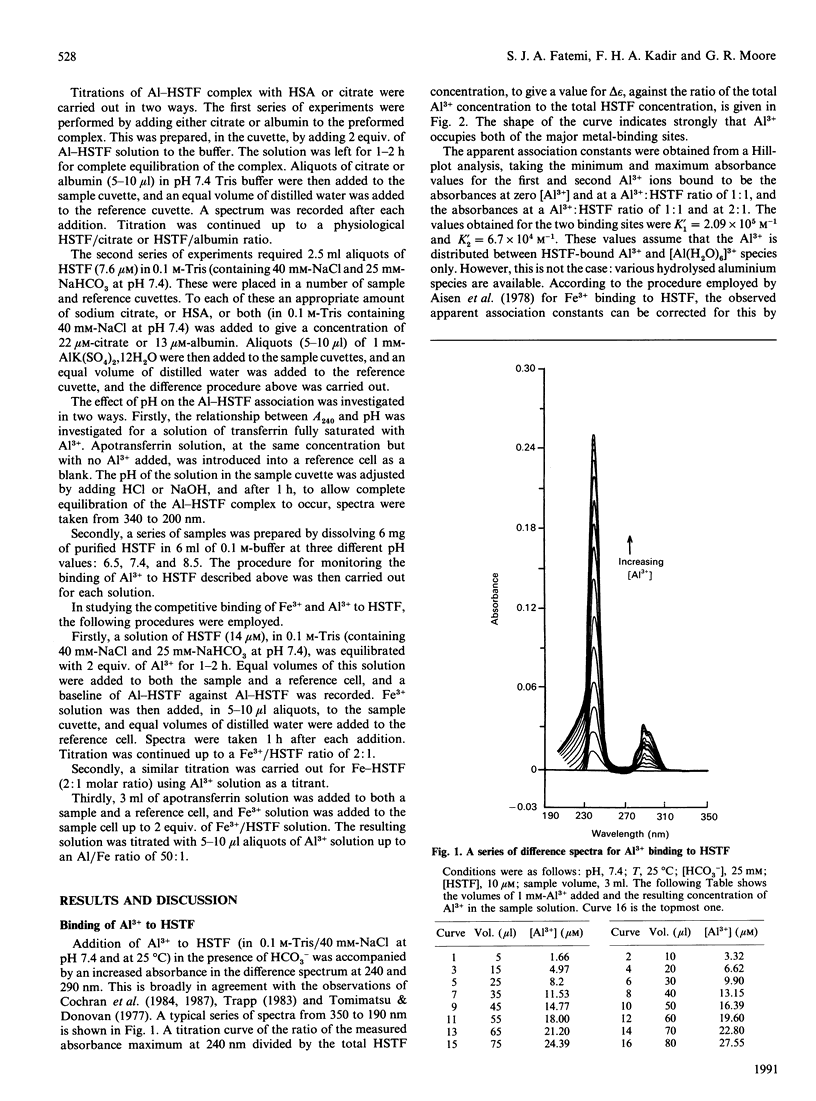
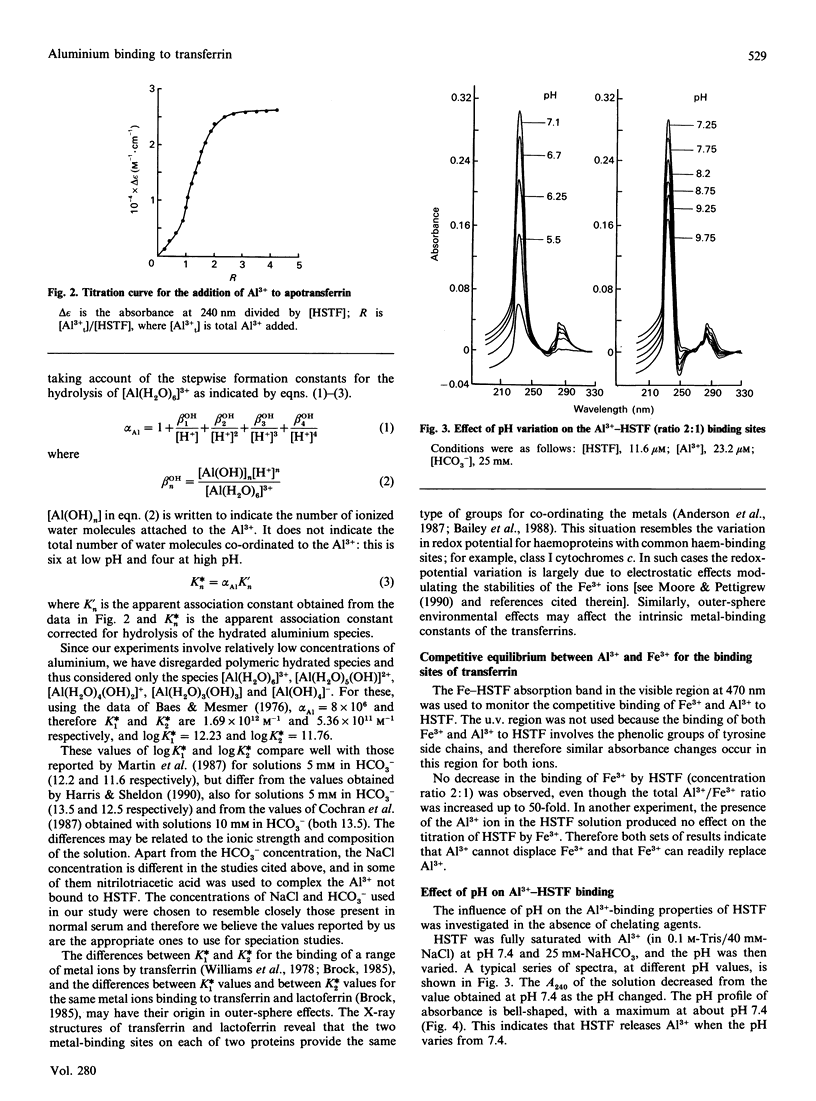
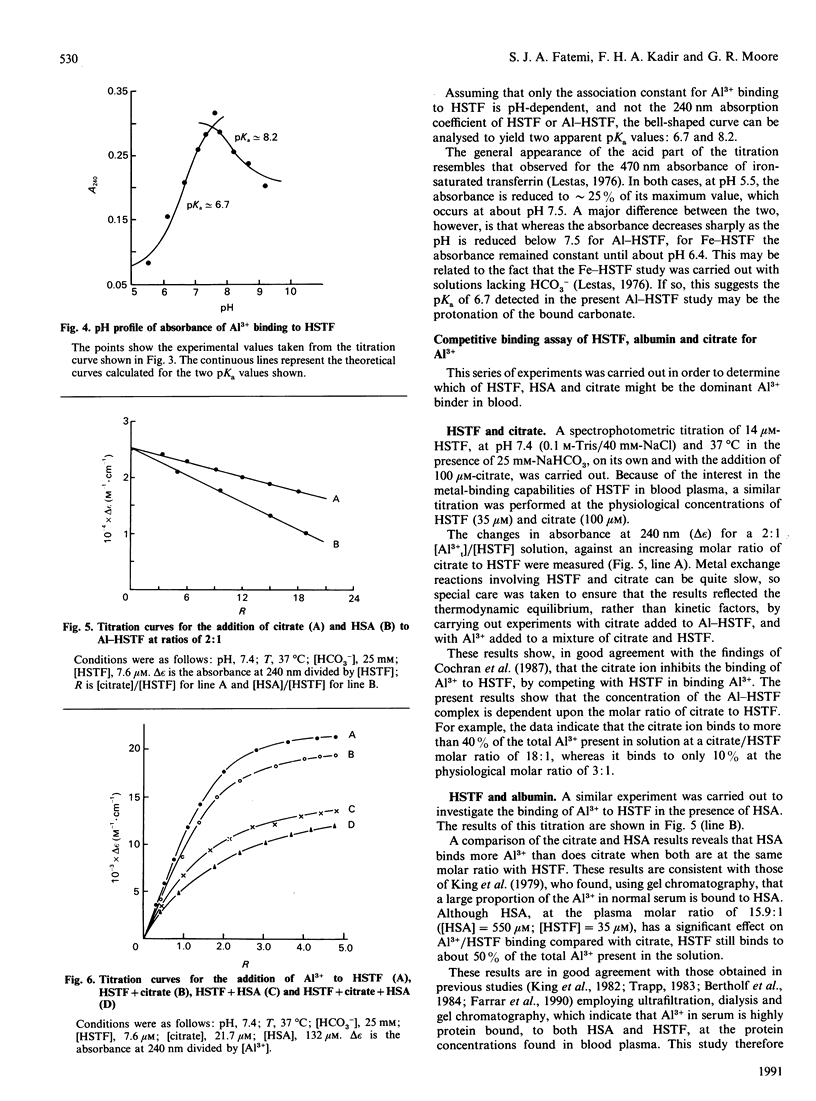
The binding of Al3+ by human serum transferrin has been investigated by u.v.-visible difference spectroscopy. In the presence of 25 mM-HCO3- at pH 7.4, the apparent association constants were found to be 1.69 x 10(12) M-1 and 5.36 x 10(11) M-1. These association constants are pH-dependent, reducing with both increasing and decreasing pH. The apparent pKa values were found to be 6.7 and 8.2. Competitive assays of binding of Al3+ to transferrin in the presence of citrate and human serum albumin at molar ratios corresponding to those found in normal plasma showed that a considerable amount of Al3+ was not bound to transferrin. Taking a concentration of 5 microM as a typical value observed for the plasma of patients on haemodialysis [Harris & Sheldon (1990) Inorg. Chem. 29, 119-124] the competitive binding assay indicate that approximately 60% of it is bound to transferrin, approximately 34% to albumin and the remainder to citrate. These results therefore suggest that, although transferrin at pH 7.4 is the major Al(3+)-binding component of plasma, an appreciable amount of Al3+ present in patients on haemodialysis may be bound to albumin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A., Zweier J. Stoichiometric and site characteristics of the binding of iron to human transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1930–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P., Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:357–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. F., Baker H. M., Dodson E. J., Norris G. E., Rumball