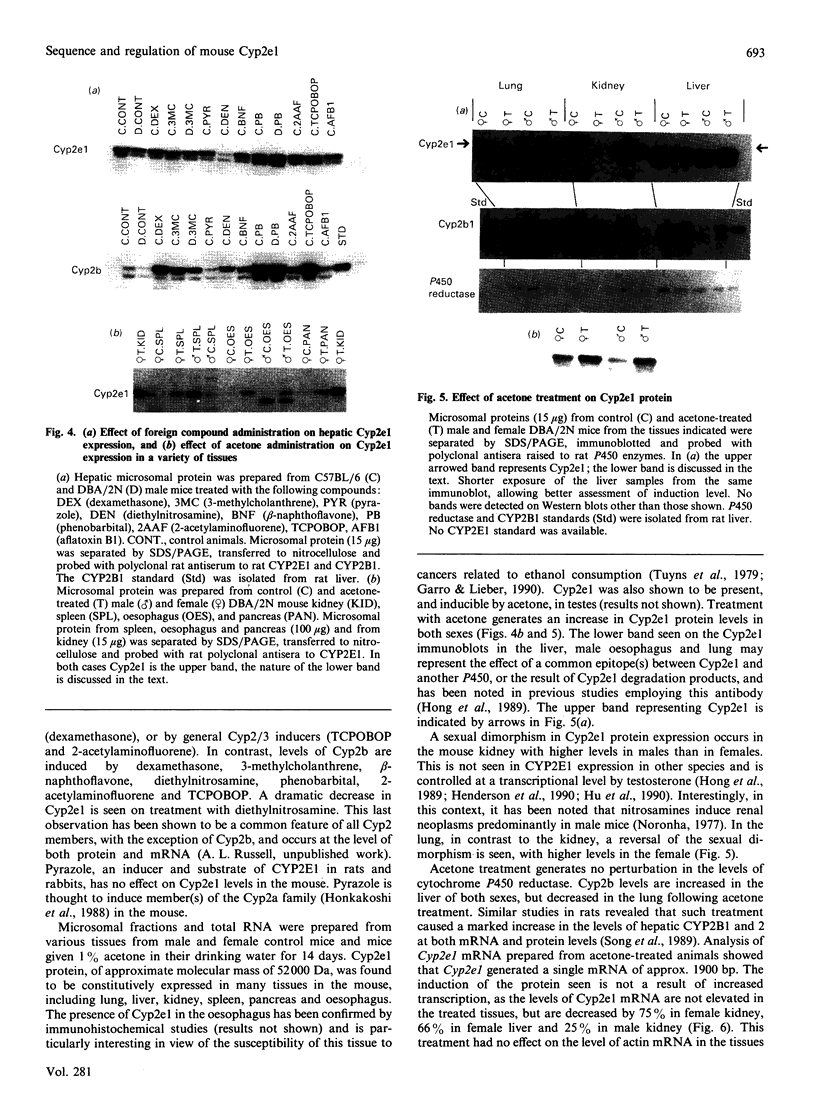
Abstract
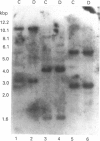
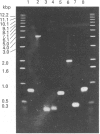
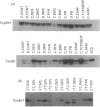
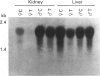
The cDNA encoding the mouse Cyp2e1 protein has been isolated and sequenced, and shown to share 92%, 79%, 80% and 79% sequence similarity over the coding region with rat, human, rabbit 1 and rabbit 2 CYP2E1 cDNA sequences respectively. The predicted Cyp2e1 protein contains 493 amino acids, with a molecular mass of 56781 Da. The protein contains many features common to other cytochrome P450s, including a potentially phosphorylatable serine residue at position 129 within a canonical cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase site. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA prepared from C57BL/6 and DBA/2N mice suggests the presence of only a single Cyp2e1 gene. The Cyp2e1 gene was isolated and its organization was established by PCR using oligonucleotides to its predicted intron/exon boundaries. These results showed that the mouse Cyp2e1 gene is approx. 11,000 bp in length and has a similar structure to the human and rat CYP2E1 genes. Cyp2e1 protein expression was studied in a variety of tissues and a sexual dimorphism in its levels in some tissues was noted. Acetone treatment induced the Cyp2e1 protein in all of the tissues studied in both sexes, but this Cyp2e1 protein induction was not accompanied by an increase in Cyp2e1 mRNA levels. Indeed, mRNA levels were seen to be decreased on treatment, suggesting that acetone administration affects either mRNA translation efficiency or protein stability. Of a wide range of drugs known to modify other cytochrome P450 levels only diethylnitrosamine had a significant effect on Cyp2e1, causing a decrease in protein levels.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Seilman S., Amelizad Z., Oesch F., Wolf C. R. Identification of human cytochromes P-450 analogous to forms induced by phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene in the rat. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):869–876. doi: 10.1042/bj2320869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström A., DePierre J. W. Rat-liver microsomal cytochrome P-450: purification, characterization, multiplicity and induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 4;853(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(86)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch H., Montesano R. Relevance of nitrosamines to human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Nov;5(11):1381–1393. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.11.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casazza J. P., Felver M. E., Veech R. L. The metabolism of acetone in rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Koeller D. M., Ramin V. C., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3693–3699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J., Lieber C. S. Alcohol and cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:219–249. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. Molecular genetics of the P-450 superfamily. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90006-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Evolution of the P450 gene superfamily: animal-plant 'warfare', molecular drive and human genetic differences in drug oxidation. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D. Minipreps of DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6737–6737. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Roles of cytochrome P-450 enzymes in chemical carcinogenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):2946–2954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson T., Tindberg N., Ingelman-Sundberg M., Köhler C. Regional distribution of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P450 IIE1 in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;34(2):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90154-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. J., Scott A. R., Yang C. S., Wolf C. R. Testosterone-mediated regulation of mouse renal cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):675–681. doi: 10.1042/bj2660675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. Y., Ning S. M., Ma B. L., Lee M. J., Pan J. M., Yang C. S. Roles of pituitary hormones in the regulation of hepatic cytochrome P450IIE1 in rats and mice. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Aug 15;281(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90422-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. Y., Pan J. M., Ning S. M., Yang C. S. Molecular basis for the sex-related difference in renal N-nitrosodimethylamine demethylase in C3H/HeJ mice. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2973–2979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkakoski P., Autio S., Juvonen R., Raunio H., Gelboin H. V., Park S. S., Pelkonen O., Lang M. A. Pyrazole is different from acetone and ethanol as an inducer of the polysubstrate monooxygenase system in mice: evidence that pyrazole-inducible P450Coh is distinct from acetone-inducible P450ac. