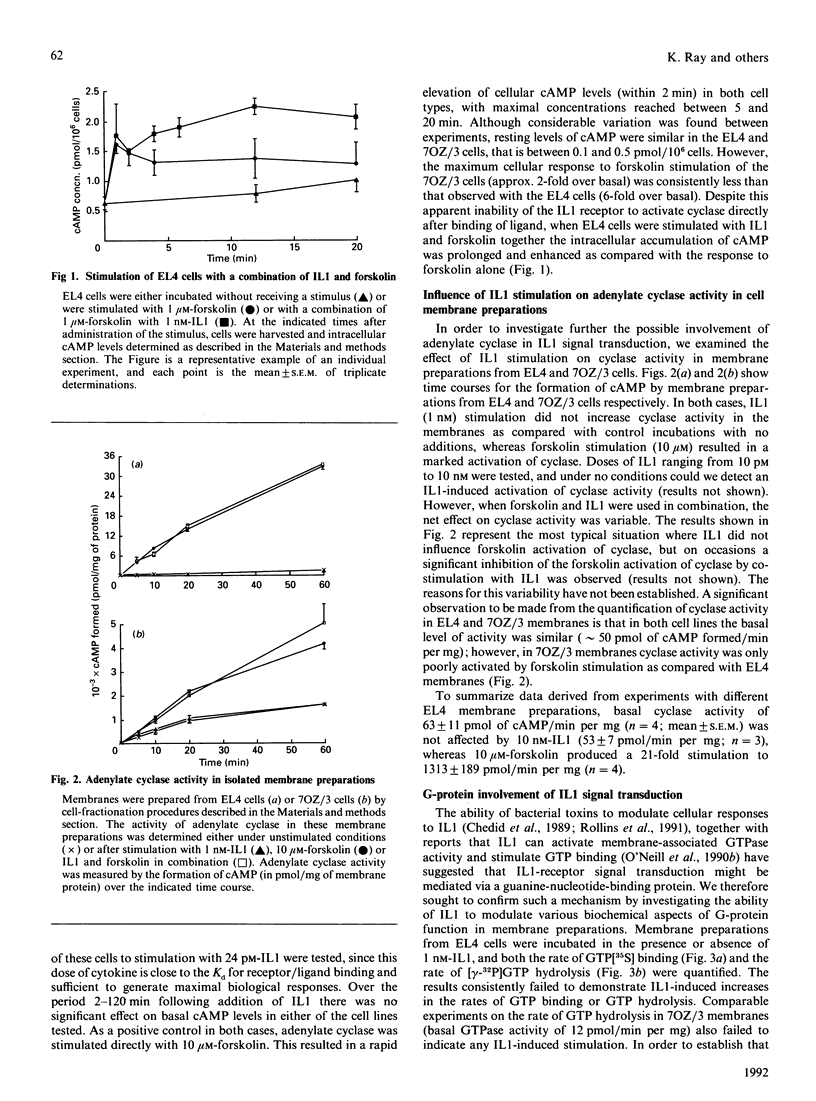
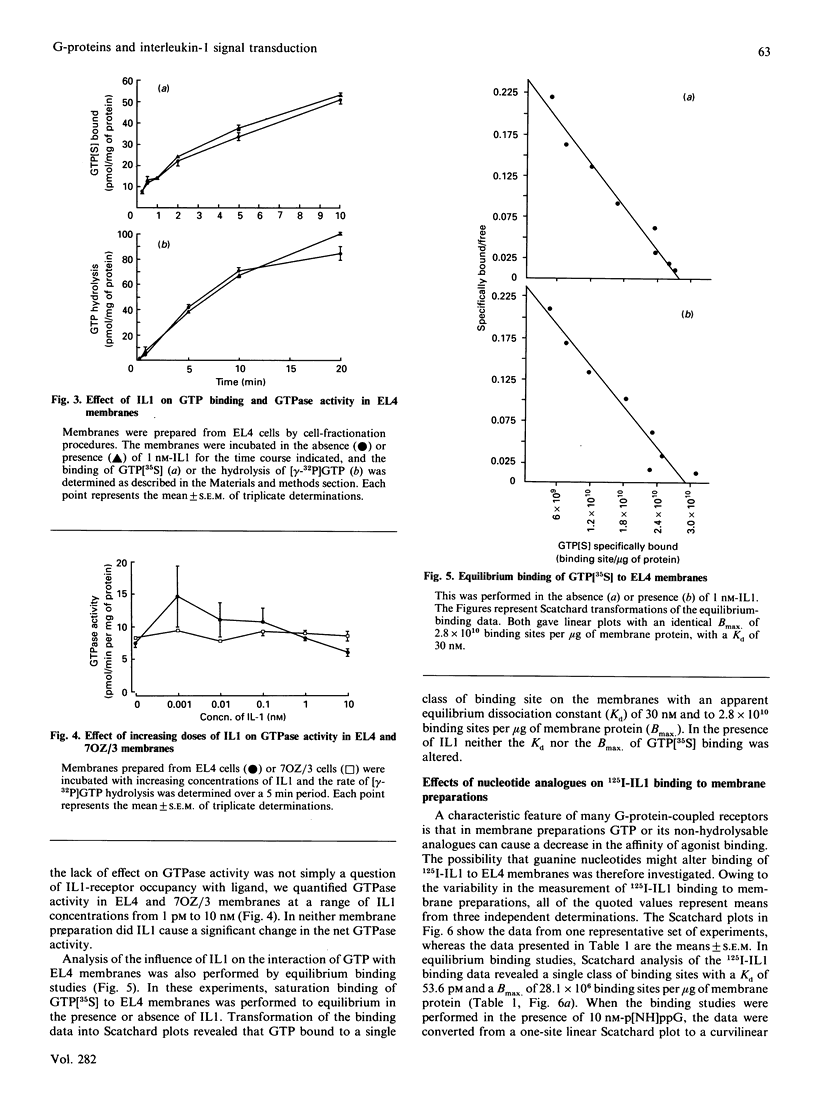
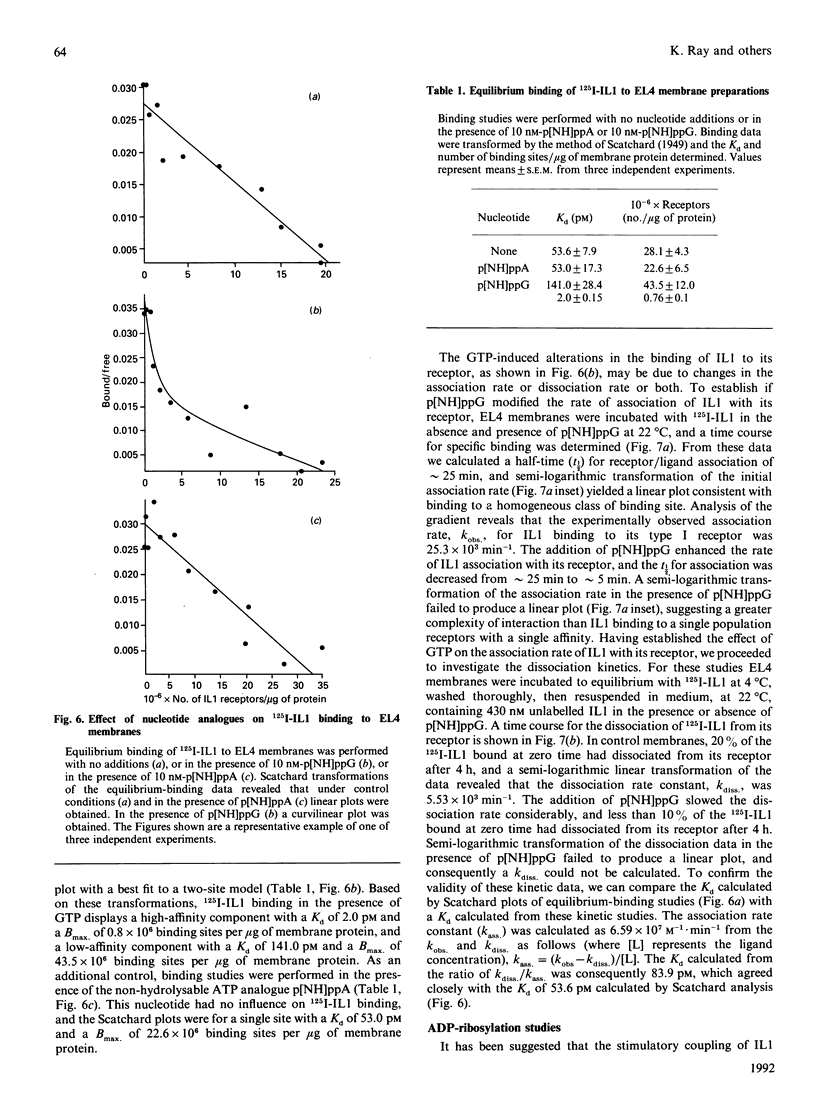
Abstract
The involvement of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins (G-proteins) and regulation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in interleukin 1 (IL1) signal transduction has been investigated in EL4 and 7OZ/3 cells expressing Type 1 and Type 2 IL1 receptors respectively. Results show that in both cell types IL1 alone failed to induce changes in cellular cAMP levels, and in membrane preparations the cytokine had no significant effect on adenylate cyclase activity. In contrast, forskolin stimulated cAMP levels in cells and membranes. IL1 did not significantly alter GTPase activity or rate of guanosine 5'-[gamma-[35S]thio]triphosphate binding measured in membrane preparations from the EL4 and 7OZ/3 cells. In EL4-cell membrane preparations the kinetics of 125I-IL1 binding were altered in the presence of guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate, resulting in the formation of a higher-affinity state for IL1 binding. Adenosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate at the same concentration was without effect. These results suggest that IL1 receptor function may be regulated by guanine nucleotides; however, the mechanism appears to differ from that exhibited by conventional G-protein-linked receptors. The lack of significant effects of IL1 on cAMP metabolism in these cells suggests that alternative pathways must exist to mediate the intracellular responses to stimulation via both types of the IL1 receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham R. T., Ho S. N., Barna T. J., McKean D. J. Transmembrane signaling during interleukin 1-dependent T cell activation. Interactions of signal 1- and signal 2-type mediators with the phosphoinositide-dependent signal transduction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2719–2728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. Down-modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity in fibroblasts treated with interleukin 1 or tumor necrosis factor is associated with phosphorylation at a site other than threonine 654. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. IL-1 and TNF transmodulate epidermal growth factor receptors by a protein kinase C-independent mechanism. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):126–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. Identification of a common class of high affinity receptors for both types of porcine interleukin-1 on connective tissue cells. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):263–266. doi: 10.1038/324263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Sims J. E., Stanton T. H., Slack J., McMahan C. J., Valentine M. A., Dower S. K. Evidence for different interleukin 1 receptors in murine B- and T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8034–8038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Toivola B., Emery D. W., Rooney J. W., Dower S. K., Rachie N. A., Sibley C. H. Role of cAMP in interleukin-1-induced kappa light chain gene expression in murine B cell line. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9413–9417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., White M. F., Connor J. R. Interleukin 1 stimulates prostaglandin synthesis and cyclic AMP accumulation in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: interactions between two second messenger systems. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid M., Shirakawa F., Naylor P., Mizel S. B. Signal transduction pathway for IL-1. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein in the activation of adenylate cyclase. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4301–4306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R., Truitt T., Kilian P. L., Stern A. S., Nunes P., Parker K. P., Kaffka K. L., Chua A. O., Lugg D. K., Gubler U. Two high-affinity interleukin 1 receptors represent separate gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8029–8033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey S. J., Rosoff P. M. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor primes neutrophils by activating a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein not associated with phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14165–14171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Gallis B., Overell R. W., McMahan C. J., DeRoos P., Ireland R., Eisenman J., Dower S. K., Sims J. E. T-cell interleukin 1 receptor cDNA expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells regulates functional responses to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Gallis B., Overell R. W., McMahan C. J., DeRoos P., Ireland R., Eisenman J., Dower S. K., Sims J. E. T-cell interleukin 1 receptor cDNA expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells regulates functional responses to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier M., Aussel C., Pelassy C., Fehlmann M. IL-1 signaling for IL-2 production in T cells involves a rise in phosphatidylserine synthesis. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3078–3080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson P. R., Skjodt H., Plested C. P., Short A. D., Virdee K., Russell R. G., Brown B. L. Interleukin-1 stimulates diglyceride accumulation in the absence of protein kinase C activation. Regul Pept. 1990 Jul 30;29(2-3):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Kronheim S. R., Hopp T. P., Cantrell M., Deeley M., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Urdal D. L. The cell surface receptors for interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta are identical. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):266–268. doi: 10.1038/324266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka M., Taii S., Yasuda K., Takakura K., Mori T. Inhibitory effects of interleukin-1 on luteinizing hormone-stimulated adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate accumulation by cultured porcine granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Jul;125(1):136–143. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-1-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Făgărăan M. O., Bishop J. F., Rinaudo M. S., Axelrod J. Interleukin 1 induces early protein phosphorylation and requires only a short exposure for late induced secretion of beta-endorphin in a mouse pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2555–2559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Leof E. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 treatment of AKR-2B cells is coupled through a pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein(s). Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):879–886. doi: 10.1042/bj2610879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Neer E. J. Subunit interactions of native and ADP-ribosylated alpha 39 and alpha 41, two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1105–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulkower K. I., Georgscu H. I., Evans C. H. Altered patterns of protein phosphorylation in articular chondrocytes treated with interleukin-1 or synovial cytokines. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Yagisawa H., Yamashita K., Yamaguchi Y., Akiyama Y. IL1 induces proliferation and IL6 mRNA expression in a human astrocytoma cell line: positive and negative modulation by chorela toxin and cAMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1242–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90657-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., Welch W. J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor increase phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein. Effects in fibroblasts, Hep G2 and U937 cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 4;258(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81671-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian P. L., Kaffka K. L., Stern A. S., Woehle D., Benjamin W. R., Dechiara T. M., Gubler U., Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Lomedico P. T. Interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta bind to the same receptor on T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4509–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton J. D., Pfeilschifter J. Interleukin 1- and tumor necrosis factor-stimulation of prostaglandin E2 synthesis in MDCK cells, and potentiation of this effect by cycloheximide. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80029-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. How does interleukin 1 activate cells? Cyclic AMP and interleukin 1 signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):390–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. The interleukins. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2379–2388. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muegge K., Williams T. M., Kant J., Karin M., Chiu R., Schmidt A., Siebenlist U., Young H. A., Durum S. K. Interleukin-1 costimulatory activity on the interleukin-2 promoter via AP-1. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):249–251. doi: 10.1126/science.2799385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Beutner U., Zubiaga A., Huber B. T. IL-1 activates two separate signal transduction pathways in T helper type II cells. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):964–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill L. A., Bird T. A., Gearing A. J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin-1 signal transduction. Increased GTP binding and hydrolysis in membranes of a murine thymoma line (EL4). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3146–3152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill L. A., Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. How does interleukin 1 activate cells? Interleukin 1 signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):392–394. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Katada T., Murayama Y., Ui M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. A simple structure encodes G protein-activating function of the IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90116-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski J., Meier K. E., Stanton T. H., Smith L. L., Bomsztyk K. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-1 alpha induce transient translocation of protein kinase C activity to membranes in a B lymphoid cell line. Evidence for a protein kinase C-independent pathway in lymphokine-induced cytoplasmic alkalinization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13786–13790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint D. J., Bolton E. J., McNamee L. A., Solari R., Hissey P. H., Champion B. R., MacKenzie A. R., Zanders E. D. Functional and phenotypic analysis of human T-cell clones which stimulate IgE production in vitro. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):68–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Wyche A., Needleman P. Temporal and pharmacological division of fibroblast cyclooxygenase expression into transcriptional and translational phases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1657–1661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkonen R., Mattila P., Häyry P., Ustinov J. Interleukin 1-induced lymphocyte binding to endothelial cells. Role of cAMP as a second messenger. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jul;20(7):1563–1567. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodan S. B., Wesolowski G., Chin J., Limjuco G. A., Schmidt J. A., Rodan G. A. IL-1 binds to high affinity receptors on human osteosarcoma cells and potentiates prostaglandin E2 stimulation of cAMP production. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1231–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins P., Witham S., Ray K., Thompson N., Sadler H., Smithers N., Grenfell S., Solari R. Modification of biological responses to interleukin-1 by agents that perturb signal transduction pathways. Cytokine. 1991 Jan;3(1):42–53. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi N., Kishimoto T., Kikutani H., Watanabe T., Yoshida N., Shimizu A., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Honjo T., Yamamura Y. Induction and regulation of immunoglobulin expression in a murine pre-B cell line, 70Z/3. I. Cell cycle-associated induction of sIgM expression and kappa-chain synthesis in 70Z/3 cells by LPS stimulation. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2654–2659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Yamashita U., Chedid M., Mizel S. B. Cyclic AMP--an intracellular second messenger for interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8201–8205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroo M., Matsushima K. Enhanced phosphorylation of 65 and 74 kDa proteins by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cytokine. 1990 Jan;2(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90038-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari R. Identification and distribution of two forms of the interleukin 1 receptor. Cytokine. 1990 Jan;2(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90039-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijelath E. S., Kardasz A. M., Drummond R., Watson J. Interleukin-one induced inositol phospholipid breakdown in murine macrophages: possible mechanism of receptor activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):392–397. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80726-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]