Abstract
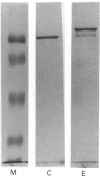
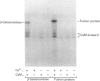
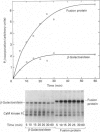
The Na+/H+ exchanger is a pH-regulatory protein that extrudes one H+ ion in exchange for one Na+ ion when intracellular pH declines. A number of studies have shown phorbol ester stimulation of activity in intact cells, leading to the idea that the exchanger is regulated by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation in vivo. cDNA encoding the protein has been cloned, and a recent model suggests a large internal cytoplasmic C-terminal domain that may be a site of regulation of the exchanger [Sardet, Franchi & Pouyssegur (1989) Cell 56, 271-280]. We examined this region of the protein using a rabbit cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger cDNA clone. cDNA of the Na+/H+ exchanger, coding for the C-terminal 178 amino acid residues, was cloned into the expression vector pEX-1 and expressed as a fusion protein with beta-galactosidase. The fusion protein reacted with an antibody produced against a synthetic peptide of the C-terminal 13 amino acid residues of the Na+/H+ exchanger, confirming the identity of the expressed protein. Control and experimental pEX-1-Na+/H+ exchanger protein was purified on a p-aminophenyl beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside-agarose column. Purified Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II readily phosphorylated the Na+/H+ exchanger protein in a Ca(2+)- and calmodulin-dependent manner in vitro, but this region of the protein was not a substrate for purified protein kinase C or for the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Control-expressed beta-galactosidase was phosphorylated to a maximal level of 0.77 +/- 0.17 mol of Pi/mol (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 6) whereas the fusion protein was phosphorylated to a maximal level of 4.09 +/- 0.39 mol of Pi/mol (n = 6), suggesting one site of phosphorylation in beta-galactosidase and three in the C-terminal domain of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Examination of the deduced amino acid sequence of this part of the exchanger reveals three consensus sequences for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. These results suggest that the exchanger may be directly regulated in vivo by calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II but not by protein kinase C or cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber D. L., McGuire M. E., Ganz M. B. Beta-adrenergic and somatostatin receptors regulate Na-H exchange independent of cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21038–21042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Aronow M. S., Brock T. A., Cragoe E., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Angiotensin II-stimulated Na+/H+ exchange in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5057–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Reinlib L., Watson A. J., Gorelick F., Rys-Sikora K., Tse M., Rood R. P., Czernik A. J., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Rabbit ileal villus cell brush border Na+/H+ exchange is regulated by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, a brush border membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8990–8994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaille J. G., Peters K. A., Fischer E. H. Isolation and properties of the rabbit skeletal muscle protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3080–3086. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Burns K., Opas M., Michalak M. The high-affinity calcium binding protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Tissue distribution, and homology with calregulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 26;982(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Leberer E., Green N. M., MacLennan D. H. The fast-twitch muscle calsequestrin isoform predominates in rabbit slow-twitch soleus muscle. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Barr A. Identification of the protein and cDNA of the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80241-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. V., Zabin I. The amino acid sequence of beta-galactosidase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1507–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. D., Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. The activity of the Na+/H+ antiporter in cultured cardiac cells is dependent on the culture conditions used. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendey B., Mamrack M. D., Putnam R. W. Thrombin induces a calcium transient that mediates an activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19540–19547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Moore J. P., Morris J. D., Taylor M. V., Rogers J., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. A common sequence of calcium and pH signals in the mitogenic stimulation of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):481–484. doi: 10.1038/313481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogue D., Michalak M., Fliegel L. The role of ion antiporters in the maintenance of intracellular pH in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;102(2):125–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00234570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Cogan M. G., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Ives H. E. Thrombin activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger in vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for a kinase C-independent pathway which is Ca2+-dependent and pertussis toxin-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14134–14140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Dolson G. M., Hise M. K., Bennett S. C., Weinman E. J. Parathyroid hormone and dibutyryl cAMP inhibit Na+/H+ exchange in renal brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F212–F218. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. J., Weissberg P. L., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Bobik A. Dependence of Na+/H+ antiport activation in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle on calmodulin, calcium, and ATP. Evidence for the involvement of calmodulin-dependent kinases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16780–16786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak M., Fliegel L., Wlasichuk K. Isolation and characterization of calcium binding glycoproteins of cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5869–5874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell G., Steplock D., Shenolikar S., Weinman E. J. Identification of a putative Na(+)-H+ exchanger regulatory cofactor in rabbit renal BBM. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F867–F871. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon L. L., Dinerstein R. J., Villereal M. L. Intracellular pH in human fibroblasts: effect of mitogens, A23187, and phospholipase activation. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):C140–C148. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.1.C140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Knapik J., Strebel F., Tarpley W. G., Gorman R. R. Regulation of Na+-H+ exchange in normal NIH-3T3 cells and in NIH-3T3 cells expressing the ras oncogene. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C756–C763. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood R. P., Emmer E., Wesolek J., McCullen J., Husain Z., Cohen M. E., Braithwaite R. S., Murer H., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Regulation of the rabbit ileal brush-border Na+/H+ exchanger by an ATP-requiring Ca++/calmodulin-mediated process. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI113665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Bertrand W., Morrison A. A photoactivatable probe for the Na+/H+ exchanger cross-links a 66-kDa renal brush border membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5341–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiporter, glycoprotein of 110 kD. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.2154036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Woo G. C., Sutherland C., Walsh M. P. Kinase activity associated with caldesmon is Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):367–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2680367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villereal M. L. Sodium fluxes in human fibroblasts: effect of serum, Ca+2, and amiloride. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Jun;107(3):359–369. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041070307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Hinkins S., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J. Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:279–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Fisher K., Steplock D., Dinh Q., Chang L., Shenolikar S. Regulation of reconstituted renal Na+/H+ exchanger by calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;103(3):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01993983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Shenolikar S. Reconstitution of cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulated renal Na+-H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1988;101(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01872815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S., Kahn A. M. cAMP-associated inhibition of Na+-H+ exchanger in rabbit kidney brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):F19–F25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.1.F19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissberg P. L., Little P. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Bobik A. The pH of spontaneously beating cultured rat heart cells is regulated by an ATP-calmodulin-dependent Na+/H+ antiport. Circ Res. 1989 Apr;64(4):676–685. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder S., Walsh M. Inhibition of the actomyosin MgATPase by chicken gizzard calponin. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;327:141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Interaction of protein kinase C with membranes is regulated by Ca2+, phorbol esters, and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15718–15722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]