Abstract
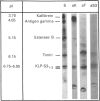
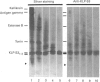
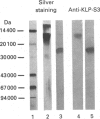
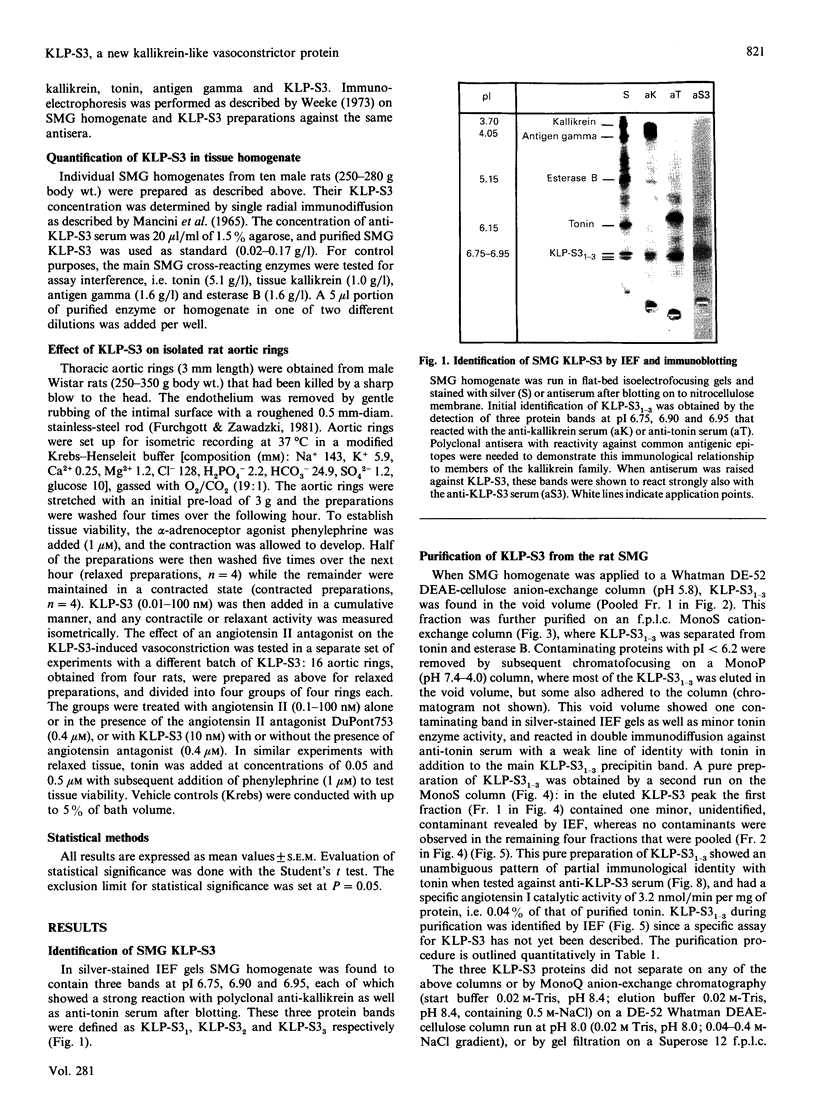
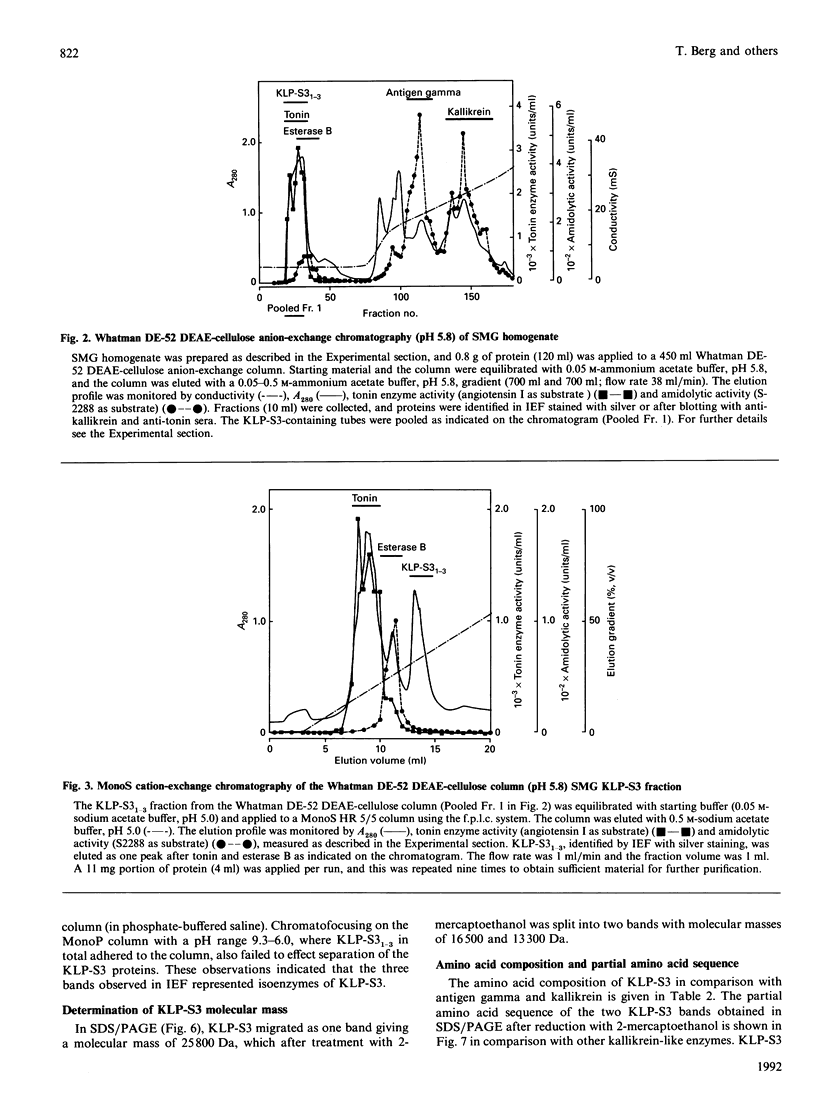
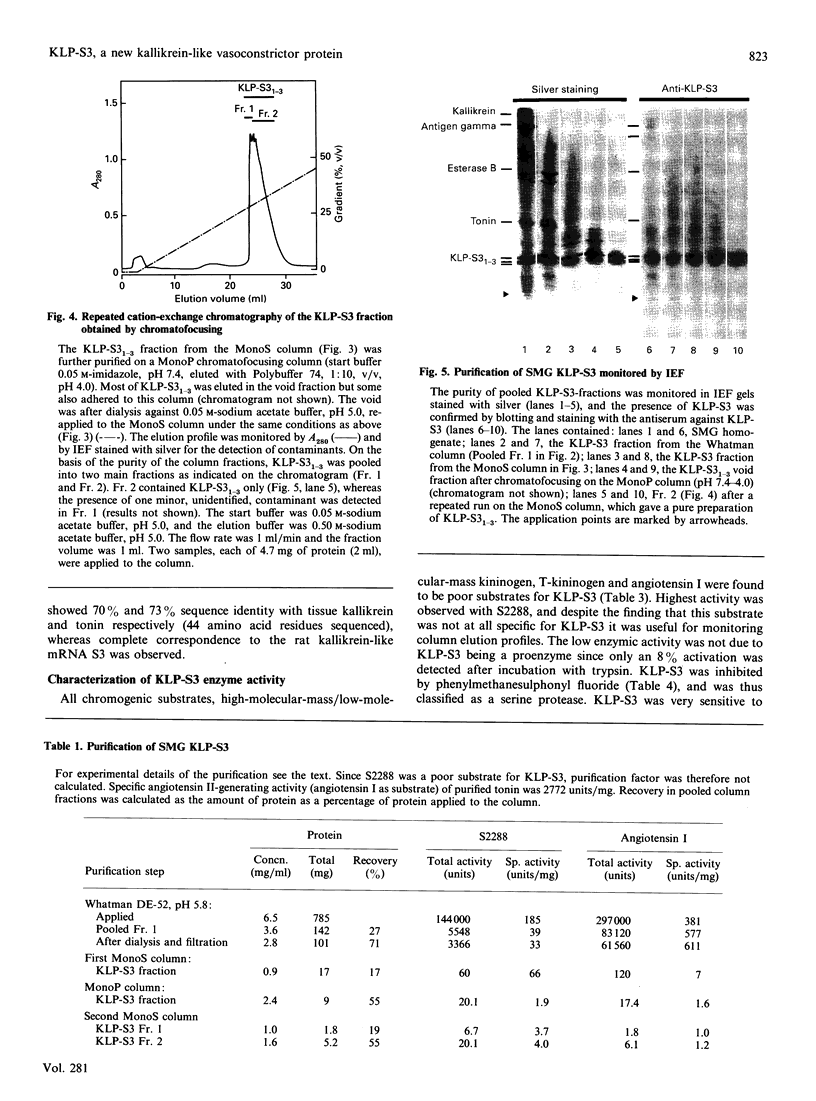
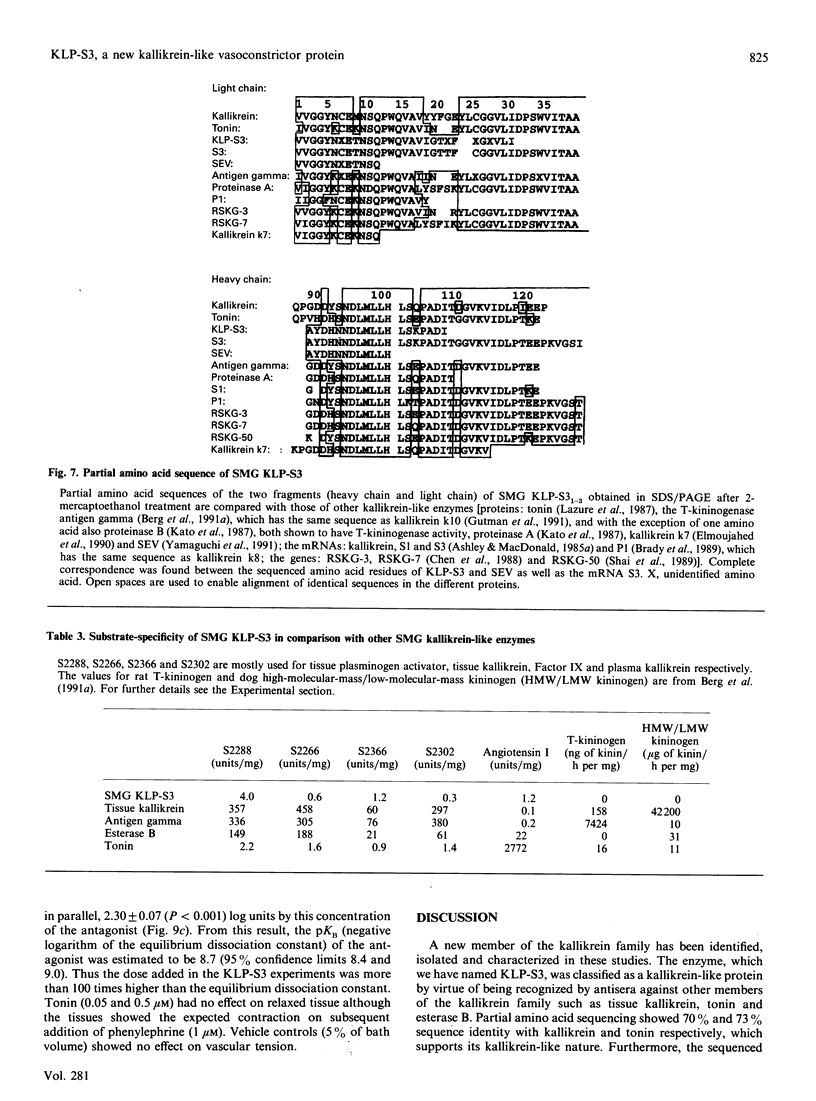
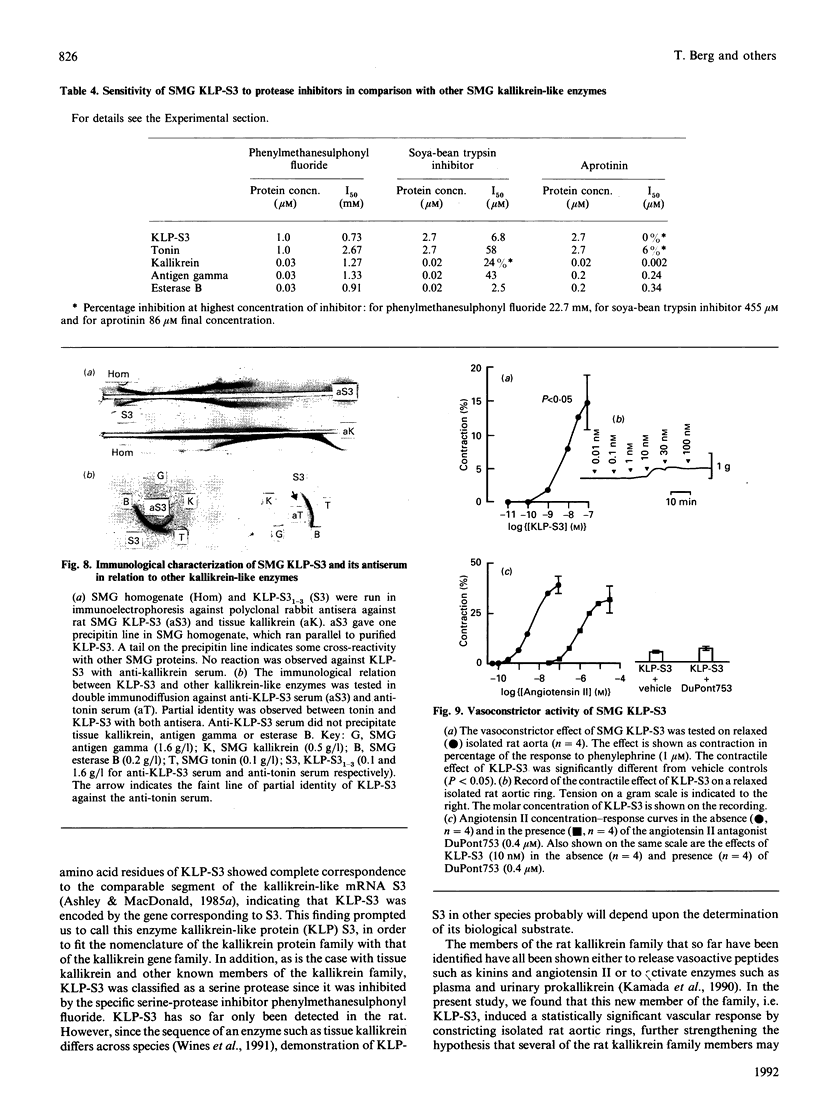
The submandibular gland of the rat contains several enzymes belonging to the kallikrein family. These include tissue kallikrein, antigen gamma (T-kininogenase), esterase B and tonin. In the present study, a new member of this family, which we have named KLP-S3, was identified and purified from the submandibular gland. KLP-S3 was classified as a kallikrein-like enzyme on the basis of its immunological similarity to other kallikrein-like enzymes and its showing 70% and 73% identity in partial amino acid sequence with tissue kallikrein and tonin respectively. Furthermore, the 44 sequenced amino acid residues showed complete correspondence to the mRNA S3 of the kallikrein gene family, which was the rationale for the name kallikrein-like protein (KLP) S3. KLP-S3 consisted of three isoenzymes with pI 6.75, 6.90 and 6.95, which significantly differed from those of other kallikrein-like enzymes. In conjunction with its immunological relationship to kallikrein, this parameter (pI) was considered robust enough to identify the enzyme during purification, since a specific physiological substrate for KLP-S3 has yet to be identified. In SDS/PAGE the three isoenzymes ran as one band with a molecular mass of 25,800 Da, which after reduction with 2-mercaptoethanol was split into two chains with molecular masses of 16,500 and 13,300 Da. In common with other kallikrein-like enzymes, KLP-S3 was inhibited by phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride, and was thus classified as a serine protease. It was also inhibited by soya-bean trypsin inhibitor but not by aprotinin. It showed weak