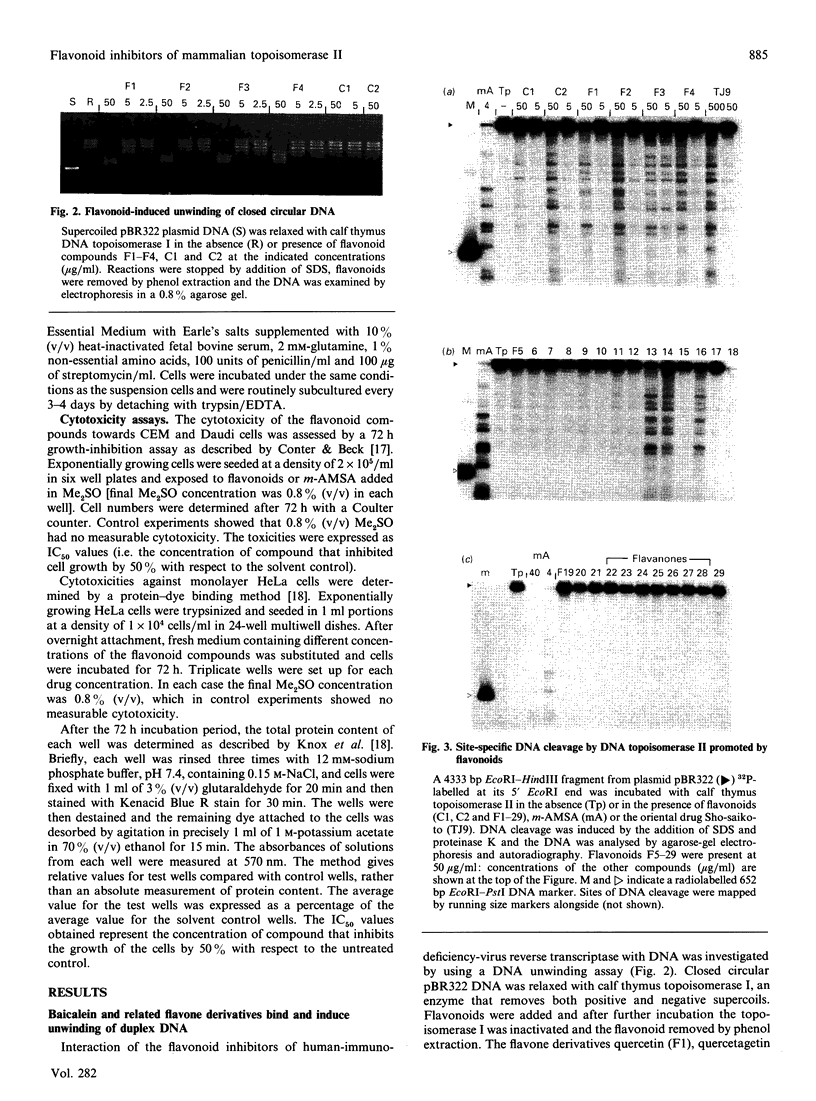
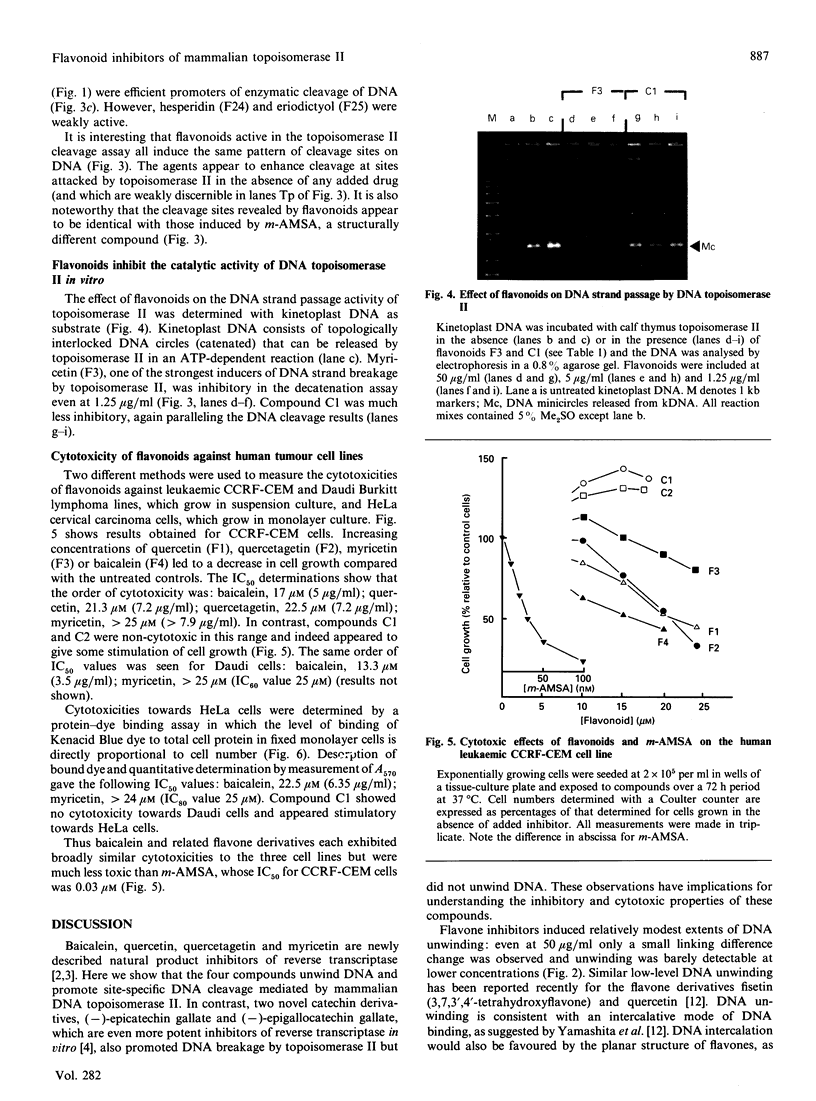
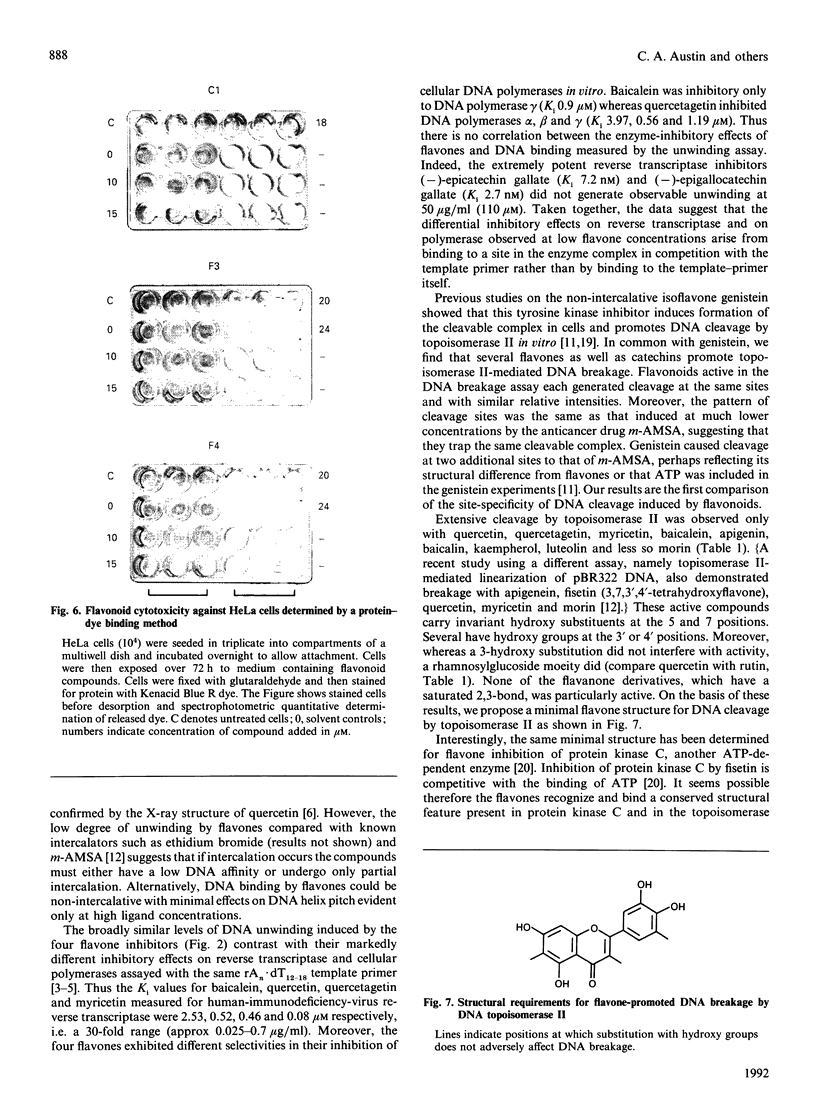
Abstract
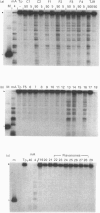
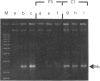
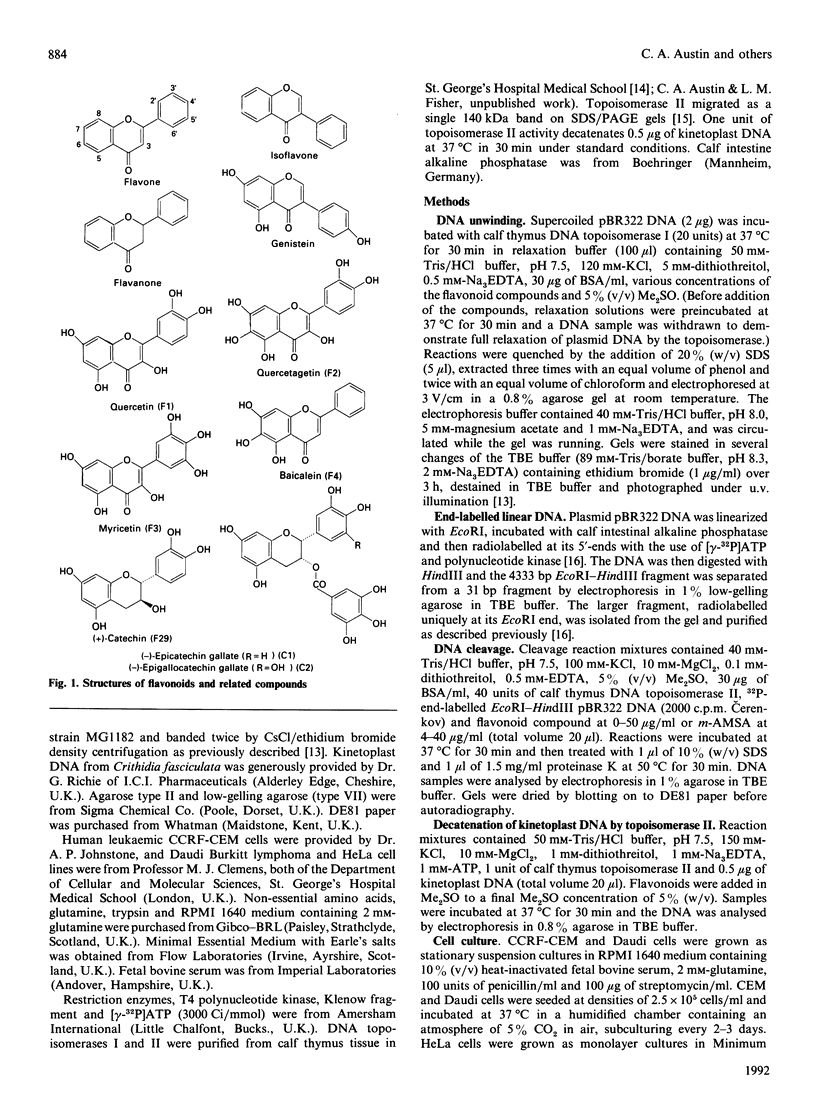
Four naturally occurring flavones (baicalein, quercetin, quercetagetin and myricetin) and two novel catechins [(-)-epicatechin gallate and (-)-epigallocatechin gallate, from the tea plant Camellia sinensis], which are known inhibitors of reverse transcriptase, were shown to induce mammalian topoisomerase II-dependent DNA-cleavage in vitro. The flavones differed from the catechins in causing unwinding of duplex DNA, but both classes of compound induced enzymic DNA breakage at the same sites on DNA. Moreover, the cleavage specificity was the same as that for the known intercalator 4'-(acridin-9-ylamino)methanesulphon-m-anisidide, suggesting that these agents trap the same cleavable complex. Analysis of some 30 flavonoid compounds allowed elucidation of the structure-function relationships for topoisomerase II-mediated DNA cleavage. For flavonoid inhibitors an unsaturated double bond between positions 2 and 3 of the pyrone ring and hydroxy groups at the 5, 7, 3' and 4' positions favoured efficient cleavage. Hydroxy substitutions could be tolerated at the 3, 6 and 5' positions. Indeed, the absence of substituents at the 3', 4' and 5' positions could be compensated by