Abstract
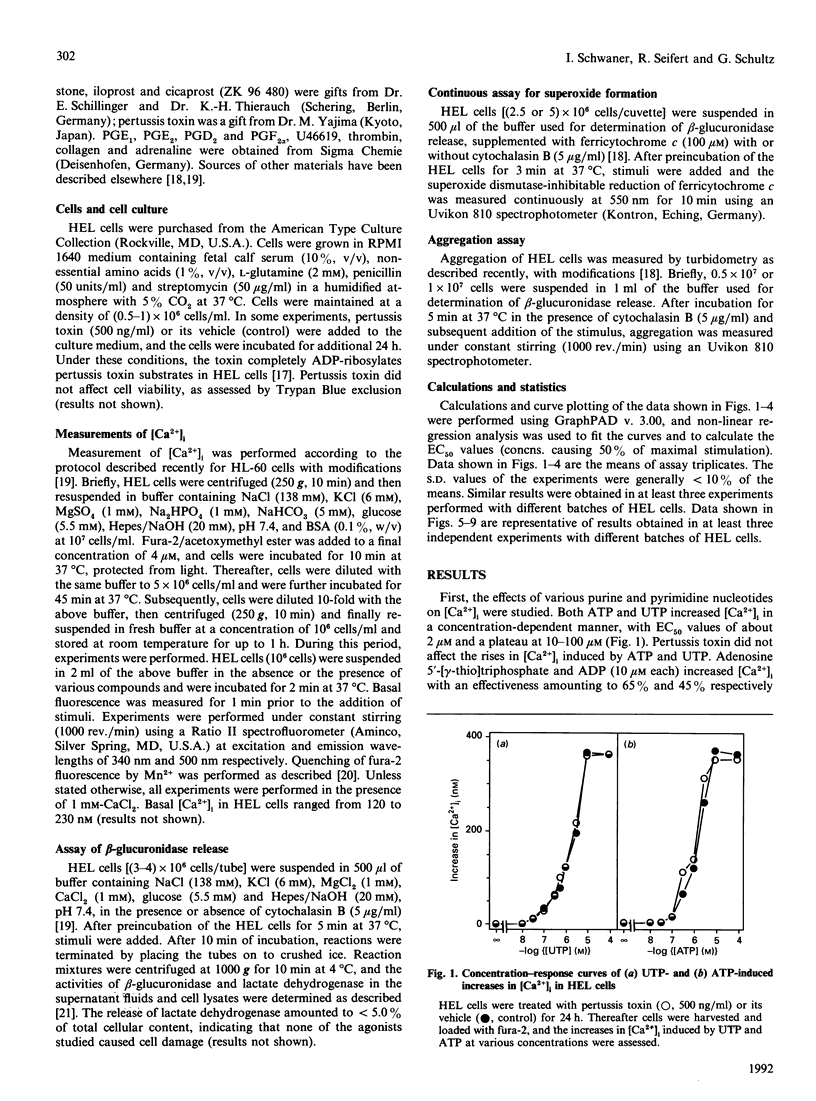
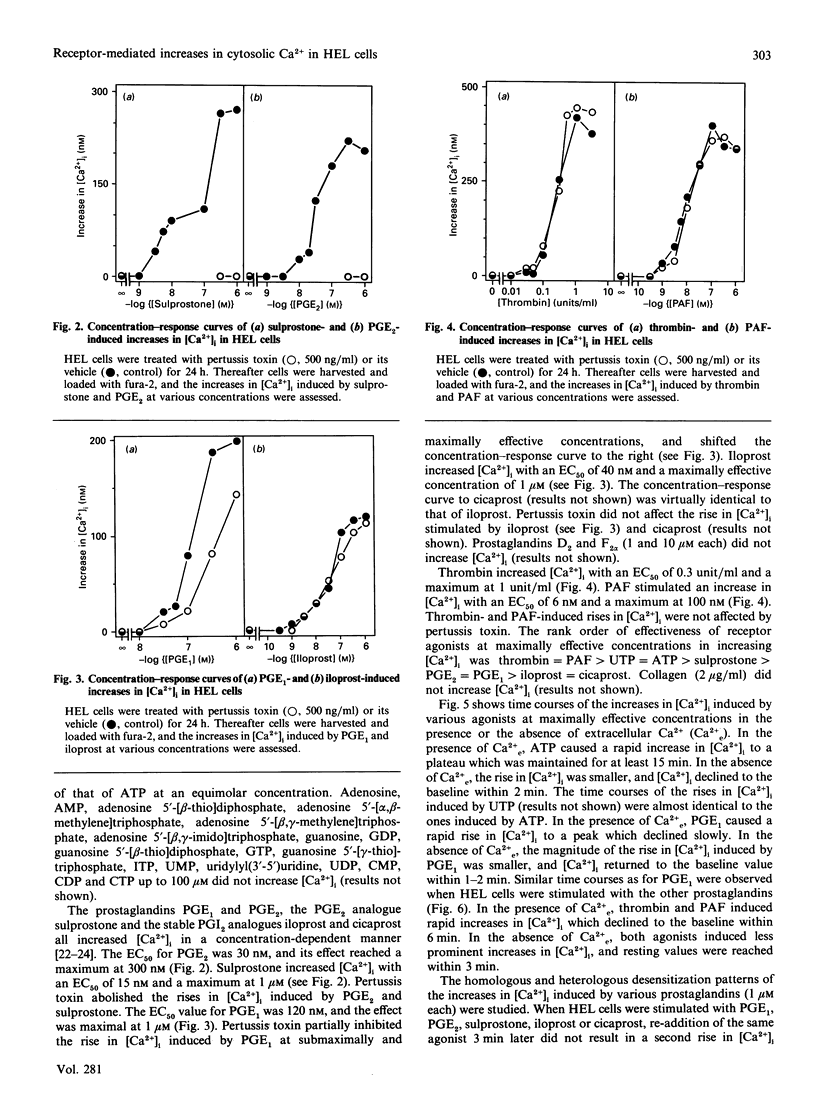
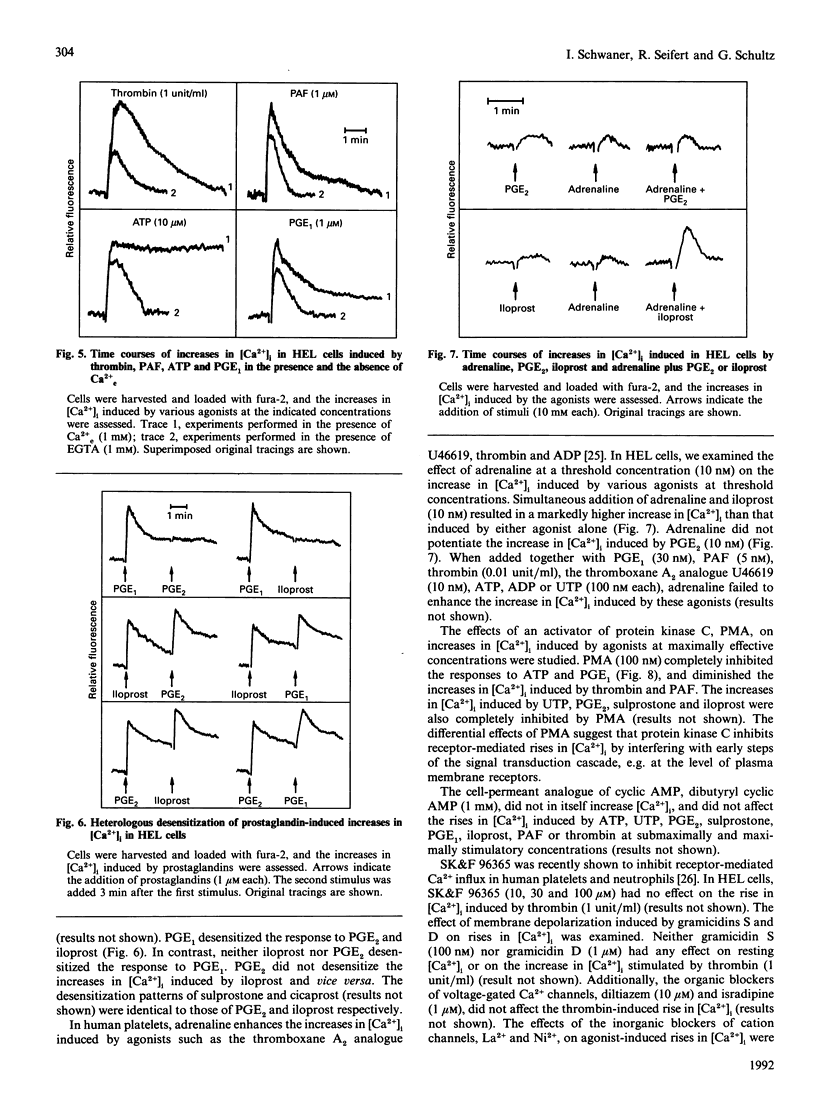
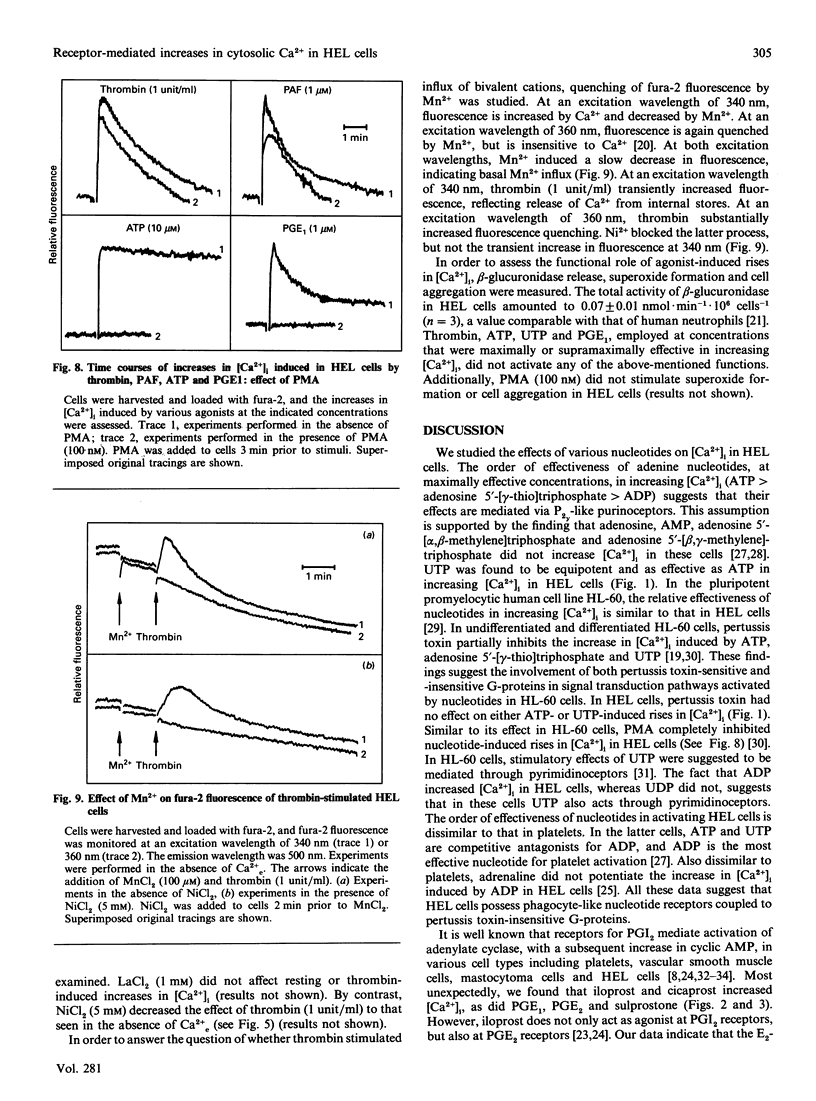
The pluripotent human erythroleukaemia cell line, HEL, possesses erythrocytic, megakaryocytic and macrophage-like properties. With respect to signal transduction, HEL cells have been used as a model system for platelets, but little attention has been paid to their phagocytic properties. We studied the effects of various receptor agonists on the intracellular free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in HEL cells. Thrombin, platelet-activating factor (PAF), ATP, UTP, prostaglandins E1 and E2 (PGE1 and PGE2), the PGE2 analogue sulprostone and the stable PGI2 analogues iloprost and cicaprost increased [Ca2+]i. ADP was less effective than ATP, and UDP was unable to increase [Ca2+]i. The increases in [Ca2+]i induced by thrombin, PAF, ATP, UTP, iloprost and cicaprost were pertussis toxin-insensitive, whereas the increases induced by PGE2 and sulprostone were completely inhibited by the toxin. The increase in [Ca2+]i induced by PGE1 was partially inhibited by pertussis toxin. PGE2 did not desensitize the increase in [Ca2+]i induced by iloprost, and vice versa. PGE1 desensitized the response to PGE2 and iloprost but not vice versa. Adrenaline potentiated the iloprost- but not the PGE2-induced rise in [Ca2+]i. The phorbol ester phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate completely blocked the rise in [Ca2+]i induced by ATP and PGE1, whereas the increases induced by thrombin and PAF were only partially inhibited. Agonists increased [Ca2+]i through release from internal stores and sustained Ca2+ influx. Thrombin stimulated Mn2+ influx, which was blocked by Ni2+. Diltiazem, isradipine, gramicidin and 1-(beta-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propoxy]-4-methoxyphenethyl)-1H-imidazole hydrochloride (SK&F 96365) did not affect agonist-induced rises in [Ca2+]i. HEL cells contained substantial amounts of beta-glucuronidase which, however, could not be released, and they did not aggregate or generate superoxide. Our data suggest that: (1) HEL cells possess nucleotide receptors with properties similar to those of phagocytes; (2) they possess receptors for PGE2 and PGI2, and PGE1 is an agonist at both receptors; (3) agonist-induced increases in [Ca2+]i are mediated through pertussis toxin-sensitive as well as -insensitive signal transduction pathways; and (4) agonists increase [Ca2+]i by mobilization from internal stores and influx from the extracellular space through cation channels with properties similar to those of phagocytes and platelets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absolom D. R. Basic methods for the study of phagocytosis. Methods Enzymol. 