Abstract
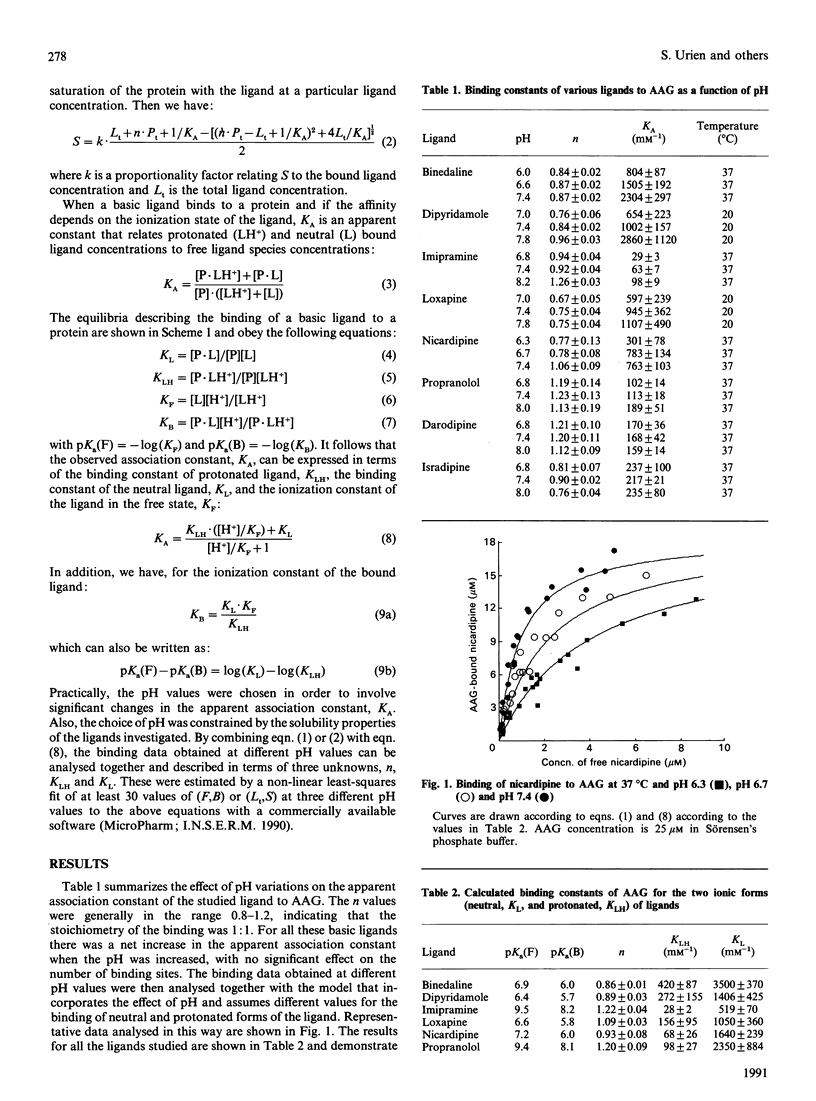
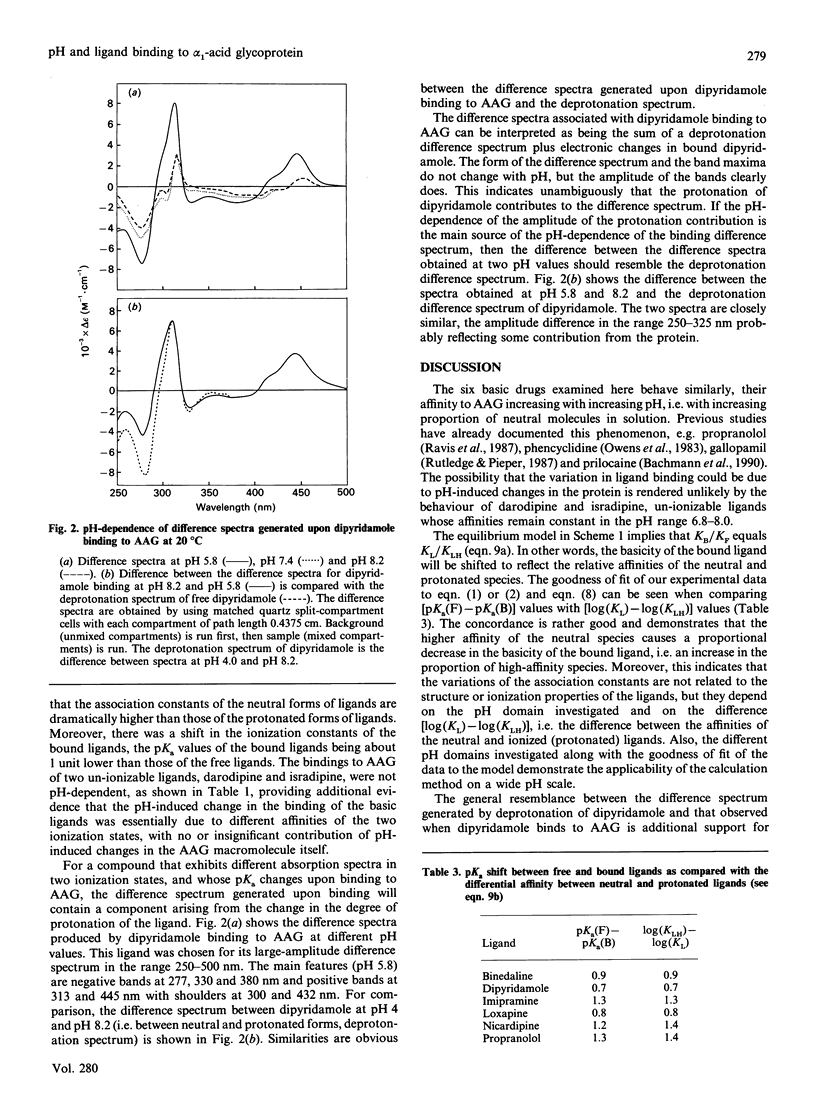
The binding interactions of a series of basic ligands with alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) were examined as a function of pH. The binding to AAG increased with increasing pH, and the binding data were satisfactorily fitted to a model that incorporates the effect of pH and discriminates the association constants of neutral (non-protonated) and protonated forms of ligands. It was shown that ligands in the neutral form have a markedly higher affinity for AAG than the protonated forms, resulting in a concomitant decrease in the pKa of bound ligands. The u.v.-visible difference spectra generated upon binding of a representative ligand to AAG also showed that there was a contribution to the binding arising from the deprotonation of the ligand. It is suggested that all tested ligands bind similarly to AAG and that hydrophobic interactions dominate high-affinity binding to AAG.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B., Biscoping J., Sinning E., Hempelmann G. Protein binding of prilocaine in human plasma: influence of concentration, pH and temperature. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1990 May;34(4):311–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1990.tb03093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. L., Schlueter K. T., Kirley T. L., Halsall H. B. Fluorescence quenching of human orosomucoid. Accessibility to drugs and small quenching agents. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):863–867. doi: 10.1042/bj2320863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer J. M., Wilting J., Janssen L. H. Drug binding to human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Mar;40(1):1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kute T., Westphal U. Steroid-protein interactions. XXXIV. Chemical modification of alpha1-acid glycoprotein for characterization of the progesterone binding site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 20;420(1):195–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens S. M., Mayersohn M., Woodworth J. R. Phencyclidine blood protein binding: influence of protein, pH and species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Sep;226(3):656–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M. Disease-induced changes in the plasma binding of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 May-Jun;5(3):246–262. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravis W. R., Parsons D. L., Wang S. J. Buffer and pH effects on propranolol binding by human albumin and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;40(7):459–463. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1988.tb05277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A. The plasma protein binding of basic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;22(5):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge D. R., Pieper J. A. Gallopamil binding to human serum proteins. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;33(4):375–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00637633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urien S., Albengres E., Zini R., Tillement J. P. Evidence for binding of certain acidic drugs to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Nov 15;31(22):3687–3689. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90597-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urien S., D'Athis P., Tillement J. P. The binding of aryl carboxylic acid derivatives to human serum albumin--a structure-activity study. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 15;33(14):2283–2289. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90668-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


