Abstract
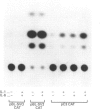
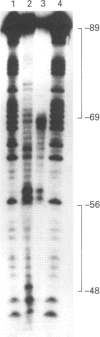
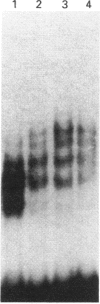
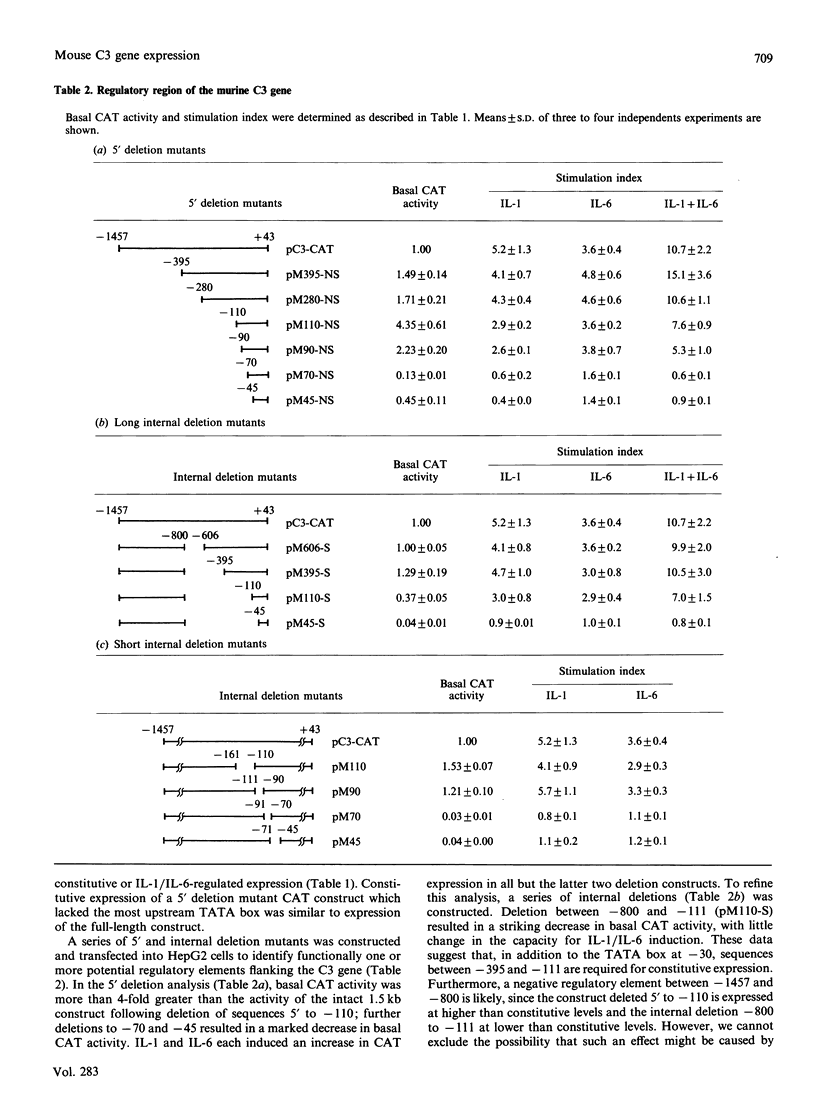
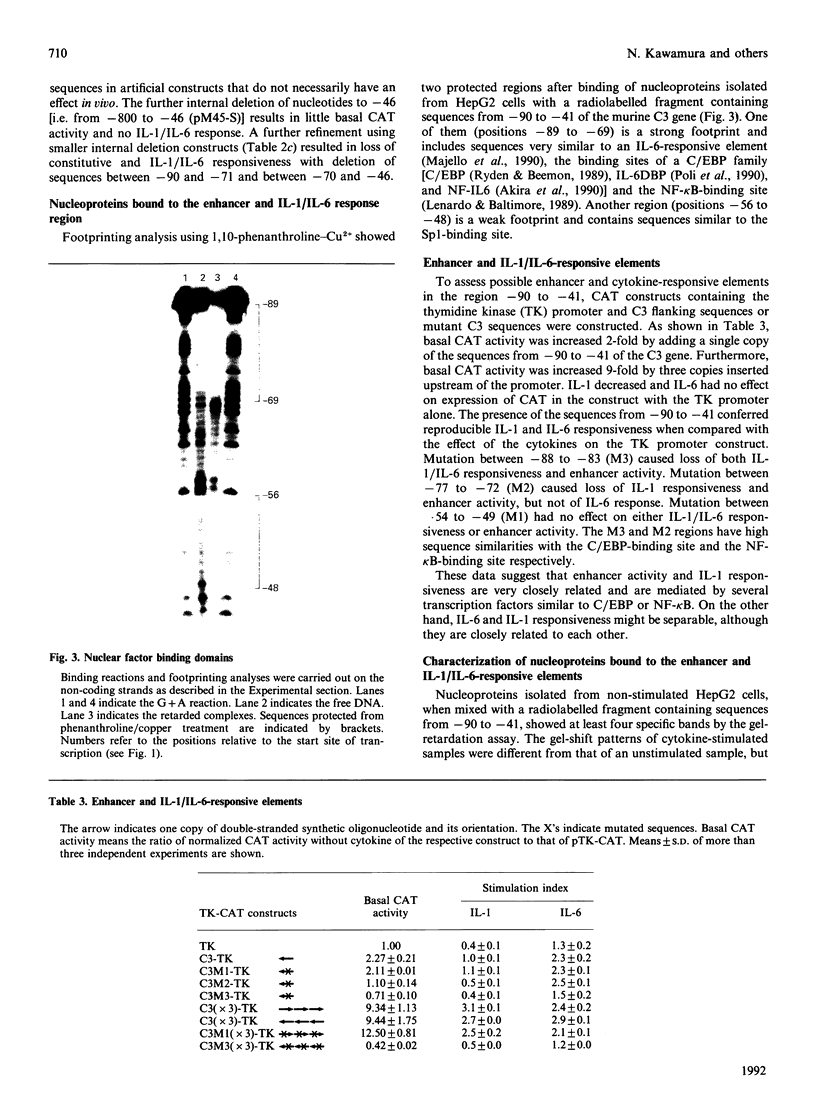
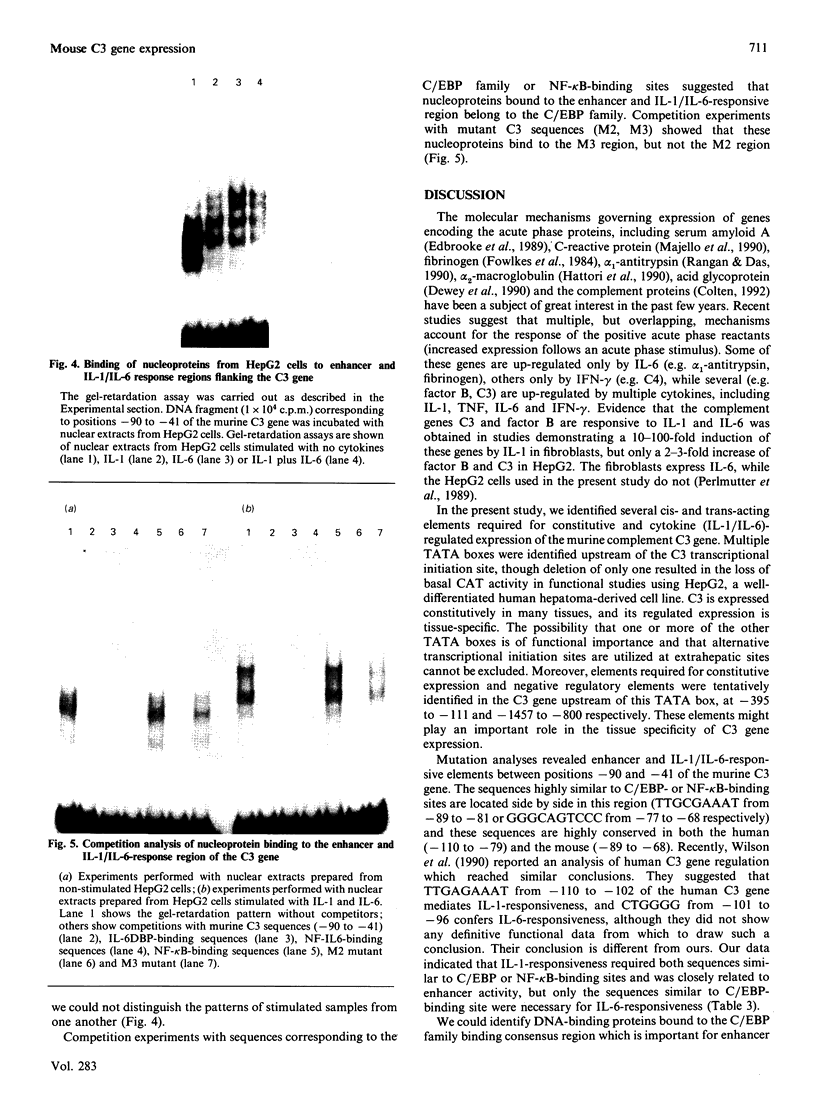
The third component of complement (C3) is an important mediator of inflammation. Murine and human genomic cosmid clones were isolated, characterized and sequenced 5' to the complement C3 gene transcriptional initiation sites to determine cis elements that participate in constitutive and regulated C3 gene expression. The murine and human 5' flanking regions are 51% identical overall, with positions -36 to -1 and -146 to -68 showing 80% identity. Four TATA boxes were identified upstream of the murine transcriptional initiation site, but deletion and transfection analysis using reporter gene constructs in HepG2 cells indicated that only the TATA element at position -30, together with sequences -395 to -111, are essential for constitutive expression of murine C3 in hepatocytes. Deletion analysis also suggested that sequences between -1457 and -800 contain regulatory elements that are involved in suppressing basal expression. Sequences between -90 to -41 confer both enhancer activity and interleukin-1/-6 (IL-1/IL-6)-responsiveness. Mutation analyses showed that both sequences between -88 and -83 and -77 to -72 are essential for enhancer activity and responsiveness to IL-1, but only sequences between -88 and -83 are necessary for IL-6-responsiveness. A gel-retardation assay showed that several nucleoproteins, perhaps of the C/EBP family, from HepG2 cells bound to sequences between -88 to -83. Collectively, these results localize cis-acting elements involved in constitutive and IL-1/IL-6-regulated murine C3 gene expression and provide evidence for specific transacting factors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Johnson A. M., Birtch A. G., Moore F. D. Human C'3: evidence for the liver as the primary site of synthesis. Science. 1969 Jan 17;163(3864):286–288. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3864.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Dierich M. P., Mūller-Eberhard H. J. Third component of complement (C3): structural properties in relation to functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade V., Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of pro-C3, a precursor of the third component of complement. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):759–765. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Ron D., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. A family of constitutive C/EBP-like DNA binding proteins attenuate the IL-1 alpha induced, NF kappa B mediated trans-activation of the angiotensinogen gene acute-phase response element. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3933–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Tissue-specific regulation of inflammation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jan;72(1):1–7. