Abstract
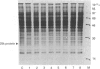
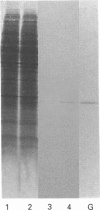
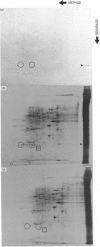
Alterations in protein synthesis in primary cultured rat liver parenchymal cells were examined after their exposure to the potent carcinogens, polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congeners. Co-planar PCB congeners (3,4,5,3',4'-PCB and 3,4,5,3',4',5'-PCB) (10 nM) induced a protein, the Mr of which was 25,000 (25 k protein) under denaturing conditions. However, non-co-planar PCB congeners and several xenobiotics, which induce microsomal proteins, did not induce the 25 k protein. By using immunoblotting, the 25 k protein was identified as glutathione S-transferase P-form (GST-P, 7-7, EC 2.5.1.18).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki Y., Lipsky M. M., Fowler B. A. Alteration in protein synthesis in primary cultures of rat kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells by exposure to gallium, indium, and arsenite. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;106(3):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90341-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki Y., Suzuki K. T. Excretion process of copper from copper pre-loaded rat liver parenchymal cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 15;34(10):1713–1716. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90639-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azais V., Arand M., Rauch P., Schramm H., Bellenand P., Narbonne J. F., Oesch F., Pascal G., Robertson L. W. A time-course investigation of vitamin A levels and drug metabolizing enzyme activities in rats following a single treatment with prototypic polychlorinated biphenyls and DDT. Toxicology. 1987 Jun;44(3):341–354. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(87)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombick D. W., Jankun J., Tullis K., Matsumura F. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin causes increases in expression of c-erb-A and levels of protein-tyrosine kinases in selected tissues of responsive mouse strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt R. K., Garfield S., Johnson K., Thorgeirsson S. S. Transformation of rat liver epithelial cells with v-H-ras or v-raf causes expression of MDR-1, glutathione-S-transferase-P and increased resistance to cytotoxic chemicals. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Dec;9(12):2329–2332. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.12.2329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caltabiano M. M., Koestler T. P., Poste G., Greig R. G. Induction of 32- and 34-kDa stress proteins by sodium arsenite, heavy metals, and thiol-reactive agents. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13381–13386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitrich R. A., Bludeau P., Stock T., Roper M. Induction of different rat liver supernatant aldehyde dehydrogenases by phenobarbital and tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6169–6176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi P. P., Kumar A., Prasad A. K., Pandya K. P., Ray P. K. Induction of glutathione-S-transferase isoenzymes by protein A in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):476–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90356-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. A. The structure-activity relationships of halogenated biphenyls as enzyme inducers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:164–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grolier P., Cassand P., Antignac E., Narbonne J. F., Albrecht R., Azais V., Robertson L. W., Oesch F. Effects of prototypic PCBs on benzo[a]pyrene mutagenic activity related to vitamin A intake. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;211(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Dannan G. A., Wright S. T., Martin M. V., Kaminsky L. S. Purification and characterization of liver microsomal cytochromes p-450: electrophoretic, spectral, catalytic, and immunochemical properties and inducibility of eight isozymes isolated from rats treated with phenobarbital or beta-naphthoflavone. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):6019–6030. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. G., Toscano W. A., Jr, Greenlee W. F. Regulation of epidermal growth factor binding in a human keratinocyte cell line by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;77(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90324-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert C. D., Harris M. W., Elwell M. R., Birnbaum L. S. Relative toxicity and tumor-promoting ability of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 2,3,4,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran (PCDF), and 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzofuran (HCDF) in hairless mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;102(2):362–377. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90033-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Tsuda H., Tatematsu M., Inoue T., Tagawa Y., Aoki T., Uwagawa S., Kagawa M., Ogiso T., Masui T. Enhancing effect of various hepatocarcinogens on induction of preneoplastic glutathione S-transferase placental form positive foci in rats--an approach for a new medium-term bioassay system. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Mar;9(3):387–394. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano T., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Structure and expression of a human class pi glutathione S-transferase messenger RNA. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5626–5630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara A., Satoh K., Nishimura K., Ishikawa T., Ruike K., Sato K., Tsuda H., Ito N. Changes in molecular forms of rat hepatic glutathione S-transferase during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1984 Jun;44(6):2698–2703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafranconi W. M., Glatt H., Oesch F. Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes of rat liver nonparenchymal cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;84(3):500–511. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Danielson U. H. Glutathione transferases--structure and catalytic activity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(3):283–337. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks T. A., Kimmel G. L., Staples R. E. Influence of symmetrical polychlorinated biphenyl isomers on embryo and fetal development in mice. I. Teratogenicity of 3, 3', 4, 4', 5, 5',-hexachlorobiphenyl. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;61(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gonzalez F. J. P450 genes: structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:945–993. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson A., Safe S. H., Robertson L. W., Thomas P. E., Ryan D. E., Reik L. M., Levin W. Immunochemical quantitation of cytochrome P-450 isozymes and epoxide hydrolase in liver microsomes from polychlorinated or polybrominated biphenyl-treated rats. A study of structure-activity relationships. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5967–5976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. E., Thomas P. E., Korzeniowski D., Levin W. Separation and characterization of highly purified forms of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 from rats treated with polychlorinated biphenyls, phenobarbital, and 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1365–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. P., Sunahara G. I., Lucier G. W., Birnbaum L. S., Nelson K. G. Decreased ligand binding to the hepatic glucocorticoid and epidermal growth factor receptors after 2,3,4,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran and 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzofuran treatment of pregnant mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1989 May;98(3):454–464. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Multiple regulatory elements and phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate 13-acetate responsiveness of the rat placental glutathione transferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9456–9460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K. Glutathione transferases as markers of preneoplasia and neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res. 1989;52:205–255. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Kitahara A., Satoh K., Ishikawa T., Tatematsu M., Ito N. The placental form of glutathione S-transferase as a new marker protein for preneoplasia in rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Gan. 1984 Mar;75(3):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Hatayama I., Tsuchida S., Sato K. Biochemical characteristics of a preneoplastic marker enzyme glutathione S-transferase P-form(7-7). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Mar;285(2):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90365-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Kitahara A., Soma Y., Inaba Y., Hatayama I., Sato K. Purification, induction, and distribution of placental glutathione transferase: a new marker enzyme for preneoplastic cells in the rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3964–3968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver G., Krauter K. S. The Ah domain of the mouse. Induction of proteins by the carcinogen 3-methylcholanthrene. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):159–165. doi: 10.1042/bj2520159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. J., Ohl V. S., Litwack G. Ligandin, the glutathione S-transferases, and chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis: a review. Cancer Res. 1977 Jan;37(1):8–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe Y., Morel F., Foriers A., Ketterer B., Vercruysse A., Guillouzo A., Rogiers V. Effect of phenobarbital on the expression of glutathione S-transferase isoenzymes in cultured rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81428-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]