a hydroxy group at position 6 (baicalein). Similar requirements have been reported for flavonoid inhibitors of protein kinase C that act competitively with ATP, suggesting interaction with a conserved protein feature. Formation of the cleavable complex is a cytotoxic lesion that may contribute to the growth-inhibitory properties of flavones observed for three human tumour cell lines. These results are discussed in regard to the selectivity of antiviral agents.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin C. A., Barot H. A., Margerrison E. E., Turcatti G., Wingfield P., Hayes M. V., Fisher L. M. Structure and partial amino acid sequence of calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II: comparison with other type II enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):763–768. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92156-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arpa P., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 17;989(2):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferriola P. C., Cody V., Middleton E., Jr Protein kinase C inhibition by plant flavonoids. Kinetic mechanisms and structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1617–1624. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M., Barot H. A., Cullen M. E. DNA gyrase complex with DNA: determinants for site-specific DNA breakage. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1411–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Sakai T. T. Interaction of bleomycin A2 with deoxyribonucleic acid: DNA unwinding and inhibition of bleomycin-induced DNA breakage by cationic thiazole amides related to bleomycin A2. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3199–3207. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The effect of quercetin on the phosphorylation activity of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):583–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox P., Uphill P. F., Fry J. R., Benford J., Balls M. The FRAME multicentre project on in vitro cytotoxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 1986 Jun-Jul;24(6-7):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(86)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovits J., Linassier C., Fossé P., Couprie J., Pierre J., Jacquemin-Sablon A., Saucier J. M., Le Pecq J. B., Larsen A. K. Inhibitory effects of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein on mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 15;49(18):5111–5117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane H., Ono K. Differential inhibitory effects of some catechin derivatives on the activities of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase and cellular deoxyribonucleic and ribonucleic acid polymerases. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2841–2845. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Nakane H., Fukushima M., Chermann J. C., Barré-Sinoussi F. Differential inhibition of the activities of reverse transcriptase and various cellular DNA polymerases by a traditional Kampo drug, sho-saiko-to. Biomed Pharmacother. 1990;44(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0753-3322(90)90063-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Nakane H., Fukushima M., Chermann J. C., Barré-Sinoussi F. Differential inhibitory effects of various flavonoids on the activities of reverse transcriptase and cellular DNA and RNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):469–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Nakane H., Fukushima M., Chermann J. C., Barré-Sinoussi F. Inhibition of reverse transcriptase activity by a flavonoid compound, 5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):982–987. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Nakane H. Mechanisms of inhibition of various cellular DNA and RNA polymerases by several flavonoids. J Biochem. 1990 Oct;108(4):609–613. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Kawada S., Nakano H. Induction of mammalian topoisomerase II dependent DNA cleavage by nonintercalative flavonoids, genistein and orobol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 15;39(4):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90153-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]