Abstract
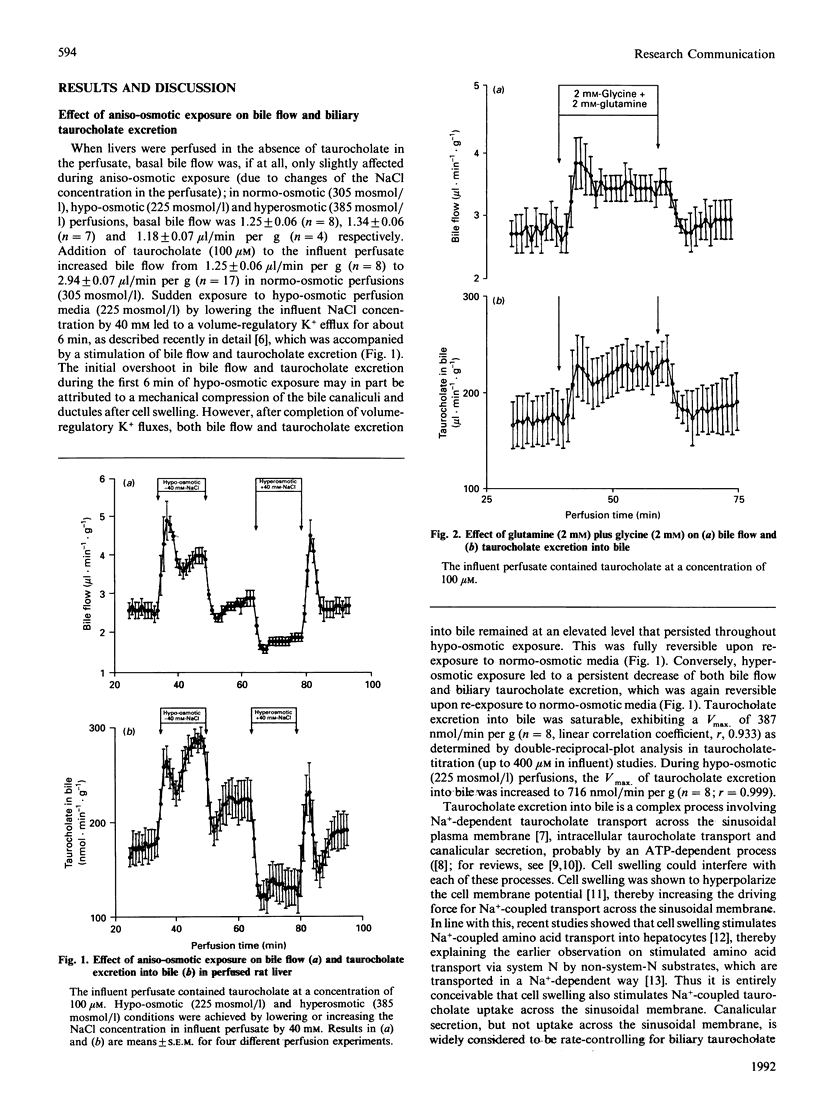
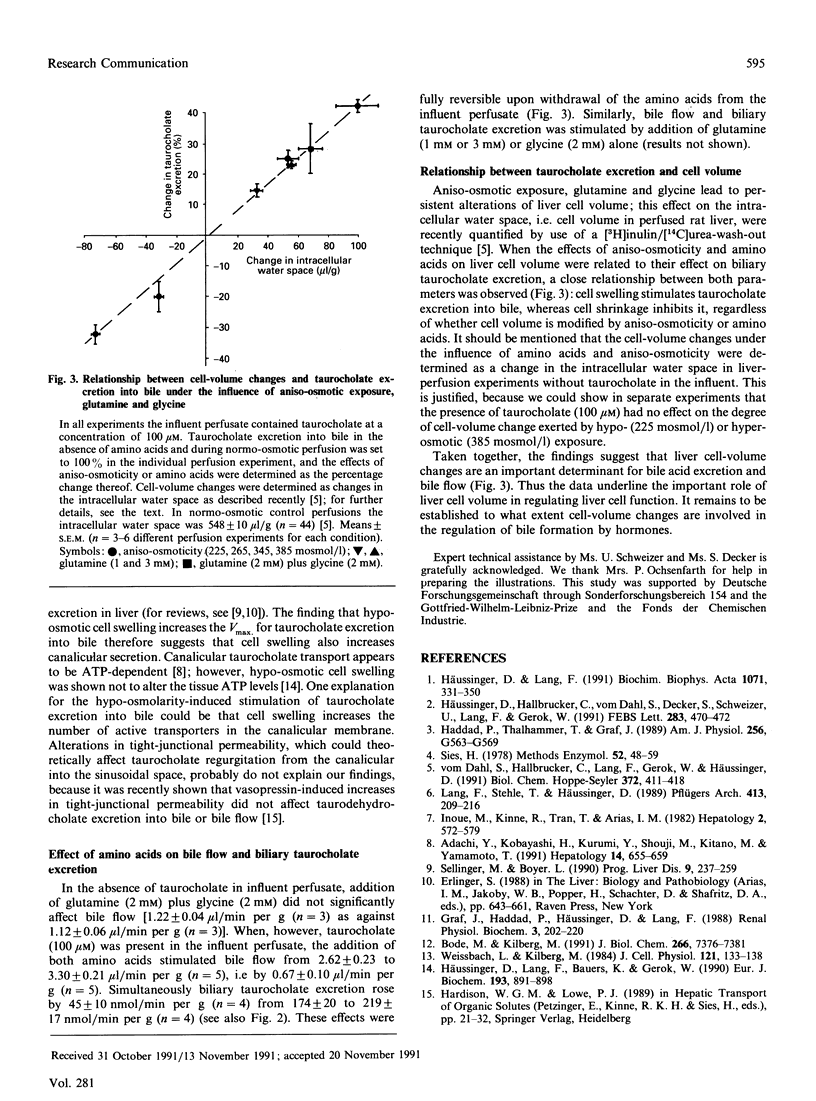
The effects of aniso-osmotically and amino-acid-induced cell-volume changes on bile flow and biliary taurocholate excretion were studied in isolated perfused rat liver. With taurocholate (100 microM) in the influent perfusate, hypo-osmotic exposure (225 mosmol/l) increased taurocholate excretion into bile and bile flow by 42 and 27% respectively, whereas inhibition by 32 and 47% respectively was observed after hyperosmotic (385 mosmol/l) exposure. The effects of aniso-moticity on taurocholate excretion into bile was observed throughout aniso-osmotic exposure, even after completion of volume-regulatory ion fluxes and were fully reversible upon re-exposure to normo-osmotic media. Hypo-osmotic cell swelling (225 mosmol/l) increased the Vmax. of taurocholate translocation from the sinusoidal compartment into bile about 2-fold. Also, cell swelling induced by glutamine and glycine stimulated both bile flow and biliary taurocholate excretion. There was a close relationship between the aniso-osmotically and amino-acid-induced change of cell volume and taurocholate excretion into bile. The data suggest that liver cell volume plays an important role in regulating bile-acid-dependent bile flow and biliary taurocholate excretion.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Kobayashi H., Kurumi Y., Shouji M., Kitano M., Yamamoto T. ATP-dependent taurocholate transport by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Hepatology. 1991 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):655–659. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(91)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode B. P., Kilberg M. S. Amino acid-dependent increase in hepatic system N activity is linked to cell swelling. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7376–7381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Haddad P., Haeussinger D., Lang F. Cell volume regulation in liver. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1988 May-Oct;11(3-5):202–220. doi: 10.1159/000173163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad P., Thalhammer T., Graf J. Effect of hypertonic stress on liver cell volume, bile flow, and volume-regulatory K+ fluxes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):G563–G569. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.3.G563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Lang F. Cell volume in the regulation of hepatic function: a mechanism for metabolic control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):331–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90001-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüssinger D., Lang F., Bauers K., Gerok W. Control of hepatic nitrogen metabolism and glutathione release by cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):891–898. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver sinusoidal membrane vesicles: evidence of sodium cotransport. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):572–579. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang F., Stehle T., Häussinger D. Water, K+, H+, lactate and glucose fluxes during cell volume regulation in perfused rat liver. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jan;413(3):209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00583532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellinger M., Boyer J. L. Physiology of bile secretion and cholestasis. Prog Liver Dis. 1990;9:237–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sies H. The use of perfusion of liver and other organs for the study of microsomal electron-transport and cytochrome P-450 systems. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:48–59. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach L., Kilberg M. S. Amino acid activation of amino acid transport System N early in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):133–138. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vom Dahl S., Hallbrucker C., Lang F., Gerok W., Häussinger D. A non-invasive technique for cell volume determination in perfused rat liver. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Jun;372(6):411–418. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.1.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