1986;132:95–180. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)32005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso M. T., Sanchez A., Garcia-Sancho J. Arachidonic acid-induced calcium influx in human platelets. Comparison with the effect of thrombin. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj2720435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T., Dahlgren C., Pozzan T., Stendahl O., Lew P. D. Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. A., Lawrence R. A., Jones R. L., Wilson N. H., Collier A. Functional and ligand binding studies suggest heterogeneity of platelet prostacyclin receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):657–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Manning D. R., Williams A. G., Woolkalis M. J., Poncz M. Receptor and G protein-mediated responses to thrombin in HEL cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplinski T. J., Niedel J. E. Cyclic nucleotide-induced maturation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):953–964. doi: 10.1172/JCI110707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari A., Gupta S., Kirschenbaum M. A. Biochemical evidence for PGI2 and PGE2 receptors in the rabbit renal preglomerular microvasculature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 12;1053(2-3):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. The HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line: proliferation, differentiation, and cellular oncogene expression. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen D. S., Lazarus H. M., Shurin S. B., Stoll S. E., Dubyak G. R. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate activates calcium mobilization in human phagocytic leukocytes and neutrophil/monocyte progenitor cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1651–1660. doi: 10.1172/JCI114064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels A. J., Lazarowski E. R., Matthews J. E., Lapetina E. G. Neuropeptide Y mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ and increases inositol phosphate production in human erythroleukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92721-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Y. J., Jones R. L., Wilson N. H. Prostaglandin E receptor subtypes in smooth muscle: agonist activities of stable prostacyclin analogues. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):97–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., Cowen D. S., Meuller L. M. Activation of inositol phospholipid breakdown in HL60 cells by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Evidence for mediation by both pertussis toxin-sensitive and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18108–18117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Pizzo P., Pozzan T. Receptor-mediated calcium influx in PC12 cells. ATP and bradykinin activate two independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20351–20355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles H. More selective ligands at eicosanoid receptor subtypes improve prospects in inflammatory and cardiovascular research. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Aug;11(8):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90224-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Rehm A. G. Evidence for the calcium-dependent activation of phospholipase D in thrombin-stimulated human erythroleukaemia cells. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):479–483. doi: 10.1042/bj2670479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto H., Negishi M., Ichikawa A. Identification of a prostacyclin receptor coupled to the adenylate cyclase system via a stimulatory GTP-binding protein in mouse mastocytoma P-815 cells. Prostaglandins. 1990 Nov;40(5):491–505. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(90)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer N., Wautier J. L., Coulombel L., Titeux M., Wautier M. P., Vainchenker W., Ruan C., Breton-Gorius J. Uncoupling in the expression of platelet GP IIb/IIIa in human endothelial cells and K562 cells: absence of immunologic crossreactivity between platelet GP IIb and the vitronectin receptor alpha chain. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1209–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Rutherford L. E., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. I. Kinetic analysis of changes in calcium permeability. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4070–4075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács T., Tordai A., Szász I., Sarkadi B., Gárdos G. Membrane depolarization inhibits thrombin-induced calcium influx and aggregation in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81532-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowski E. R., Winegar D. A., Nolan R. D., Oberdisse E., Lapetina E. G. Effect of protein kinase A on inositide metabolism and rap 1 G-protein in human erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13118–13123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P., Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Receptor-activated single channels in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10479–10483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Papayannopoulou T. HEL cells: a new human erythroleukemia cell line with spontaneous and induced globin expression. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1233–1235. doi: 10.1126/science.6177045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux P. R., Mais D. E., Carr C., Halushka P. V. Human erythroleukemia cells express functional thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Sep;250(3):923–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKernan R. M., Howard M. J., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. Compartmentation of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;32(1):258–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Armstrong W. P., Benham C. D., Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Jaxa-Chamiec A., Leigh B. K., McCarthy S. A., Moores K. E., Rink T. J. SK&F 96365, a novel inhibitor of receptor-mediated calcium entry. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):515–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2710515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Jacob R., Hallam T. J. Use of manganese to discriminate between calcium influx and mobilization from internal stores in stimulated human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1522–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brass L. F., Williams A., Bokoch G. M., LaMorte V. J., Motulsky H. J. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in human erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4986–4991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi M., Mitsuhashi T., Payan D. G. Multiple signaling pathways of histamine H2 receptors. Identification of an H2 receptor-dependent Ca2+ mobilization pathway in human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18356–18362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Michel M. C. Neuropeptide Y mobilizes Ca2+ and inhibits adenylate cyclase in human erythroleukemia cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):E880–E885. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.6.E880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R., Furci L., FitzGerald G. A. Induction of prostacyclin receptor expression in human erythroleukemia cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):172–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Yamamoto M., Ushikubi F., Okuma M., Fujiwara M., Narumiya S. Expression of thromboxane A2 receptor in cultured human erythroleukemia cells and its induction by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):958–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92815-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I. L., Breitman T. R., Gallo R. C. Priming of human myeloid leukemic cell lines HL-60 and U-937 with retinoic acid for differentiation effects of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-inducing agents and a T-lymphocyte-derived differentiation factor. Cancer Res. 1982 Oct;42(10):3928–3933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Nakamoto B., Yokochi T., Chait A., Kannagi R. Human erythroleukemia cell line (HEL) undergoes a drastic macrophage-like shift with TPA. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):832–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Involvement of pyrimidinoceptors in the regulation of cell functions by uridine and by uracil nucleotides. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Wenzel K., Eckstein F., Schultz G. Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides potentiate activation of NADPH oxidase and degranulation by chemotactic peptides and induce aggregation of human neutrophils via G proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):277–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior J., Marshall K., Sangha R., Baxter G. S., Clayton J. K. In vitro characterization of prostanoid EP-receptors in the non-pregnant human myometrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):747–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabilio A., Rosa J. P., Testa U., Kieffer N., Nurden A. T., Del Canizo M. C., Breton-Gorius J., Vainchenker W. Expression of platelet membrane glycoproteins and alpha-granule proteins by a human erythroleukemia cell line (HEL). EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):453–459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. T., Scrutton M. C., Wallis R. B. Synergistic responses in human platelets. Comparison between aggregation, secretion and cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):399–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weich H. A., Herbst D., Schairer H. U., Hoppe J. Platelet-derived growth factor. Phorbol ester induces the expression of the B-chain but not of the A-chain in HEL cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel-Seifert K., Seifert R. Nucleotide-, chemotactic peptide- and phorbol ester-induced exocytosis in HL-60 leukemic cells. Immunobiology. 1990 Nov;181(4-5):298–316. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Woolkalis M. J., Poncz M., Manning D. R., Gewirtz A. M., Brass L. F. Identification of the pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins in platelets, megakaryocytes, and human erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H., Turner J. T., Halenda S. P. Activation of phospholipase D by E-series prostaglandins in human erythroleukemia cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschauer A., van Breemen C., Bühler F. R., Nelson M. T. Calcium channels in thrombin-activated human platelet membrane. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):703–705. doi: 10.1038/334703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