S. V., Waters J. M., Baker E. N. Structure of human lactoferrin at 3.2-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1769–1773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S., Evans R. W., Garratt R. C., Gorinsky B., Hasnain S., Horsburgh C., Jhoti H., Lindley P. F., Mydin A., Sarra R. Molecular structure of serum transferrin at 3.3-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5804–5812. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertholf R. L., Wills M. R., Savory J. Quantitative study of aluminum binding to human serum albumin and transferrin by a chelex competitive binding assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):1020–1024. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M., Coates J., Neoh S. The competitive equilibrium between aluminium and ferric ions for the binding sites of transferrin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80926-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M., Cochran M., Coates J. H., Kurucsev T. Direct spectrophotometric determination of the two site binding of aluminum to transferrin. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 15;40(24):2337–2341. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90507-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G., Altmann P., Welch S., Wychrij O., Ghose B., Lejeune J., Corbett J., Prasher V., Blair J. A. Defective gallium-transferrin binding in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome: possible mechanism for accumulation of aluminium in brain. Lancet. 1990 Mar 31;335(8692):747–750. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90868-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Metabolism and possible health effects of aluminum. Environ Health Perspect. 1986 Mar;65:363–441. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8665363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. R., Pecoraro V. L. Thermodynamic binding constants for gallium transferrin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):292–299. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. W., Savory J., Wills M. R. Aluminum distribution in serum following hemodialysis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1982 Mar-Apr;12(2):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. W., Wills M. R., Savory J. Serum binding of aluminum. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;26(1):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lestas A. N. The effect of pH upon human transferrin: selective labelling of the two iron-binding sites. Br J Haematol. 1976 Mar;32(3):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. B. Citrate binding of Al3+ and Fe3+. J Inorg Biochem. 1986 Oct-Nov;28(2-3):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(86)80081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. B., Savory J., Brown S., Bertholf R. L., Wills M. R. Transferrin binding of Al3+ and Fe3+. Clin Chem. 1987 Mar;33(3):405–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman H., Skillen A. W., Ward M. K., Channon S. M., Kerr D. N. Affinity of the aluminium binding protein. Int J Artif Organs. 1986 Mar;9(2):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp G. A. Plasma aluminum is bound to transferrin. Life Sci. 1983 Jul 25;33(4):311–316. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(83)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