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva F. P., Hoecker G. F., Day N. K., Vienne K., Rubinstein P. Murine complement component 3: genetic variation and linkage to H-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):963–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey M. J., Rheaume C., Berger F. G., Baumann H. Inducible and tissue-specific expression of rat alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4392–4398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Burt D. W., Cheshire J. K., Woo P. Identification of cis-acting sequences responsible for phorbol ester induction of human serum amyloid A gene expression via a nuclear factor kappaB-like transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1908–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein L. P., Hansen P. J., Ballow M., Davis A. E., 3rd, Davis J. S., 4th, Alper C. A., Rosen F. S., Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of the third component of complement (C3) in vitro by monocytes from both normal and homozygous C3-deficient humans. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):963–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI108876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falus A., Beuscher H. U., Auerbach H. S., Colten H. R. Constitutive and IL 1-regulated murine complement gene expression is strain and tissue specific. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):856–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong K. Y., Botto M., Walport M. J., So A. K. Genomic organization of human complement component C3. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):579–586. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Mullis N. T., Comeau C. M., Crabtree G. R. Potential basis for regulation of the coordinately expressed fibrinogen genes: homology in the 5' flanking regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2313–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger G., Thomas M. L., Tack B. F., Williams J., Colten H. R., Abraham G. N. NH2-terminal structure and cleavage of guinea pig pro-C3, the precursor of the third complement component. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12617–12619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Kikuchi N., Ikenaka T., Inoue K. Structures of sugar chains of the third component of human complement. J Biochem. 1985 Oct;98(4):863–874. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Abraham L. J., Northemann W., Fey G. H. Acute-phase reaction induces a specific complex between hepatic nuclear proteins and the interleukin 6 response element of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2364–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima M., Tobe T., Sakamoto T., Tomita M. Biosynthesis of the internal thioester bond of the third component of complement. J Biochem. 1984 Nov;96(5):1539–1546. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Strunk R. C. Synovial fibroblast-like cells synthesize seven proteins of the complement system. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Erickson B. W. An equilibrium model of the metastable binding sites of alpha 2-macroglobulin and complement proteins C3 and C4. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11864–11867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D., Zimmermann R., Heisig M., Heinrich P. C. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the interleukin-6 dependent expression of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1121–1138. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundwall A., Wetsel R. A., Domdey H., Tack B. F., Fey G. H. Structure of murine complement component C3. I. Nucleotide sequence of cloned complementary and genomic DNA coding for the beta chain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13851–13856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Mallat M. Primary cultures of murine astrocytes produce C3 and factor B, two components of the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Constitutive and IL-6-induced nuclear factors that interact with the human C-reactive protein promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):457–465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. The estrogen-responsive element as an inducible enhancer: DNA sequence requirements and conversion to a glucocorticoid-responsive element. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3719–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Gitlin J. D., Colten H. R. Regulation of human and murine complement: comparison of 5' structural and functional elements regulating human and murine complement factor B gene expression. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;89(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00228274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J., Schreiner G. F., Nonaka M., Beuscher H. U., Colten H. R. Local extrahepatic expression of complement genes C3, factor B, C2, and C4 is increased in murine lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1676–1684. doi: 10.1172/JCI113780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R., Adams S. P., May L. T., Sehgal P. B., Fallon R. J. A cytokine-selective defect in interleukin-1 beta-mediated acute phase gene expression in a subclone of the human hepatoma cell line (HEPG2). J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7669–7674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangan V. S., Das G. C. Purification and biochemical characterization of hepatocyte nuclear factor 2 involved in liver-specific transcription of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8874–8879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Colten H. R. Rheumatoid arthritis. Biosynthesis of complement proteins by synovial tissues. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1284–1288. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Kugler W., Wagner U., Kaling M. Liver cell specific gene transcription in vitro: the promoter elements HP1 and TATA box are necessary and sufficient to generate a liver-specific promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):939–953. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer V. L., Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. A wide variety of DNA sequences can functionally replace a yeast TATA element for transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):636–645. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher V. J., Thorbecke G. J. Sites of synthesis of serum proteins. OI. Serum proteins produced by macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):643–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Eidlen D. M., Mason R. J. Pulmonary alveolar type II epithelial cells synthesize and secrete proteins of the classical and alternative complement pathways. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1172/JCI113472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. E., Peterlin B. M. Transcriptional enhancers in the HLA-DQ subregion. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3315–3319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom S. A., Komm B. S., Ponce-de-Leon H., Yi Z., Teuscher C., Lyttle C. R. Estrogen regulation of tissue-specific expression of complement C3. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16941–16947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomana M., Niemann M., Garner C., Volanakis J. E. Carbohydrate composition of the second, third and fifth components and factors B and D of human complement. Mol Immunol. 1985 Feb;22(2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(85)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik D. P., Amiguet P., Moffat G. J., Fey M., Amiguet-Barras F., Wetsel R. A., Tack B. F. Structural features of the human C3 gene: intron/exon organization, transcriptional start site, and promoter region sequence. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1080–1085. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Geihl D. K., Choudhury G. G., Minter A., Martinez L., Weber D. K., Sakaguchi A. Y. Site-directed deletion mutagenesis using phagemid vectors and genetic selection. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):1000-6, 1008-10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. B., Pantazis P., Davies P. F. The third component of complement is transcribed and secreted by cultured human endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):9–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Fleischer D. T., Haviland D. L. Deficiency of the murine fifth complement component (C5). A 2-base pair gene deletion in a 5'-exon. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2435–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Lundwall A., Davidson F., Gibson T., Tack B. F., Fey G. H. Structure of murine complement component C3. II. Nucleotide sequence of cloned complementary DNA coding for the alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13857–13862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Solomon E., Chambers S., Bodmer W. F., Povey S., Fey G. Assignment of the structural gene for the third component of human complement to chromosome 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Juan T. S., Wilde M. D., Fey G. H., Darlington G. J. A 58-base-pair region of the human C3 gene confers synergistic inducibility by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6181–6191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won K. A., Baumann H. NF-AB, a liver-specific and cytokine-inducible nuclear factor that interacts with the interleukin-1 response element of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3001–3008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. C., Morley B. J., Campbell R. D. Cell-specific expression of the human complement protein factor B gene: evidence for the role of two distinct 5'-flanking elements. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]