Abstract
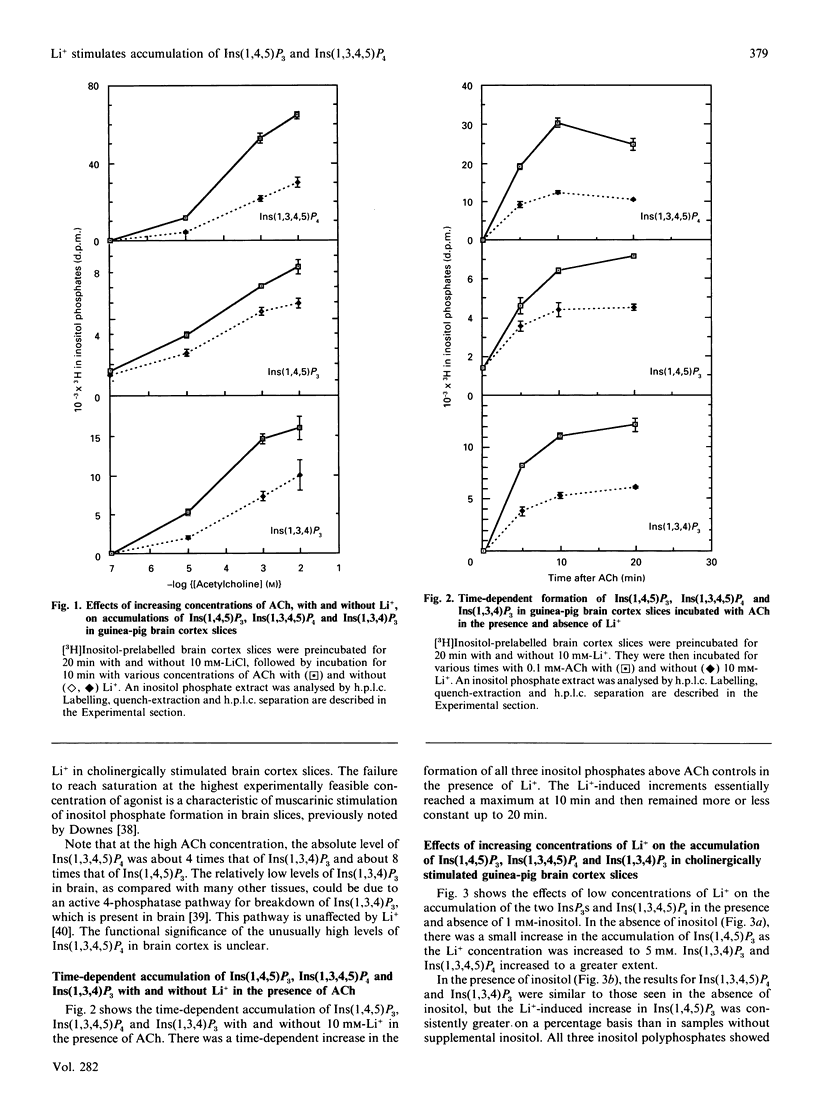
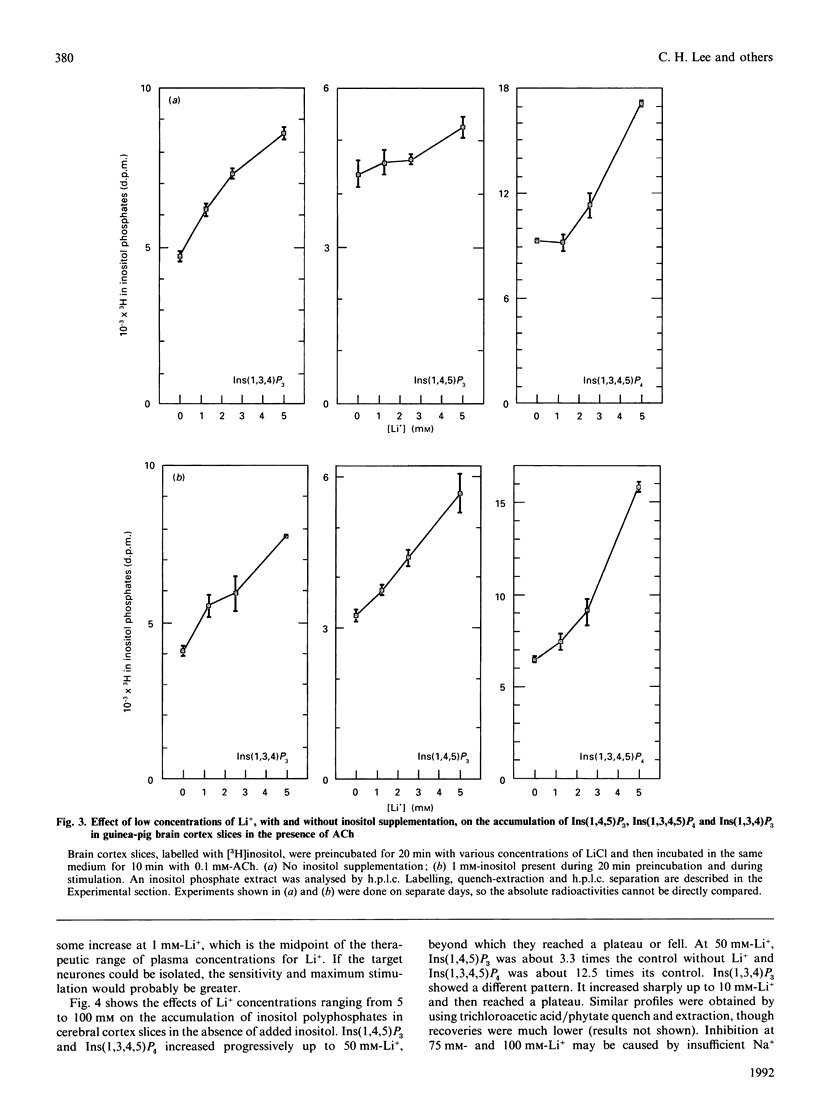
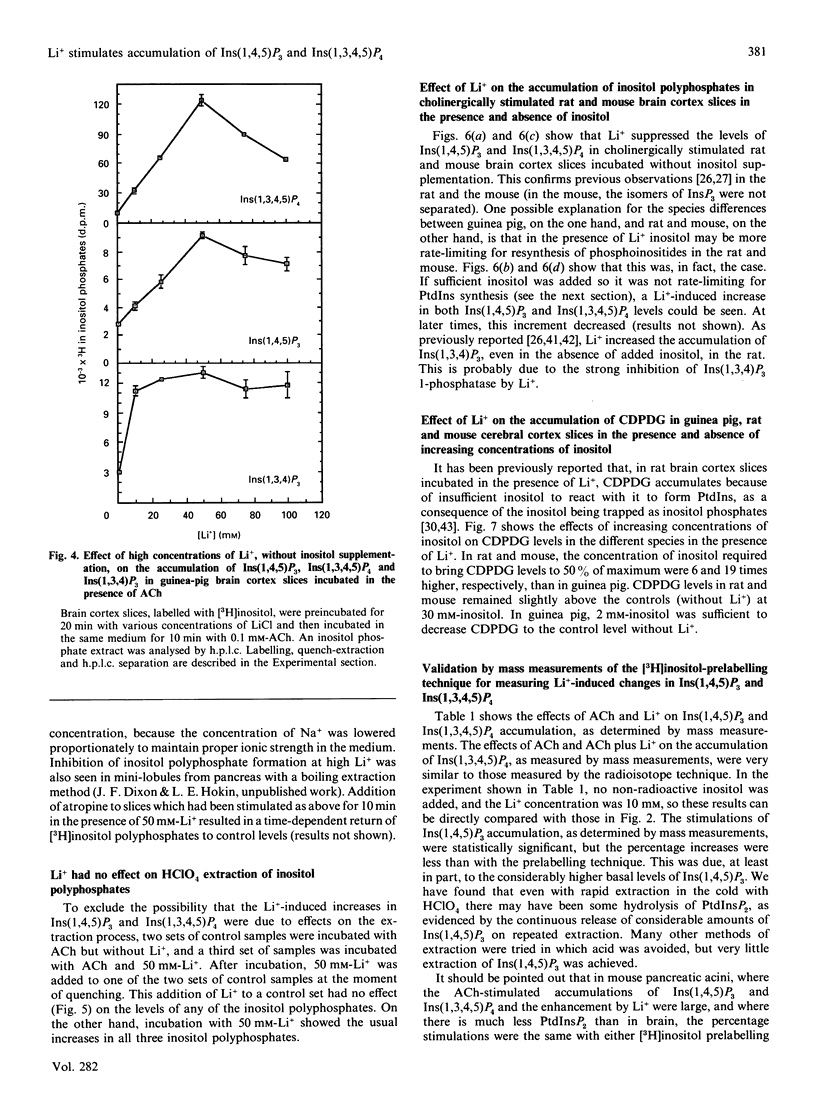
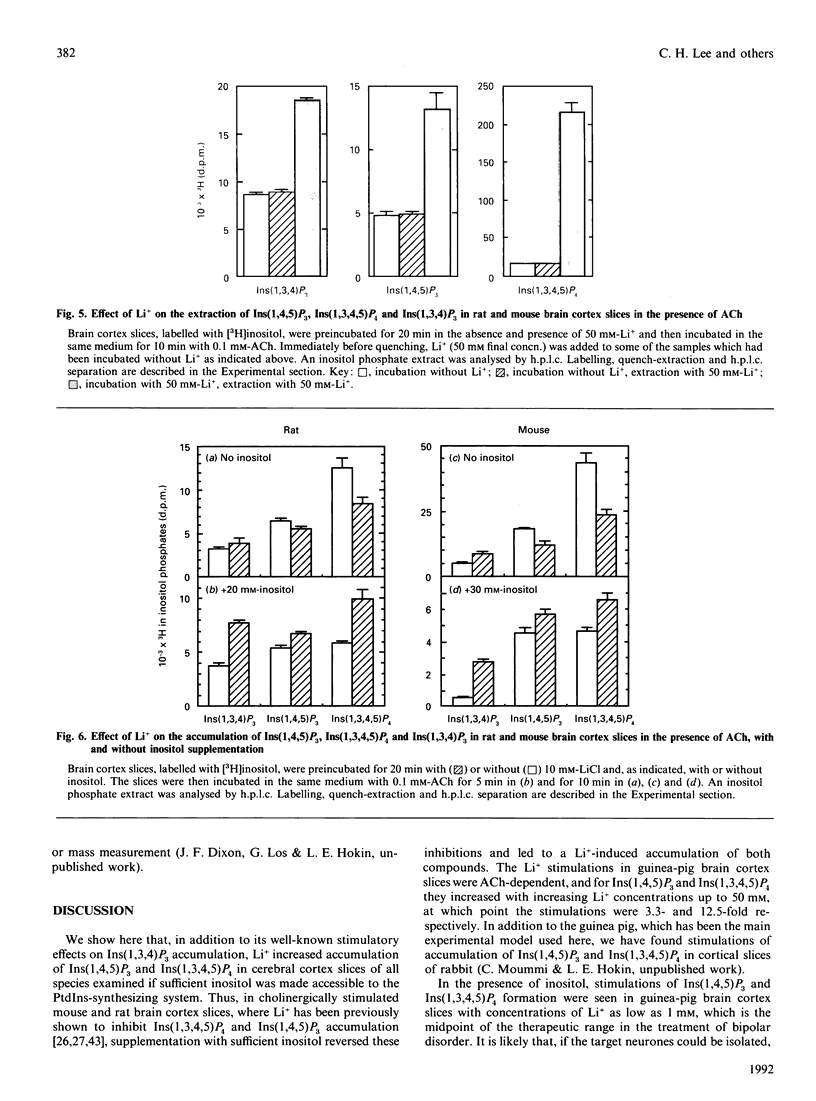
Li+, beginning at a concentration as low as 1 mM, produced a time- and dose-dependent increase in accumulation of [3H]Ins(1,4,5)P3 and [3H]Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 in acetylcholine (ACh)-stimulated guinea-pig brain cortex slices prelabelled with [3H]inositol and containing 1 mM-inositol in the final incubation period. Similar results were obtained by mass measurement of samples incubated with 10 mM-Li+ by using a receptor-binding assay, although the percentage stimulation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 accumulation by Li+ was somewhat less by this assay. The increase in accumulation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 by Li+ was absolutely dependent on the presence of ACh. In the absence of added inositol, 1-5 mM-Li+ produced smaller increases in Ins(1,4,5)P3, but the Li(+)-dependent increase in Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 was not as affected by inositol omission. In previous studies with cholinergically stimulated rat and mouse brain cortex slices, Li+ inhibited accumulation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in rat and inhibited Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 accumulation in rat and mouse [Batty & Nahorski (1987) Biochem. J. 247, 797-800; Whitworth & Kendall (1988) J. Neurochem. 51, 258-265]. We found that Li+ inhibited both Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 accumulation in these species, but we could reverse this inhibition by adding 10-30 mM-inositol; we then observed a Li(+)-induced increase in Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4. The species differences observed in the absence of supplemented inositol were explained by the fact that a much higher concentration of inositol was required to bring the Li(+)-elevated levels of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDPDG) down to baseline in the rat and mouse. These data suggest that inositol is more rate-limiting for phosphatidylinositol synthesis in the presence of Li+ in rat and mouse, which can account for the previous reports of inhibition of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 accumulation by this ion in these species. Thus, in all species examined. Li+ could be shown to increase accumulation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 in cholinergically stimulated brain cortex slices if the slices were supplemented with sufficient inositol to bring the Li(+)-elevated level of CDPDG down to near baseline, as seen in the absence of Li+. In guinea-pig brain cortex slices, increases in Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 accumulation could then be seen at Li+ concentrations as low as 1 mM, which falls within the therapeutic range of plasma concentrations in the treatment of manic-depressive disorders. These observations may have therapeutic implications.