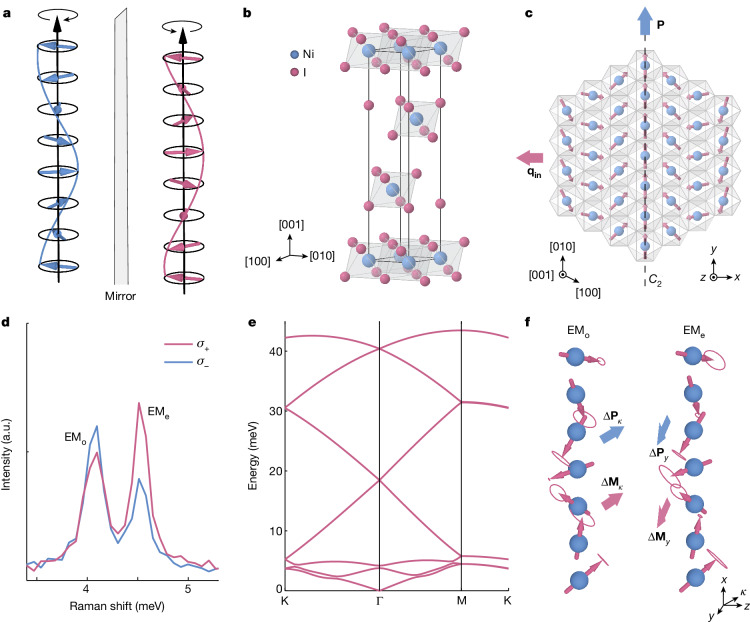
Fig. 1. Crystal structure and electromagnon modes of NiI2.
a, Spin-spiral ordering exemplified by two spin helices with opposite left and right handedness. b, The rhombohedral crystal structure of NiI2 at high temperature. The nickel (blue) and iodine (red) atoms are arranged in triangular lattice layers. c, The spin-spiral order depicted on the (001) plane below THM ≈ 60 K with propagation vector q = (0.138a*, 0, 1.457c*) and in-plane component qin, and electric polarization P along y, parallel to the C2 axis. Also shown is the x, y, z coordinate system, where y ∥ [010] and z ∥ [001]. d, Low-frequency spontaneous Raman scattering measurement of exfoliated NiI2 with σ+ (red) and σ− (blue) circularly polarized light obtained at 2.4 K. The two peaks at 4.09 meV and 4.51 meV are the EMo and EMe electromagnons, respectively. e, Energy–momentum dispersion of the electromagnon modes calculated by DFT on a 7 × 1 unit cell of monolayer NiI2. f, Eigenvector spin precessions of EMo and EMe, shown alongside the calculated ΔP and ΔM vectors for each mode. a.u., arbitrary units.