Abstract
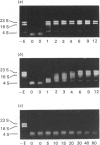
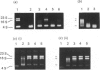
We have studied the inhibition of bovine pancreatic RNAase (RNAase A) and bovine seminal RNAase in its native dimeric form (RNAase BS-1) and in monomeric carboxymethylated form (MCM RNAase BS-1) by human placental RNAase inhibitor (RNAase inhibitor) in order to understand the effect of enzyme structure on its response to the inhibitor. Study of the inhibition as a function of inhibitor concentration revealed that RNAase A and MCM RNAase BS-1 were inhibited fully and the inhibitor-sensitivities of the two were comparable. But under identical inhibitor concentrations RNAase BS-1 was found to be virtually insensitive to the inhibitor; at higher (3-10-fold) inhibitor concentrations marginal inhibition of the native enzyme could be observed. When RNAase BS-1 was pretreated with 5 mM-dithiothreitol (DTT) and assayed, it exhibited greater inhibitor-sensitivity, presumably as a result of its partial monomerization on exposure to DTT. This DTT-mediated change in the response of RNAase BS-1 to the inhibitor did not, however, seem to occur either in the assay conditions (which included DTT) or even when the enzyme was pretreated with DTT in the presence of the substrate, suggesting an effect of the substrate on the enzyme behaviour towards the inhibitor. Independently, gel-filtration runs revealed that, although DTT treatment caused monomerization of RNase BS-1, this change did not take place when DTT treatment was carried out in the presence of the substrate. From our observations, we infer that differential inhibitor-sensitivity of the dimeric and monomeric forms of RNAase BS-1, the relative contents of the two forms and the influence of the substrate on them may be important determinants of the net enzyme activity in the presence of the inhibitor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn P., Gavilanes J. G. Identification of lysine residues in the binding domain of ribonuclease A for the RNase inhibitor from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):316–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn P., Gavilanes J. G. The role of lysine-41 of ribonuclease A in the interaction with RNase inhibitor from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10959–10965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn P., Jailkhani B. L. Ribonuclease inhibitor from human placenta: interaction with derivatives of ribonuclease A. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12488–12493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn P., Wilson G., Moore S. Ribonuclease inhibitor from human placenta. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5904–5910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N. A., Knowler J. T. Purification and characterisation of ribonuclease activities that interact with the cytoplasmic inhibitor protein of rat tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton L. E., Blackburn P., Moore S. Ribonuclease inhibitor from bovine brain. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Nov;16(5):359–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton L. E., Fucci N. P. Ribonuclease inhibitors from the livers of five mammalian species. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Apr;19(4):372–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. On the aggregation of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso S., Giordano F., Mattia C. A., Mazzarella L., Zagari A. Refinement of the structure of bovine seminal ribonuclease. Biopolymers. 1983 Jan;22(1):327–332. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Floridi A., De Prisco R., Pignero A., Leone E. [Bull semen ribonucleases. 1. Purification and physico-chemical properties of the major component]. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 27;26(2):153–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Malorni M. C., Parente A. Dissociation of bovine seminal ribonuclease into catalytically active monomers by selective reduction and alkylation of the intersubunit disulfide bridges. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1116–1122. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fominaya J. M., García-Segura J. M., Ferreras M., Gavilanes J. G. Theoretical treatment of tight-binding inhibition of an enzyme. Ribonuclease inhibitor as special case. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):517–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2530517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Crestfield A. M. On the structure of ribonuclease dimer. Isolation and identification of monomers derived from inactive carboxymethyl dimers. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3875–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Crestfield A. M. Preparation and properties of two active forms of ribonuclease dimer. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3868–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball S. R., Meyer W. L. Multiple forms of ribonuclease II in mouse liver: relative sizes, subcellular distributions, and pH-activity profiles. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;65(1):27–34. doi: 10.1139/o87-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matousek J. The effect of bovine seminal ribonuclease (AS RNase) on cells of Crocker tumour in mice. Experientia. 1973;29(7):858–859. doi: 10.1007/BF01946329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarto N., Tajana G. F., D'Alessio G. Synthesis of seminal ribonuclease in isolated lobules of bull seminal vesicles. J Reprod Fertil. 1987 May;80(1):81–89. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0800081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Sitaram N., Bhargava P. M., Scheit K. H. A new pyrimidine-specific ribonuclease from bovine seminal plasma that is active on both single and double-stranded polyribonucleotides and that can distinguish between Mg2+-containing and Mg2+-depleted naturally occurring RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):525–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Human placental ribonuclease inhibitor abolishes both angiogenic and ribonucleolytic activities of angiogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2238–2241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Interaction of human placental ribonuclease with placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2246–2255. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Parente A., Farina B., Greco L., La Montagna R., Leone E. Complete amino-acid sequence of bovine seminal ribonuclease, a dimeric protein from seminal plasma. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Oct;368(10):1305–1312. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamburrini M., Piccoli R., De Prisco R., Di Donato A., D'Alessio G. Fast and high-yielding procedures for the isolation of bovine seminal RNAase. Ital J Biochem. 1986 Jan-Feb;35(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P. M., Lerea K. M., Kull F. J. The ribonuclease inhibitors from porcine thyroid and liver are slow, tight-binding inhibitors of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1154–1160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vescia S., Tramontano D. Antitumoral action of bovine seminal ribonuclease. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 May 26;36(3):125–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02357027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vescia S., Tramontano D., Augusti-Tocco G., D'Alessio G. In vitro studies on selective inhibition of tumor cell growth by seminal ribonuclease. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3740–3744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Donato A., D'Alessio G. Intrachain disulfide bridges of bovine seminal ribonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 28;579(2):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]