Abstract
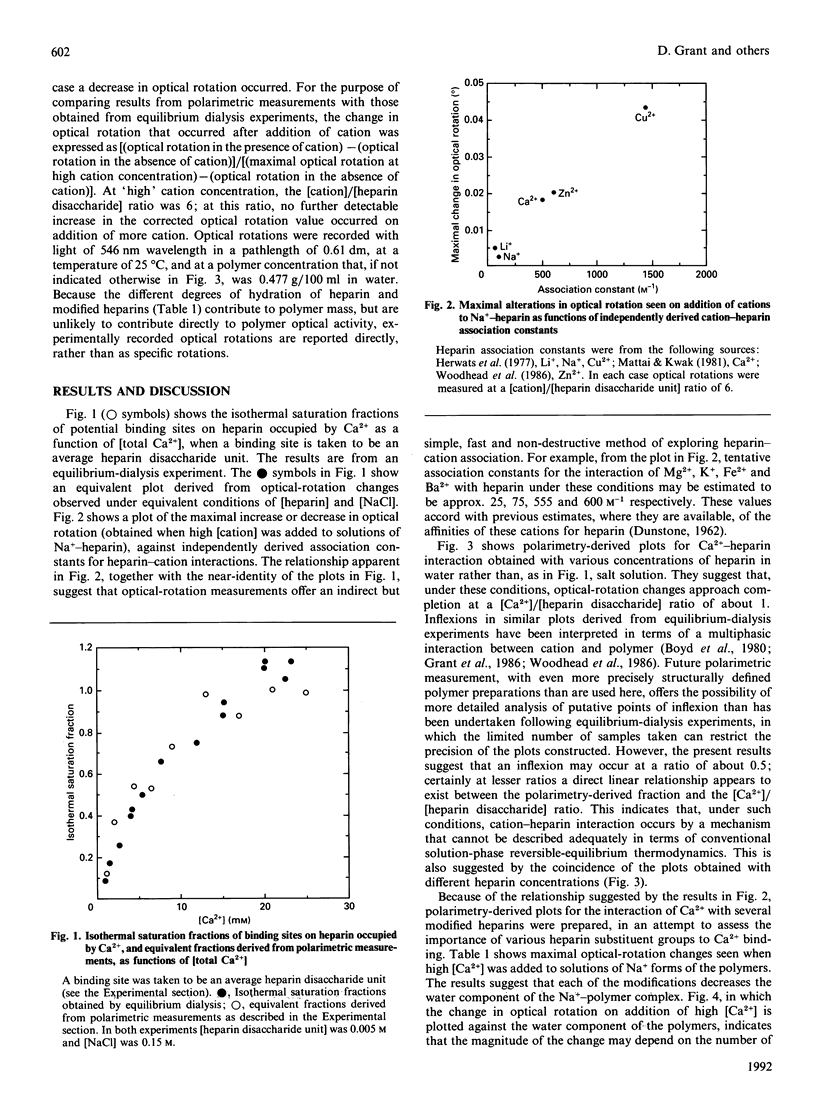
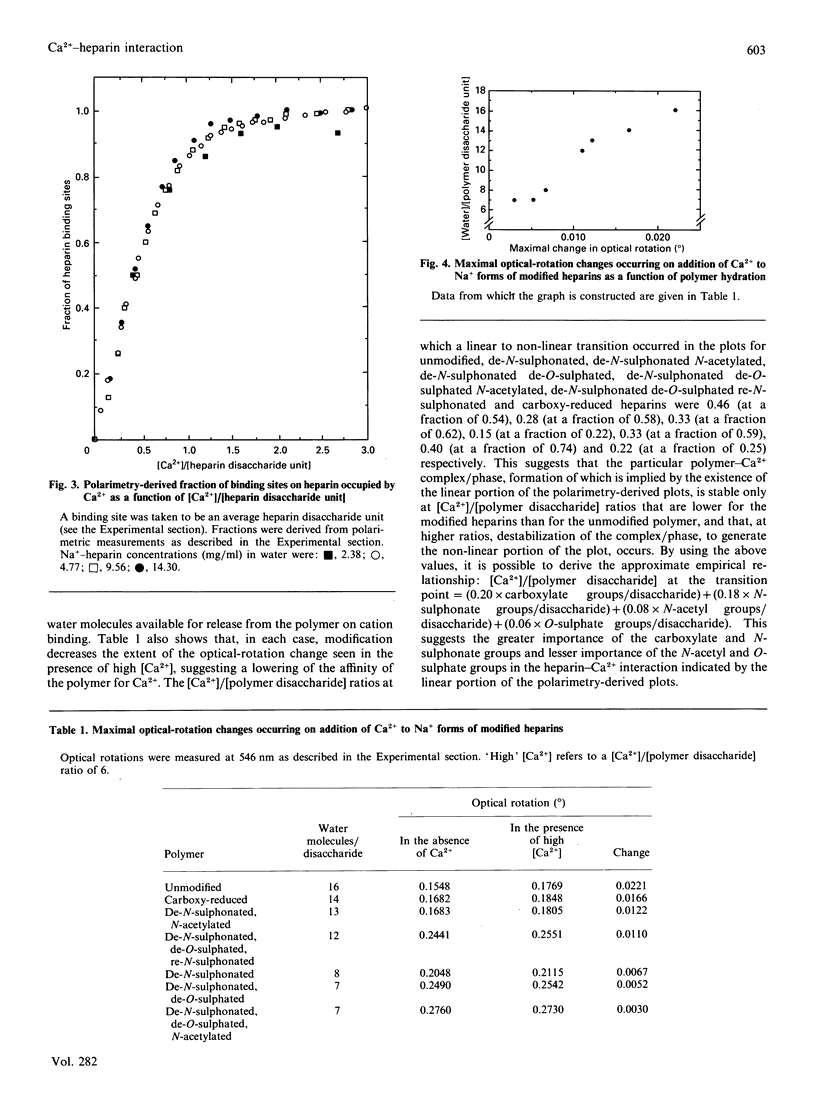
Possible inflexions in isothermal binding plots derived from equilibrium-dialysis measurements and in equivalent plots obtained by polarimetric measurements accord with the possibility that discrete Ca(2+)-heparin-water complexes/phases may exist, the nature and proportions of which depend on the conditions under which the interaction occurs. Analysis of the plots obtained by polarimetric study of chemically modified heparins suggests, for individual substituents groups, an order of importance of carboxylate greater than N-sulphonate greater than N-acetyl greater than O-sulphate for the Ca(2+)-heparin interaction occurring at [Ca2+]/[heparin disaccharide] ratios of less than 0.5. At higher ratios, transitions occur that eventually lead to the formation of a complex in which the stoichiometry of association is 1 Ca2+ ion/heparin disaccharide unit.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayotte L., Perlin A. S. N.m.r. spectroscopic observations related to the function of sulfate groups in heparin. Calcium binding vs. biological activity. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Jan 1;145(2):267–277. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J., Williamson F. B., Gettins P. A physico-chemical study of heparin. Evidence for a calcium-induced co-operative conformational transition. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 25;137(2):175–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunstone J. R. Ion-exchange reactions between acid mucopolysaccharides and various cations. Biochem J. 1962 Nov;85(2):336–351. doi: 10.1042/bj0850336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D., Long W. F., Moffat C. F., Williamson F. B. Infrared spectroscopy of chemically modified heparins. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):1035–1038. doi: 10.1042/bj2611035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D., Long W. F., Williamson F. B. A model of two conformational forms of heparins/heparans suggested by infrared spectroscopy. Med Hypotheses. 1987 Oct;24(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(87)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D., Long W. F., Williamson F. B. Infrared spectroscopy of heparin-cation complexes. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):143–149. doi: 10.1042/bj2440143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R. E., Settine J. M. An accurate colorimetric method for measurement of sulfaminohexose in heparins and heparan sulfates. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90528-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long W. F., Williamson F. B. Potentiation by calcium ions of the antithrombin III inhibition of thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90645-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattai J., Kwak J. C. Quantitative similarity of zinc and calcium binding to heparin in excess salt solution. Biophys Chem. 1988 Sep;31(3):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)80035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead N. E., Long W. F., Williamson F. B. Binding of zinc ions to heparin. Analysis by equilibrium dialysis suggests the occurrence of two, entropy-driven, processes. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2370281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


