Abstract
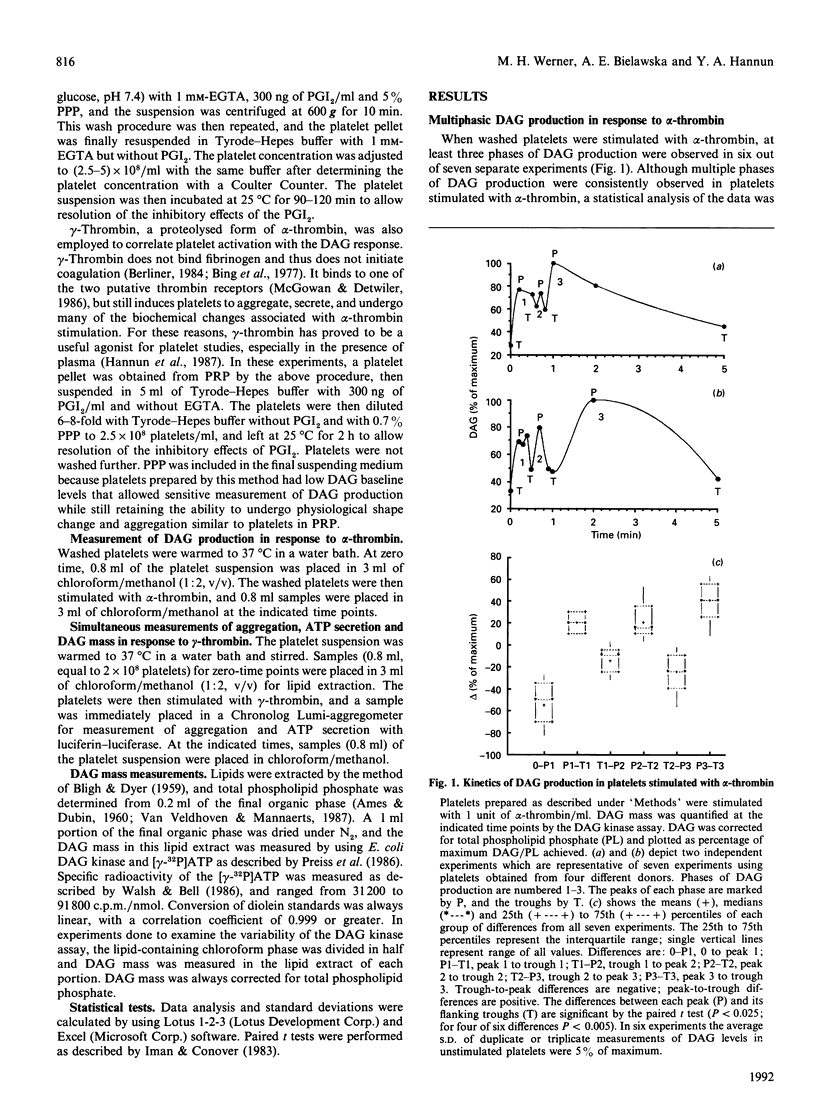
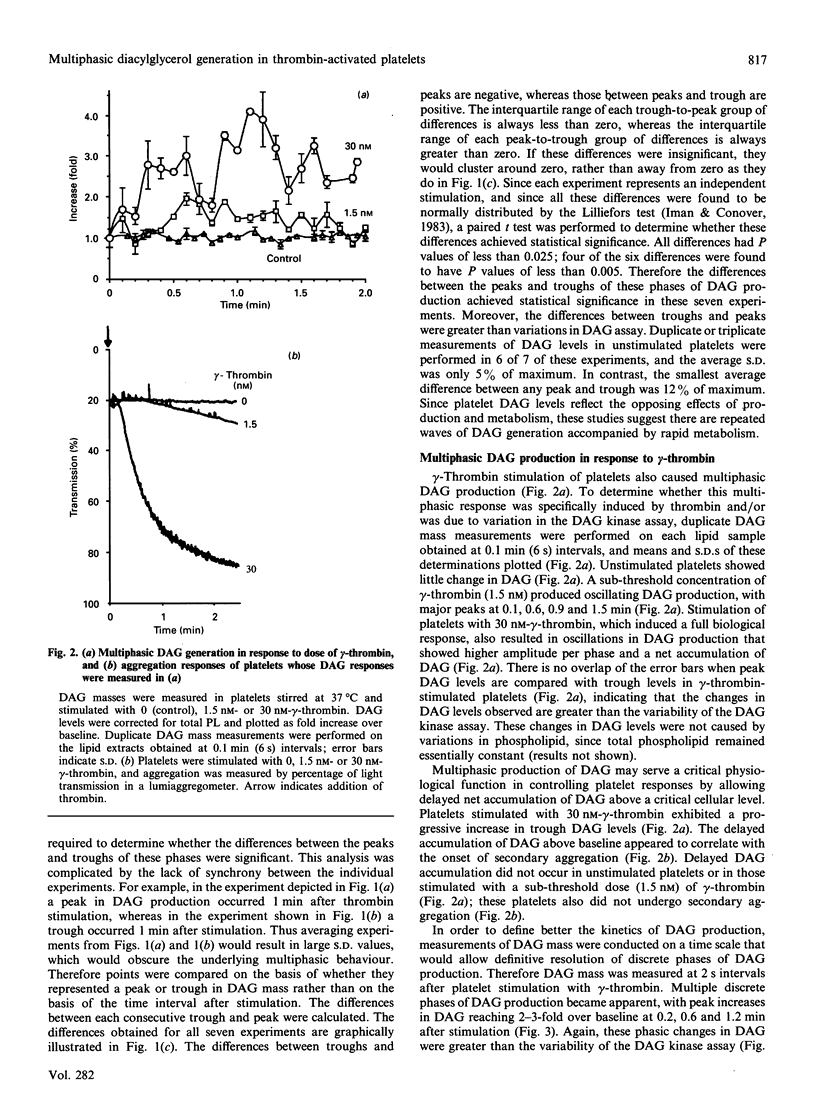
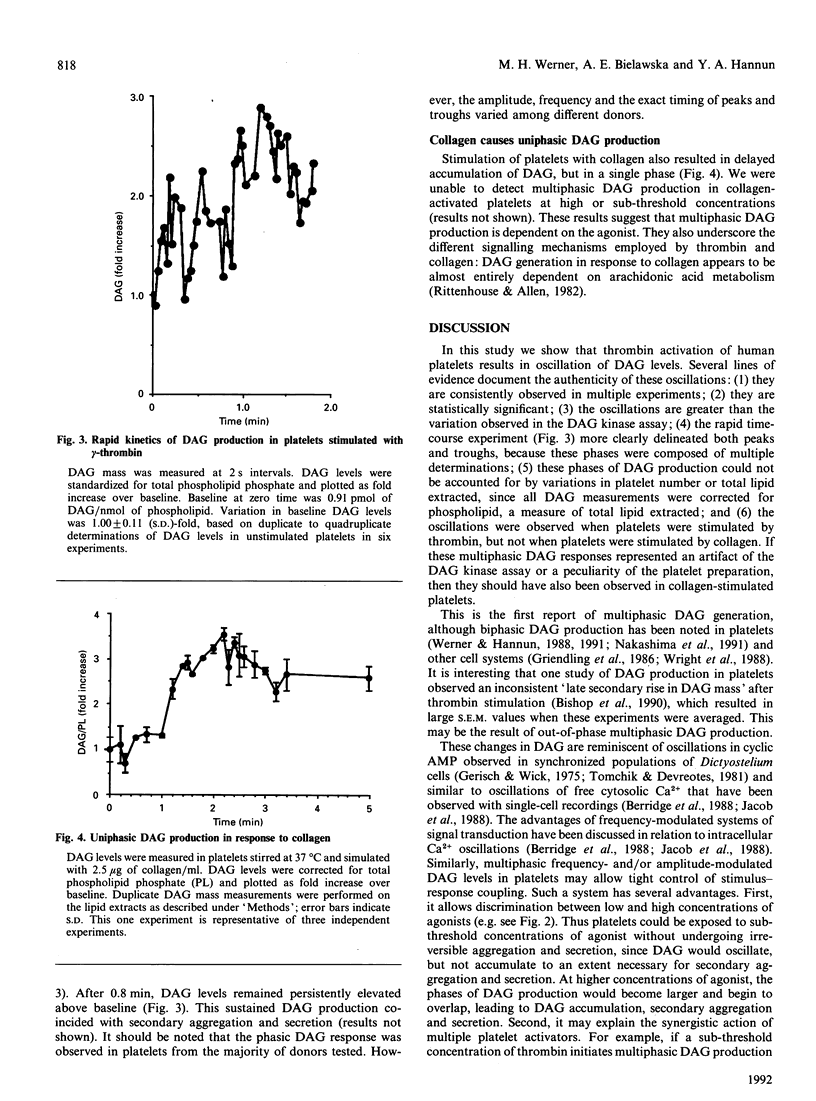
The diacylglycerol (DAG)/protein kinase C pathway plays an important role in platelet aggregation and granule secretion. In this study, we examined the detailed kinetics of DAG formation in response to platelet stimulation. Both alpha- and gamma-thrombin caused multiphasic generation of DAG mass, with DAG production reaching peaks at 0.3-0.6 min intervals. A sub-threshold concentration of gamma-thrombin (1.5 nM) produced oscillations of DAG, but peak DAG levels rapidly returned to baseline (unstimulated) values. Intermediate concentrations of gamma-thrombin (8-30 nM) resulted in prominent phases of DAG production whose troughs became significantly elevated compared with baseline levels. This delayed accumulation of DAG coincided in time with the onset of secretion and irreversible aggregation. In contrast, stimulation of platelets with collagen resulted in delayed single-phase DAG production. The kinetics of DAG production in stimulated platelets may control both the timing and the degree of DAG accumulation. This may ensure that protein kinase C is activated optimally at the onset of secondary aggregation and secretion. This is the first report of oscillating DAG production in a biological system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga H. S., Simons E. R., Brass L. F., Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of phospholipases A and C in human platelets exposed to epinephrine: role of glycoproteins IIb/IIIa and dual role of epinephrine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9197–9201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J. Structure-function relationships in human alpha- and gamma-thrombins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;61(2):159–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00222493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Spatial and temporal aspects of cell signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):325–343. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Cory M., Fenton J. W., 2nd Exo-site affinity labeling of human thrombins. Similar labeling on the A chain and B chain/fragments of clotting alpha- and nonclotting gamma/beta-thrombins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8027–8034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., August J., Petrin J. M., Pai J. K. Regulation of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol second-messenger formation in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Potentiation by protein kinase C inhibitors. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):465–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2690465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., Bell R. M. Functions of diacylglycerol in glycerolipid metabolism, signal transduction and cellular transformation. Oncogene Res. 1988 Feb;2(3):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. A., Drotts D., Weil G. J., Simons E. R. Flow cytometric measurements of cytoplasmic calcium changes in human platelets. Cytometry. 