reactivity against the chromogenic substrates S2288, S2266, S2366 and S2302 (D-Ile-Pro-Arg 4-nitroanilide, D-Val-Leu-Arg 4-nitroanilide, Glu-Pro-Arg 4-nitroanilide and D-Pro-Phe-Arg 4-nitroanilide respectively) and did not cleave rat T-kininogen or dog high-molecular-mass/low-molecular-mass kininogen. Its specific angiotensin II-generating activity (angiotensin I as substrate) was 0.04% of that of rat tonin. KLP-S3 (1-100 nM) induced a statistically significant angiotensin-independent contraction of isolated rat aorta rings. The maximum contraction was 15% of the response to the alpha-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine (1 microM). The concentration of KLP-S3 in the rat submandibular gland was by single radial immunodiffusion estimated to be 47 +/- 3 micrograms/mg of protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amundsen E., Putter J., Friberger P., Knos M., Larsbraten M., Claeson G. Methods for the determination of glandular kallikrein by means of a chromogenic tripeptide substrate. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;120A:83–95. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0926-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Kallikrein-related mRNAs of the rat submaxillary gland: nucleotide sequences of four distinct types including tonin. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4512–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Tissue-specific expression of kallikrein-related genes in the rat. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4520–4527. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlas A., Gao X. X., Greenbaum L. M. Isolation of a thiol-activated T-kininogenase from the rat submandibular gland. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 29;218(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Holck M., Johansen L. Isolation, characterization, and localization of antigen gamma, a serine proteinase of the "kallikrein-family" in the rat submandibular gland. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Nov;368(11):1455–1467. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Wassdal I., Mindroiu T., Sletten K., Scicli G., Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. T-kininogenase activity of the rat submandibular gland is predominantly due to the kallikrein-like serine protease antigen gamma. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):19–25. doi: 10.1042/bj2800019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. M., Wines D. R., MacDonald R. J. Expression of two kallikrein gene family members in the rat prostate. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5203–5210. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Gautvik K. M., Nustad K., Pierce J. V. Rat submandibular gland kallikreins: purification and cellular localization. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Feb;56(2):155–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. P., Chao J., Chao L. Molecular cloning and characterization of two rat renal kallikrein genes. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7189–7196. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell G. G., 3rd, Sletten K., Johansson B., Westermark P. Evidence that the amyloid fibril protein in senile systemic amyloidosis is derived from normal prealbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):648–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmoujahed A., Gutman N., Brillard M., Gauthier F. Substrate specificity of two kallikrein family gene products isolated from the rat submaxillary gland. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80903-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Schiffrin E. L., Thibault G., Boucher R., Genest J. Effects of tonin on the response to norepinephrine by the aortic strip of the hypertensive rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;59(8):790–793. doi: 10.1139/y81-116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman N., Elmoujahed A., Brillard M., Du Sorbier B. M., Gauthier F. Microheterogeneity of rat submaxillary gland kallikrein k10, a member of the kallikrein family. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):425–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman N., Moreau T., Alhenc-Gelas F., Baussant T., el Moujahed A., Akpona S., Gauthier F. T-kinin release from T-kininogen by rat-submaxillary-gland endopeptidase K. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):577–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen L., Bergundhaugen H., Berg T. Rapid purification of tonin, esterase B, antigen psi and kallikrein from rat submandibular gland by fast protein liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jan 30;387:347–359. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)94537-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamada M., Furuhata N., Yamaguchi T., Ikekita M., Kizuki K., Moriya H. Observation of tissue prokallikrein activation by some serine proteases, arginine esterases in rat submandibular gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91935-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Nakanishi E., Enjyoji K., Hayashi I., Oh-ishi S., Iwanaga S. Characterization of serine proteinases isolated from rat submaxillary gland: with special reference to the degradation of rat kininogens by these enzymes. J Biochem. 1987 Dec;102(6):1389–1404. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khullar M., Scicli G., Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. Purification and characterization of a serine protease (esterase B) from rat submandibular glands. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):1851–1857. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazure C., Leduc R., Seidah N. G., Thibault G., Genest J., Chrétien M. The complete amino acid sequence of rat submaxillary gland tonin does contain the aspartic acid at the active site: confirmation by protein sequence analysis. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;65(4):321–337. doi: 10.1139/o87-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik T. B., Carretero O. A., Hayashi H., Scicli G. A., Johansen L. Immunohistochemical localization of tonin and its relation to kallikrein in rat salivary glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Nov;30(11):1123–1129. doi: 10.1177/30.11.6292285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shai S. Y., Woodley-Miller C., Chao J., Chao L. Characterization of genes encoding rat tonin and a kallikrein-like serine protease. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5334–5343. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Husebekk A., Husby G. The amino acid sequence of an amyloid fibril protein AA isolated from the horse. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jul;26(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wines D. R., Brady J. M., Southard E. M., MacDonald R. J. Evolution of the rat kallikrein gene family: gene conversion leads to functional diversity. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jun;32(6):476–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02102650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong W., Chen L. M., Chao J. Purification and characterization of a kallikrein-like T-kininogenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2822–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. A novel serine protease with vasoconstrictor activity coded by the kallikrein gene S3. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5011–5017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. A potent vasoconstrictor in the rat submandibular gland. Hypertension. 1991 Jan;17(1):101–106. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]