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Dec;267(2):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. J., Rhoten W. B., Yang C. S. Mouse renal cytochrome P450IIE1: immunocytochemical localization, sex-related difference and regulation by testosterone. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 15;40(12):2597–2602. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90576-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson I., Ekström G., Scholte B., Puzycki D., Jörnvall H., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Ethanol-, fasting-, and acetone-inducible cytochromes P-450 in rat liver: regulation and characteristics of enzymes belonging to the IIB and IIE gene subfamilies. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1925–1934. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juchau M. R. Substrate specificities and functions of the P450 cytochromes. Life Sci. 1990;47(26):2385–2394. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Szczesna-Skorupa E. Cytochrome P-450 membrane signals. Drug Metab Rev. 1989;20(2-4):811–820. doi: 10.3109/03602538909103580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khani S. C., Porter T. D., Coon M. J. Isolation and partial characterization of the gene for cytochrome P-450 3a (P-450ALC) and a second closely related gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khani S. C., Porter T. D., Fujita V. S., Coon M. J. Organization and differential expression of two highly similar genes in the rabbit alcohol-inducible cytochrome P-450 subfamily. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7170–7175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khani S. C., Zaphiropoulos P. G., Fujita V. S., Porter T. D., Koop D. R., Coon M. J. cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of ethanol-inducible rabbit liver cytochrome P-450 isozyme 3a (P-450ALC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):638–642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. G., Novak R. F. Induction of rat hepatic P450IIE1 (CYP 2E1) by pyridine: evidence for a role of protein synthesis in the absence of transcriptional activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1072–1079. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90976-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. G., Shehin S. E., States J. C., Novak R. F. Evidence for increased translational efficiency in the induction of P450IIE1 by solvents: analysis of P450IIE1 mRNA polyribosomal distribution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 30;172(2):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90740-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop D. R., Casazza J. P. Identification of ethanol-inducible P-450 isozyme 3a as the acetone and acetol monooxygenase of rabbit microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13607–13612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop D. R., Coon M. J. Ethanol oxidation and toxicity: role of alcohol P-450 oxygenase. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1986;10(6 Suppl):44S–49S. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1986.tb05179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop D. R., Morgan E. T., Tarr G. E., Coon M. J. Purification and characterization of a unique isozyme of cytochrome P-450 from liver microsomes of ethanol-treated rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8472–8480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota S., Lasker J. M., Lieber C. S. Molecular regulation of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P450-IIEI in hamsters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindros K. O., Cai Y. A., Penttilä K. E. Role of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 IIE1 in carbon tetrachloride-induced damage to centrilobular hepatocytes from ethanol-treated rats. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1092–1097. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry T. J., Lindquist S. The preferential translation of Drosophila hsp70 mRNA requires sequences in the untranslated leader. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Barlow D. P., Hill R. E., Hogan B. L., Hastie N. D. Pattern of serum protein gene expression in mouse visceral yolk sac and foetal liver. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1881–1885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. W., Yang C. S. Studies on the mechanisms of induction of N-nitrosodimethylamine demethylase by fasting, acetone, and ethanol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Mar;229(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Schmidt W. E., Stier A. The site of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase catalyzed phosphorylation of cytochrome P-450 LM2. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Strobel H. W. Evolution of cytochrome P-450 proteins. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Nov;4(6):572–593. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Strobel H. W. On the membrane topology of vertebrate cytochrome P-450 proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6038–6050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha R. F. Decreased incidence of renal tumors in DMN treated Balb/C mice after orchiectomy. J Surg Oncol. 1977;9(5):463–468. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930090508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B. Enzyme induction in the cytochrome P-450 system. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(2):241–298. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Past M. R., Cook D. E. Effect of diabetes on rat liver cytochrome P-450. Evidence for a unique diabetes-dependent rat liver cytochrome P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;31(20):3329–3334. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. D., Khani S. C., Coon M. J. Induction and tissue-specific expression of rabbit cytochrome P450IIE1 and IIE2 genes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Gunsalus I. C., Wagner G. C., Kraut J. The 2.6-A crystal structure of Pseudomonas putida cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16122–16130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Howard A. J. High-resolution crystal structure of cytochrome P450cam. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):687–700. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard G. A., Jr, Haff A. C., Skutches C. L., Paul P., Holroyde C. P., Owen O. E. Plasma acetone metabolism in the fasting human. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):619–626. doi: 10.1172/JCI109344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. E., Levin W. Purification and characterization of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(2):153–239. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. E., Ramanathan L., Iida S., Thomas P. E., Haniu M., Shively J. E., Lieber C. S., Levin W. Characterization of a major form of rat hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 induced by isoniazid. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6385–6393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnier G. G., Laethem C. L., Koop D. R. Identification and induction of cytochromes P450, P450IIE1 and P450IA1 in rabbit bone marrow. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):790–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B. J., Gelboin H. V., Park S. S., Yang C. S., Gonzalez F. J. Complementary DNA and protein sequences of ethanol-inducible rat and human cytochrome P-450s. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the rat enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16689–16697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B. J., Matsunaga T., Hardwick J. P., Park S. S., Veech R. L., Yang C. S., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Stabilization of cytochrome P450j messenger ribonucleic acid in the diabetic rat. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Aug;1(8):542–547. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-8-542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B. J., Veech R. L., Park S. S., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Induction of rat hepatic N-nitrosodimethylamine demethylase by acetone is due to protein stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3568–3572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireos G., Penn M. D., Greer H. 5' untranslated sequences are required for the translational control of a yeast regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuyns A. J., Péquignot G., Abbatucci J. S. Oesophageal cancer and alcohol consumption; importance of type of beverage. Int J Cancer. 1979 Apr 15;23(4):443–447. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno M., McBride O. W., Yang C. S., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Human ethanol-inducible P450IIE1: complete gene sequence, promoter characterization, chromosome mapping, and cDNA-directed expression. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):9006–9013. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno M., Song B. J., Kozak C., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. The rat P450IIE1 gene: complete intron and exon sequence, chromosome mapping, and correlation of developmental expression with specific 5' cytosine demethylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4956–4962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Thomas P. E., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Purification and characterization of ethanol-inducible human hepatic cytochrome P-450HLj. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Oct;258(1):292–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. S., Yoo J. S., Ishizaki H., Hong J. Y. Cytochrome P450IIE1: roles in nitrosamine metabolism and mechanisms of regulation. Drug Metab Rev. 1990;22(2-3):147–159. doi: 10.3109/03602539009041082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]