Abstract
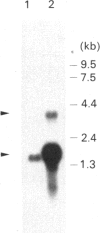
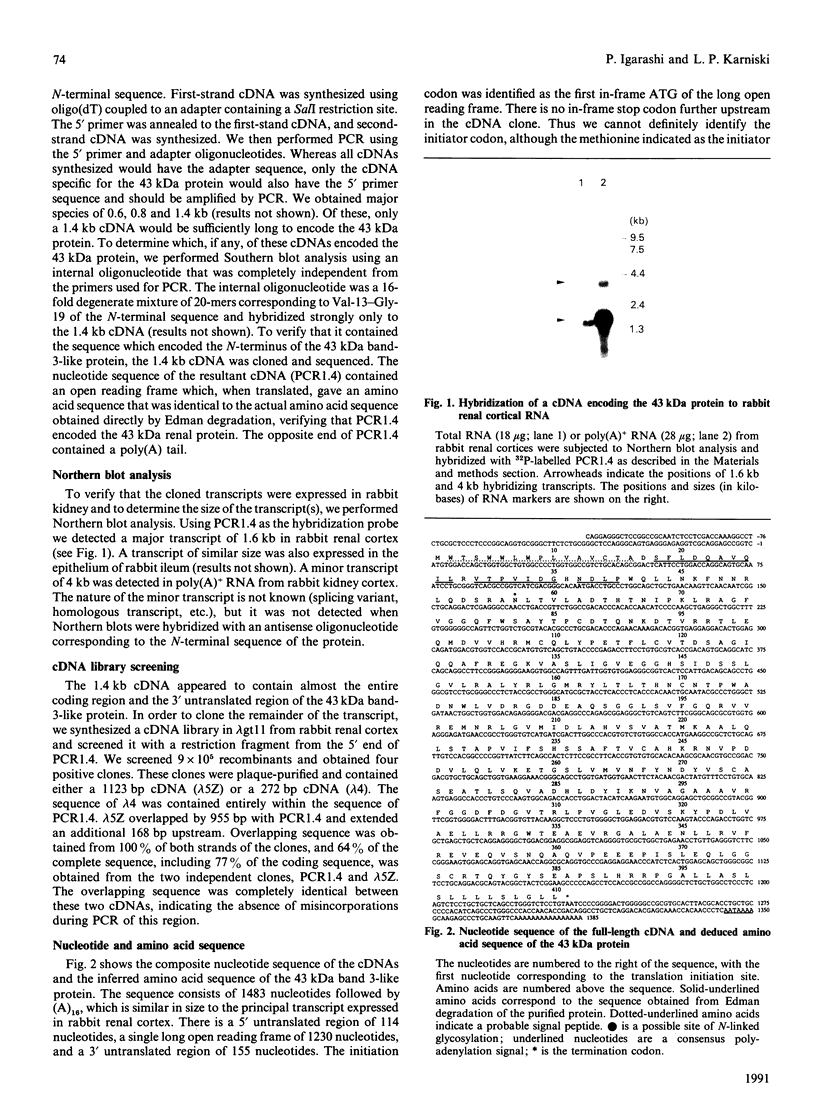
Distinct anion transport processes have been identified in the mammalian renal proximal tubule, but none of the responsible proteins or genes have been isolated. A 43 kDa rabbit microvillus membrane protein that is immunologically related to the erythroid anion exchanger (band 3) was a candidate for a renal anion transporter. To examine the structural relationship with band 3, we cloned cDNAs encoding the 43 kDa protein. The 43 kDa band-3-like protein was purified, and a novel sequence of 24 amino acids was obtained from the N-terminus. Degenerate oligonucleotides were synthesized based on this sequence, and the polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity was used to amplify and clone a 1330 bp cDNA from rabbit renal cortex. Additional overlapping 272 bp and 1123 bp cDNAs were obtained by synthesizing and screening a rabbit renal cortical cDNA library. The composite sequence was 1483 bp, terminated with (A)16, and was similar in size to the principal transcript expressed in rabbit renal cortex. The single long open reading frame was predicted to encode a protein composed of 410 amino acids with a molecular mass of 45,193 Da; 15 amino acids predicted to reside at the N-terminus were absent in the mature protein and may constitute a signal peptide. There was only limited sequence similarity with human erythroid band 3. Rather, the sequence was highly similar to microsomal dipeptidase, including the presence of a signal peptide and a consensus sequence for covalent linkage to glycosylphosphatidylinositol. In summary, the 43 kDa protein from rabbit renal cortex that is recognized by a monospecific antibody to erythroid band 3 is most likely a microvillus membrane dipeptidase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi H., Kubota I., Okamura N., Iwata H., Tsujimoto M., Nakazato H., Nishihara T., Noguchi T. Purification and characterization of human microsomal dipeptidase. J Biochem. 1989 Jun;105(6):957–961. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi H., Tawaragi Y., Inuzuka C., Kubota I., Tsujimoto M., Nishihara T., Nakazato H. Primary structure of human microsomal dipeptidase deduced from molecular cloning. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3992–3995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper S. L., Kopito R. R., Libresco S. M., Lodish H. F. Cloning and characterization of a murine band 3-related cDNA from kidney and from a lymphoid cell line. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17092–17099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. The renal proximal tubule: a model for diversity of anion exchangers and stilbene-sensitive anion transporters. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:419–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstedt J. W., Aronson P. S. pH gradient-stimulated transport of urate and p-aminohippurate in dog renal microvillus membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):931–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI109748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius F. C., 3rd, Alper S. L., Garcia A. M., Lodish H. F. The major kidney band 3 gene transcript predicts an amino-terminal truncated band 3 polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7784–7787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. J., Di Shih Y., Forrester L. J., Zahler W. L. Specificity and inhibition studies of human renal dipeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 21;956(2):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90256-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. J., Forrester L. J., Zahler W. L., Burks M. Beta-lactamase activity of purified and partially characterized human renal dipeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14586–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. V., Lazarides E. Alternative primary structures in the transmembrane domain of the chicken erythroid anion transporter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1327–1335. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Ship S., Rothstein A. Anion transport in relation to proteolytic dissection of band 3 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):294–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi P., Aronson P. S. Covalent modification of the renal Na+/H+ exchanger by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):860–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L., Anderson M. P., Monaghan R. Monoclonal antibodies against human erythrocyte band 3 protein. Localization of proteolytic cleavage sites and stilbenedisulfonate-binding lysine residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9002–9010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L., Nicknish J. S. Erythrocyte band 3 protein: evidence for multiple membrane-crossing segments in the 17 000-dalton chymotryptic fragment. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6432–6436. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Structure and function of the red blood cell anion transport protein. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:397–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Anion exchange pathways for Cl- transport in rabbit renal microvillus membranes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F513–F521. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Chloride/formate exchange with formic acid recycling: a mechanism of active chloride transport across epithelial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6362–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Jennings M. L. Identification and partial purification of a band 3-like protein from rabbit renal brush border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4564–4570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellokumpu S., Neff L., Jämsä-Kellokumpu S., Kopito R., Baron R. A 115-kD polypeptide immunologically related to erythrocyte band 3 is present in Golgi membranes. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1308–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.2461589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopito R. R., Lee B. S., Simmons D. M., Lindsey A. E., Morgans C. W., Schneider K. Regulation of intracellular pH by a neuronal homolog of the erythrocyte anion exchanger. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopito R. R., Lodish H. F. Primary structure and transmembrane orientation of the murine anion exchange protein. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):234–238. doi: 10.1038/316234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak E. M., Tate S. S. Glutathione-degrading enzymes of microvillus membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6322–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudrycki K. E., Shull G. E. Primary structure of the rat kidney band 3 anion exchange protein deduced from a cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8185–8192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawby W. J., Findlay J. B. Characterization and partial sequence of di-iodosulphophenyl isothiocyanate-binding peptide from human erythrocyte anion-transport protein. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 1;205(3):465–475. doi: 10.1042/bj2050465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre T., Curthoys N. P. Renal catabolism of glutathione. Characterization of a particulate rat renal dipeptidase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of cysteinylglycine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11915–11921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka E., Matsuki S., Ikehara M., Takahashi Y., Matsubara K. An alternative approach to deoxyoligonucleotides as hybridization probes by insertion of deoxyinosine at ambiguous codon positions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2605–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostedgaard L. S., Jennings M. L., Karniski L. P., Schuster V. L. A 45-kDa protein antigenically related to band 3 is selectively expressed in kidney mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):981–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passow H. Molecular aspects of band 3 protein-mediated anion transport across the red blood cell membrane. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1986;103:61–203. doi: 10.1007/3540153330_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rached E., Hooper N. M., James P., Semenza G., Turner A. J., Mantei N. cDNA cloning and expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes of pig renal dipeptidase, a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored ectoenzyme. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):755–760. doi: 10.1042/bj2710755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Bonsib S. M., Jennings M. L. Two types of collecting duct mitochondria-rich (intercalated) cells: lectin and band 3 cytochemistry. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C347–C355. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Martin P. G., High S. The complete amino acid sequence of the human erythrocyte membrane anion-transport protein deduced from the cDNA sequence. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj2560703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch C. L., Campbell B. J. Uptake of glycine from L-alanylglycine into renal brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):39–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01875375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]