1988 Mar;9(2):138–142. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. A., Weil G. J., Simons E. R. Simultaneous flow cytometric measurements of thrombin-induced cytosolic pH and Ca2+ fluxes in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11522–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Wick U. Intracellular oscillations and release of cyclic AMP from Dictyostelium cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):364–370. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Greenberg C. S., Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of agonist-dependent secretion and activation of human platelets implies that protein kinase C is a necessary and common event of the signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13620–13626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A., Holmsen H. K. Thrombin-induced platelet responses differ in requirement for receptor occupancy. Evidence for tight coupling of occupancy and compartmentalized phosphatidic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9393–9396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A., Rongved S. Tight coupling of thrombin-induced acid hydrolase secretion and phosphatidate synthesis to receptor occupancy in human platelets. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):157–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2220157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. M., Detwiler T. C. Thrombin-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis in platelets. Receptor occupancy and desensitization. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):11–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2420011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Repetitive spikes in cytoplasmic calcium evoked by histamine in human endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):40–45. doi: 10.1038/335040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. C., Ware J. A., Cliveden P. B., Smith M., Dvorak A. M., Salzman E. W. Measurement of ionized calcium in blood platelets with the photoprotein aequorin. Comparison with Quin 2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2069–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavis R. D., Bell R. M., Vagelos P. R. Effect of phospholipase C hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids on membranous enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2835–2841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan E. B., Detwiler T. C. Modified platelet responses to thrombin. Evidence for two types of receptors or coupling mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima S., Suganuma A., Matsui A., Nozawa Y. Thrombin induces a biphasic 1,2-diacylglycerol production in human platelets. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):355–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2750355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Allen C. L. Synergistic activation by collagen and 15-hydroxy-9 alpha,11 alpha-peroxidoprosta-5,13-dienoic acid (PGH2) of phosphatidylinositol metabolism and arachidonic acid release in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1216–1224. doi: 10.1172/JCI110720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN I., SHAPIRO B. A rapid and simple method for the determination of esterified fatty acids and for total fatty acids in blood. J Clin Pathol. 1953 May;6(2):158–160. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Siegel F. L., Lapetina E. G. Arachidonic acid stimulates the formation of 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid in human platelets. Degree of phospholipase C activation correlates with protein phosphorylation, platelet shape change, serotonin release, and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11236–11242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Weber P. C., Lapetina E. G. Activation of phospholipase C is dissociated from arachidonate metabolism during platelet shape change induced by thrombin or platelet-activating factor. Epinephrine does not induce phospholipase C activation or platelet shape change. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8286–8292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarver A. P., King W. G., Rittenhouse S. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate are minor components of total mass of inositol trisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17268–17271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomchik K. J., Devreotes P. N. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate waves in Dictyostelium discoideum: a demonstration by isotope dilution--fluorography. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.6259734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Veldhoven P. P., Mannaerts G. P. Inorganic and organic phosphate measurements in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90649-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. P., Bell R. M. sn-1,2-Diacylglycerol kinase of Escherichia coli. Mixed micellar analysis of the phospholipid cofactor requirement and divalent cation dependence. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6239–6247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Hannun Y. A. Delayed accumulation of diacylglycerol in platelets as a mechanism for regulation of onset of aggregation and secretion. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. M., Rangan L. A., Shin H. S., Raben D. M. Kinetic analysis of 1,2-diacylglycerol mass levels in cultured fibroblasts. Comparison of stimulation by alpha-thrombin and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9374–9380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