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. H., Blisner M. E., Holland W. H., Hipps P. P., Sherman W. R. Increased brain myo-inositol 1-phosphate in lithium-treated rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):664–670. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Majerus P. W. The metabolism of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate to inositol 1,3-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9444–9447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. H., Letcher A. J., Nahorski S. R. Accumulation of inositol polyphosphate isomers in agonist-stimulated cerebral-cortex slices. Comparison with metabolic profiles in cell-free preparations. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):23–32. doi: 10.1042/bj2580023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Rapid accumulation and sustained turnover of inositol phosphates in cerebral-cortex slices after muscarinic-receptor stimulation. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):237–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2600237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I., Nahorski S. R. Lithium inhibits muscarinic-receptor-stimulated inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2470797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Neural and developmental actions of lithium: a unifying hypothesis. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Ca2+ regulates the inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway in intact and broken preparations of insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11931–11934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: I. Receptor characterisation. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1379–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Willcocks A. L., Mulloy B., Potter B. V., Nahorski S. R. Characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate- and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate-binding sites in rat cerebellum. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):861–867. doi: 10.1042/bj2740861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changya L., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Potter B. V., Petersen O. H. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate is essential for sustained activation of the Ca2+-dependent K+ current in single internally perfused mouse lacrimal acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):85–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01870793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. J., Irvine R. F., Dawson A. P. Synergistic control of Ca2+ mobilization in permeabilized mouse L1210 lymphoma cells by inositol 2,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):549–553. doi: 10.1042/bj2710549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean N. M., Moyer J. D. Separation of multiple isomers of inositol phosphates formed in GH3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):361–366. doi: 10.1042/bj2420361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvaux A., Erneux C., Moreau C., Dumont J. E. Enzymic dephosphorylation of D-myo-inositol 1,4-bisphosphate in rat brain. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):193–198. doi: 10.1042/bj2420193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Kinetic analysis of the formation of inositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate in carbachol-stimulated pancreatic minilobules. Half is formed by direct phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11721–11724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donié F., Reiser G. A novel, specific binding protein assay for quantitation of intracellular inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP4) using a high-affinity InsP4 receptor from cerebellum. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P. Receptor-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in the central nervous system. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):413–428. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Joels L. A., Hughes P. J. The interaction of lithium ions with inositol lipid signalling systems. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):32–35. doi: 10.1042/bst0150032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely J. A., Hunyady L., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate stimulates calcium release from bovine adrenal microsomes by a mechanism independent of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):333–338. doi: 10.1042/bj2680333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghalayini A., Eichberg J. Purification of phosphatidylinositol synthetase from rat brain by CDP-diacylglycerol affinity chromatography and properties of the purified enzyme. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey P. P. Potentiation by lithium of CMP-phosphatidate formation in carbachol-stimulated rat cerebral-cortical slices and its reversal by myo-inositol. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2580621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graur D., Hide W. A., Li W. H. Is the guinea-pig a rodent? Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):649–652. doi: 10.1038/351649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol cyclic 1:2,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in intact rat parotid acinar cells. Relationship to calcium signalling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn R. C., Bansal V. S., Majerus P. W. Pathway for inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate and 1,4-bisphosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn R. C., Majerus P. W. Inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase from calf brain. Purification and inhibition by Li+, Ca2+, and Mn2+. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15946–15952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Inositol(1,3,4,5)tetrakisphosphate-induced activation of sea urchin eggs requires the presence of inositol trisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Acute and chronic lithium treatments influence agonist and depolarization-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):1023–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. D., Challiss R. A., Ragan C. I., Nahorski S. R. Reduced inositol polyphosphate accumulation and inositol supply induced by lithium in stimulated cerebral cortex slices. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):781–786. doi: 10.1042/bj2670781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Ross T. S., Lips D. L. Inositol phosphates: synthesis and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3051–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H. Does inositol tetrakisphosphate play a role in the receptor-mediated control of calcium mobilization? Cell Calcium. 1989 Jul;10(5):375–383. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana R. S., Hokin L. E. Role of phosphoinositides in transmembrane signaling. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):115–164. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman M., Nen W., Hokin L. E. Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol increases arachidonic acid levels in guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):823–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Munsell L. Y., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P. Effects of systemically administered lithium on phosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain, kidney, and testis. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):798–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A. B., Estevez V. A., Ferris C. D., Danoff S. K., Barrow R. K., Prestwich G. D., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol hexakisphosphate receptor proteins: isolation and characterization from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3165–3169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitworth P., Heal D. J., Kendall D. A. The effects of acute and chronic lithium treatment on pilocarpine-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in mouse brain in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitworth P., Kendall D. A. Lithium selectively inhibits muscarinic receptor-stimulated inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in mouse cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):258–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Hansen C. A., Johanson R. A., Coll K. E., Williamson M. Formation and metabolism of inositol phosphates: the inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;232:183–195. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0007-7_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]