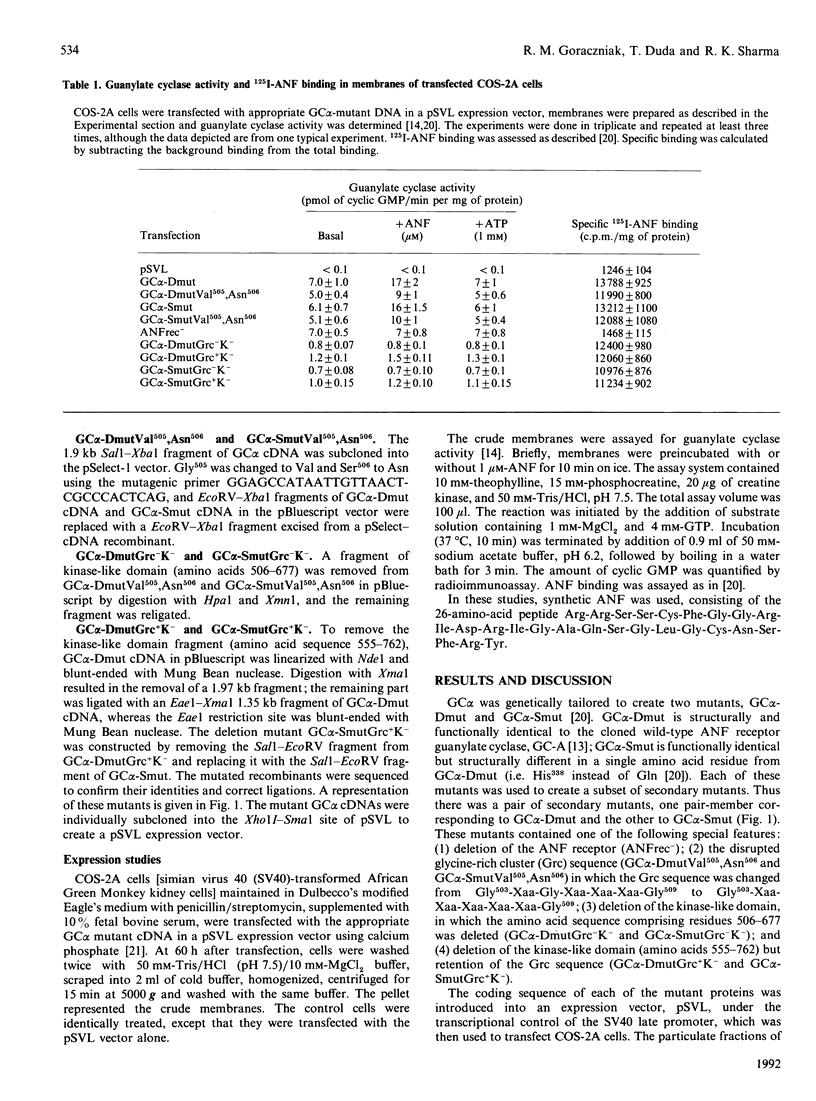
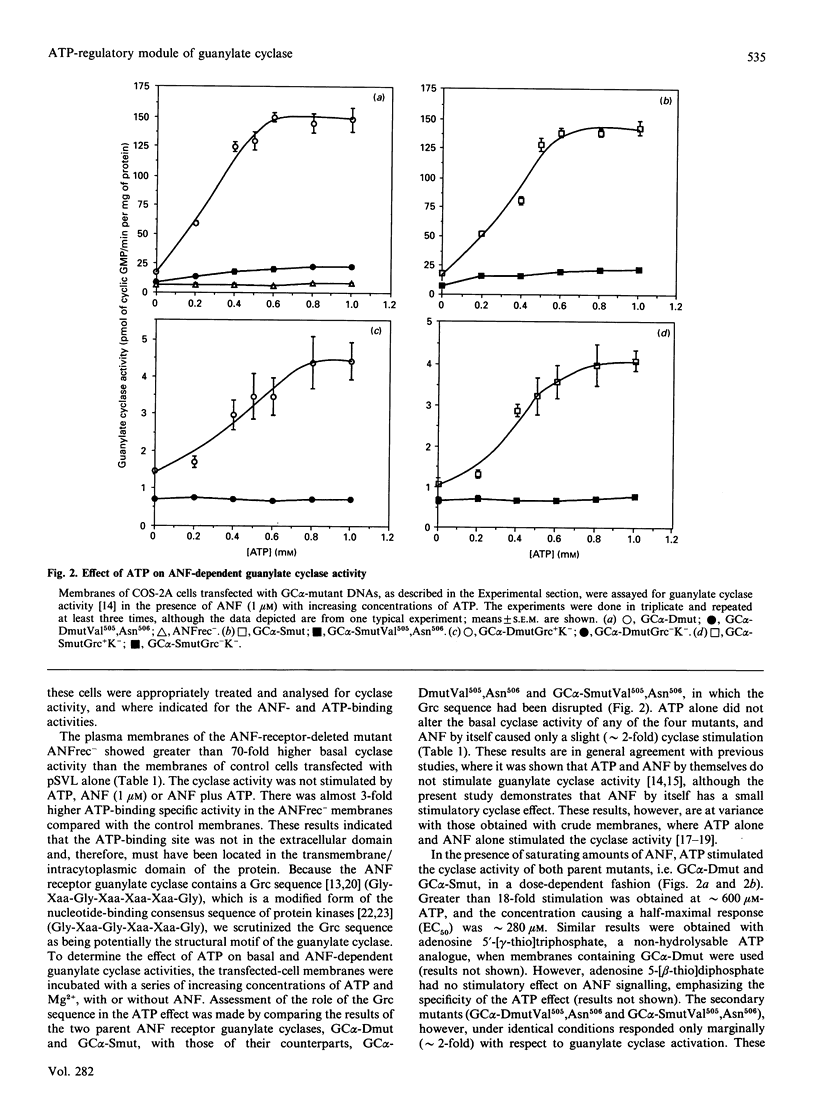
Abstract
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)-dependent guanylate cyclase is a single-chain transmembrane-spanning protein, containing an ANF receptor and having catalytic activity. ANF binding to the receptor domain activates the catalytic domain, generating the second messenger cyclic GMP. Obligatory in this activation process is an intervening step regulated by ATP, but its mechanism is not known. Through a programme of site-directed and deletion mutagenesis/expression studies, we report herein the identity of a structural motif (Gly503-Arg-Gly-Ser-Asn-Tyr-Gly509) that binds ATP and amplifies the ANF-dependent cyclase activity; this, therefore, represents an ATP-regulatory module (ARM) of the enzyme, which plays a pivotal role in ANF signalling.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bex F., Corbin A. Atrial natriuretic factor stimulates testosterone production by mouse interstitial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 10;115(1):125–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Kohse K. P., Chang B., Hirata M., Jiang B., Douglas J. E., Murad F. Characterization of ATP-stimulated guanylate cyclase activation in rat lung membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 9;1052(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90071-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L., Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Chin H. M., Goeddel D. V., Schulz S. A membrane form of guanylate cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):78–83. doi: 10.1038/338078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L. The protein kinase domain of the ANP receptor is required for signaling. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1392–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2571188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Singh S., Garbers D. L. Adenine nucleotides are required for activation of rat atrial natriuretic peptide receptor/guanylyl cyclase expressed in a baculovirus system. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4088–4093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duda T., Goraczniak R. M., Sharma R. K. Site-directed mutational analysis of a membrane guanylate cyclase cDNA reveals the atrial natriuretic factor signaling site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7882–7886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L. The guanylyl cyclase receptor family. New Biol. 1990 Jun;2(6):499–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzano H., Wu H. I., Waldman S. A. Adenine nucleotide regulation of particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 8;1077(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3043–3046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keown W. A., Campbell C. R., Kucherlapati R. S. Methods for introducing DNA into mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:527–537. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85043-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Andresen J. W., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Chang L. Y., Saheki S., Leitman D. C., Nakane M., Murad F. Co-purification of an atrial natriuretic factor receptor and particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5817–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Inagami T., Ui M. Participation of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the activation of membrane-bound guanylate cyclase by the atrial natriuretic factor. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 27;219(2):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marala R. B., Sharma R. K. Characterization of atrial-natriuretic-factor-receptor-coupled membrane guanylate cyclase from rat and mouse testes. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2510301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marala R. B., Sharma R. K. Ubiquitous and bifunctional 180 kDa atrial natriuretic factor-dependent guanylate cyclase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1991 Jan 16;100(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00230806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marala R. B., Sitaramayya A., Sharma R. K. Dual regulation of atrial natriuretic factor-dependent guanylate cyclase activity by ATP. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., McNicoll N., Liu B., Ong H., De Léan A. Atrial natriuretic factor R1 receptor from bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa: purification, characterization, and modulation by amiloride. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8151–8158. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay A. K., Schumacher M., Leidenberger F. A. Steroidogenic effect of atrial natriuretic factor in isolated mouse Leydig cells is mediated by cyclic GMP. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):463–467. doi: 10.1042/bj2390463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey K. N., Singh S. Molecular cloning and expression of murine guanylate cyclase/atrial natriuretic factor receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12342–12348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. K., Marala R. B., Jaiswal R. K., Sharma R. K. Coexistence of guanylate cyclase and atrial natriuretic factor receptor in a 180-kD protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.2881352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Geller D. M., Manning P. T., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Smith C. E., Needleman P. Ser-Leu-Arg-Arg-atriopeptin III: the major circulating form of atrial peptide. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):397–400. doi: 10.1126/science.3160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Snajdar R. M., Imada T., Tamura M., Pandey K. N., Misono K. S., Inagami T. Purification and characterization of two types of atrial natriuretic factor receptors from bovine adrenal cortex: guanylate cyclase-linked and cyclase-free receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


