Abstract
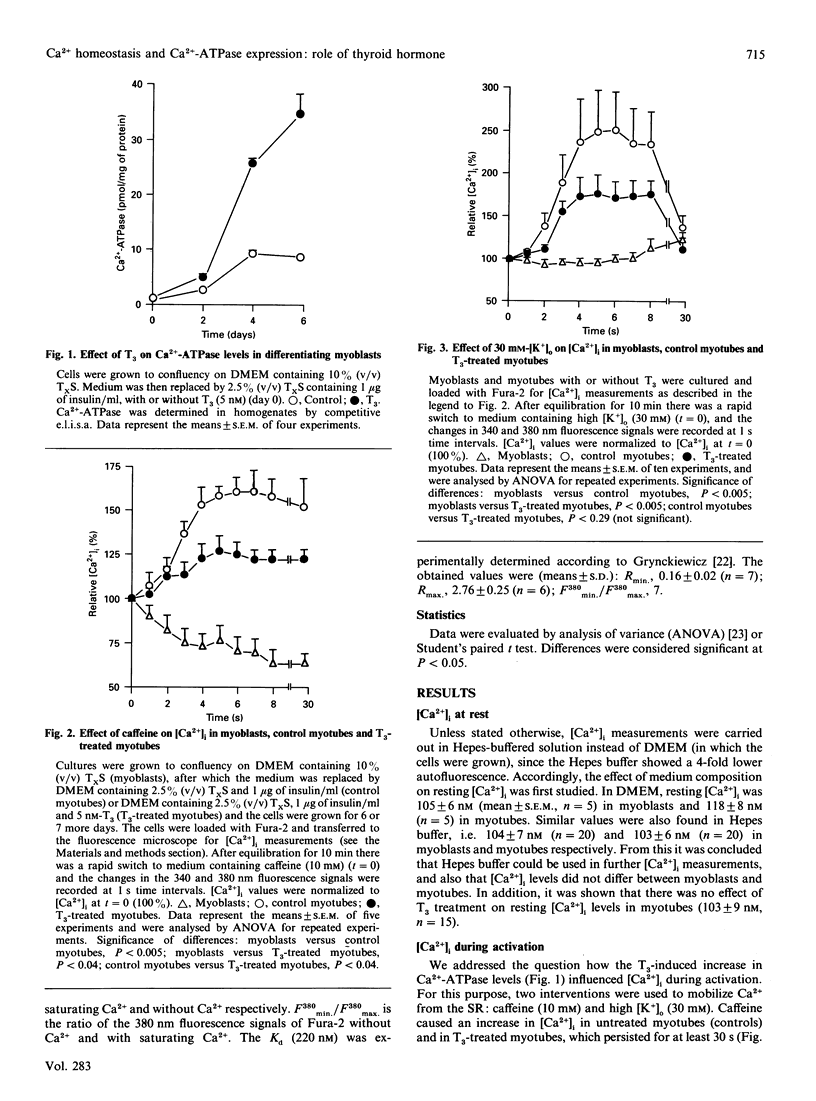
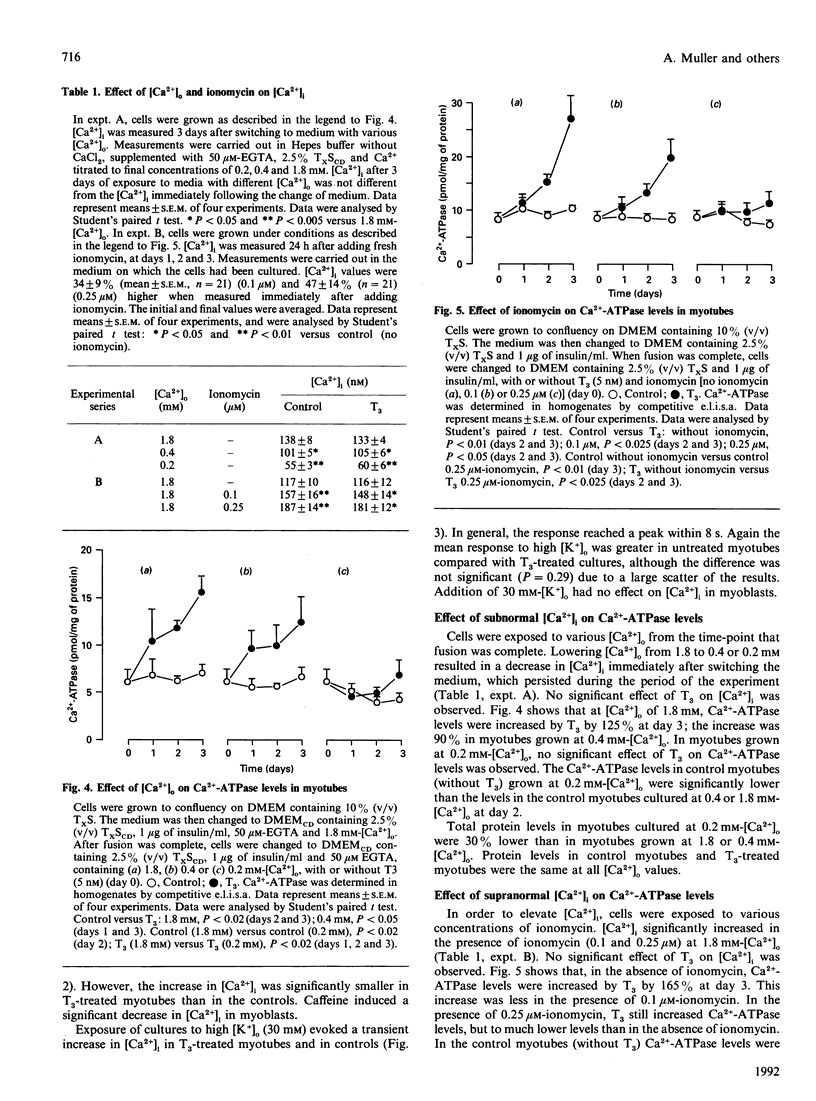
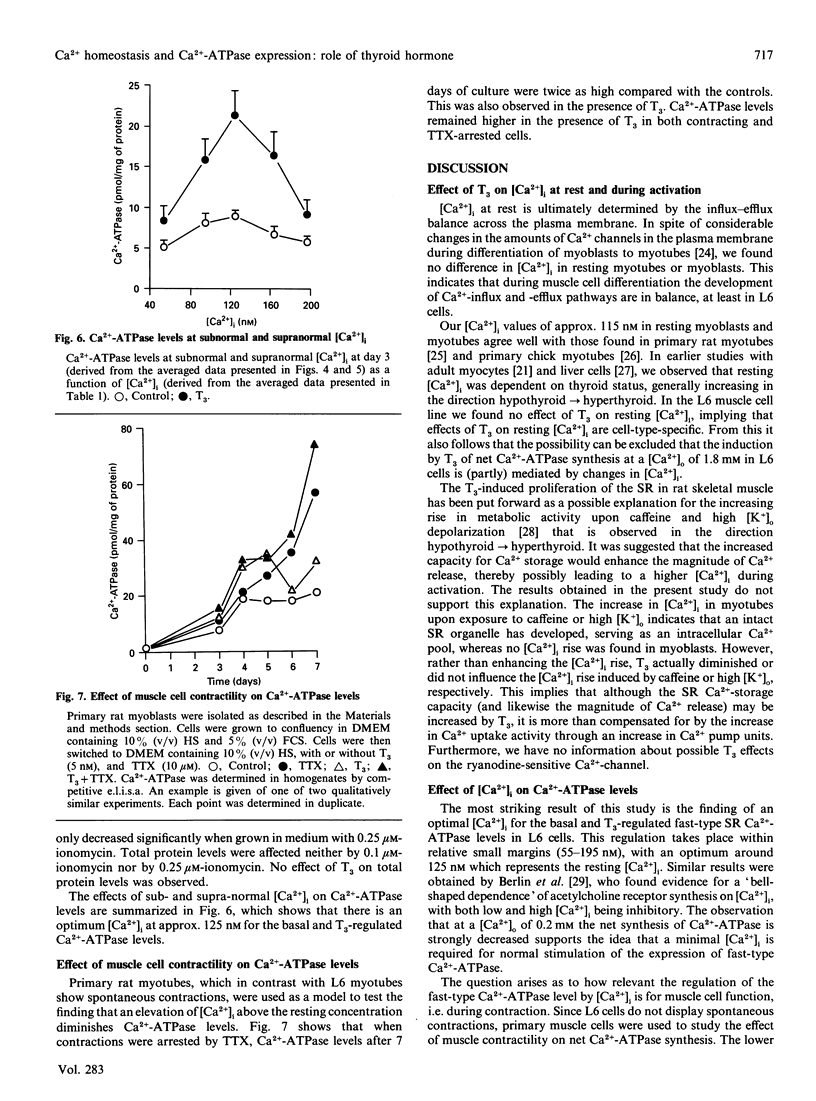
The effect of thyroid hormone (L-tri-iodothyronine; T3) on the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in L6 myotubes was studied at rest and during activation to explore the possible mediating role of [Ca2+]i in the T3-induced net synthesis of fast-type sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+)-ATPase. The mean [Ca2+]i at rest was approx. 115 nM in myoblasts, control myotubes and T3-treated myotubes. Therefore it is unlikely that the T3-induced elevation of Ca(2+)-ATPase levels is mediated by [Ca2+]i changes. To investigate the influence of the 4-fold higher Ca(2+)-ATPase levels in T3-treated myotubes (compared with controls) on [Ca2+]i, interventions with caffeine (10 mM) and a high extracellular K+ concentration ([K+]o) (30 mM) were applied which initially mobilize Ca2+ predominantly from the SR. The results showed a lower (caffeine) or not significantly different (high [K+]o) increase in [Ca2+]i in T3-treated myotubes compared with controls. No rise in [Ca2+]i was found in myoblasts with caffeine or high [K+]o. The role of [Ca2+]i in the regulation of Ca(2+)-ATPase levels was investigated by varying [Ca2+]i through exposure of cells to different concentrations of extracellular Ca2+ (0.2-1.8 mM) and ionomycin (0.1-0.25 microM). At subnormal [Ca2+]i (55 nM) the T3-induced net synthesis of Ca(2+)-ATPase was virtually abolished, and at supranormal [Ca2+]i (195 nM) it was greatly depressed. Intermediate stimulation of net Ca(2+)-ATPase synthesis was found at [Ca2+]i of 95 and 165 nM, with an optimum at approx. 125 nM. Similar but less pronounced effects were found for the basal Ca(2+)-ATPase levels. In contracting primary rat myotubes, Ca(2+)-ATPase levels were significantly lower than in tetrodotoxin-arrested myotubes. The same results were obtained in the presence of T3. Since the mean [Ca2+]i in contracting cells is higher than in resting cells, these data agree with those obtained in the L6 cells with ionomycin. A major conclusion of this study is the existence of a [Ca2+]i optimum, near resting levels, for the expression of the fast-type Ca(2+)-ATPase in the L6 muscle cell line.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beekman R. E., van Hardeveld C., Simonides W. S. Thyroid status and beta-agonistic effects on cytosolic calcium concentrations in single rat cardiac myocytes activated by electrical stimulation or high-K+ depolarization. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):563–569. doi: 10.1042/bj2680563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Wozniak M. A., Cannell M. B., Bloch R. J., Lederer W. J. Measurement of intracellular Ca2+ in BC3H-1 muscle cells with Fura-2: relationship to acetylcholine receptor synthesis. Cell Calcium. 1990 May;11(5):371–384. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs F. N., Lee K. F., Feher J. J., Wechsler A. S., Ohlendieck K., Campbell K. Ca-ATPase isozyme expression in sarcoplasmic reticulum is altered by chronic stimulation of skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80025-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charuk J. H., Holland P. C. Effect of tetrodotoxin relaxation of cultured skeletal muscle on the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-transport ATPase. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Mar;144(1):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90448-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. The rate of tetanic relaxation is correlated with the density of calcium ATPase in the terminal cisternae of thyrotoxic skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):433–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00373620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson H., Heilbronn E. Extracellularly applied ATP alters the calcium flux through dihydropyridine-sensitive channels in cultured chick myotubes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):878–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R. H., Winder W. W., Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K., Holloszy J. O. Contractile, biochemical, and histochemical properties of thyrotoxic rat soleus muscle. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):C14–C20. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.238.1.C15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Magri K. A. Effects of growth factors on myogenic differentiation. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C701–C711. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grouselle M., Koenig J., Lascombe M. L., Chapron J., Méléard P., Georgescauld D. Fura-2 imaging of spontaneous and electrically induced oscillations of intracellular free Ca2+ in rat myotubes. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Mar;418(1-2):40–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00370450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha D. B., Boland R., Martonosi A. Synthesis of the calcium transport ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum and other muscle proteins during development of muscles cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 12;585(2):165–187. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. C., MacLennan D. H. Assembly of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biosynthesis of the adenosine triphosphatase in rat skeletal muscle cell culture. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2030–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ince C., van Dissel J. T., Diesselhoff M. M. A teflon culture dish for high-magnification microscopy and measurements in single cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Mar;403(3):240–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00583594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Kracke M. R. Measurement of cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in cultured muscle cells by aequorin and quin 2. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C512–C523. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolesz F., Sreter F. A. Development, innervation, and activity-pattern induced changes in skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:531–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. H., Witzmann F. A., Fitts R. H. Effect of thyrotoxicosis on sarcoplasmic reticulum in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C151–C155. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg I. R. Skeletal myoblasts in culture. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:511–527. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Härtner K. T., Brandl C. J., Fujii J., Tada M., MacLennan D. H., Pette D. Slow/cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and phospholamban mRNAs are expressed in chronically stimulated rabbit fast-twitch muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 20;185(1):51–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. N., Dux L., Terjung R. L., Roufa D. Regulation of membrane assembly during development of sarcoplasmic reticulum: the possible role of calcium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:485–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A., van Hardeveld C., Simonides W. S., van Rijn J. The elevation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase levels by thyroid hormone in the L6 muscle cell line is potentiated by insulin-like growth factor-I. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2750035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Vrbová G. Neural control of phenotypic expression in mammalian muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve. 1985 Oct;8(8):676–689. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Garcia L., Dimitriadou V., Pincon-Raymond M., Rieger F., Lazdunski M. Ontogenesis and localization of Ca2+ channels in mammalian skeletal muscle in culture and role in excitation-contraction coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2933–2937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D., Wu F. S., Martonosi A. N. The effect of Ca2+ ionophores upon the synthesis of proteins in cultured skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 5;674(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. L. Increases in muscle Ca2+ mediate changes in acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholine receptors caused by muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7121–7125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Stanley F., Casanova J. Depletion of L-3,5,3'-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine in euthyroid calf serum for use in cell culture studies of the action of thyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):80–85. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonides W. S., van Hardeveld C. Effects of the thyroid status on the sarcoplasmic reticulum in slow skeletal muscle of the rat. Cell Calcium. 1986 Jun;7(3):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonides W. S., van Hardeveld C. The effect of hypothyroidism on sarcoplasmic reticulum in fast-twitch muscle of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 21;844(2):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreter F. A., Lopez J. R., Alamo L., Mabuchi K., Gergely J. Changes in intracellular ionized Ca concentration associated with muscle fiber type transformation. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C296–C300. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm H., van Hardeveld C. Effect of hypothyroidism on the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in rat hepatocytes during rest and following stimulation by noradrenaline or vasopressin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 21;885(2):206–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hardeveld C., Clausen T. Effect of thyroid status on K+-stimulated metabolism and 45Ca exchange in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):E421–E430. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.4.E421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubrzycka-Gaarn E., MacDonald G., Phillips L., Jorgensen A. O., MacLennan D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to the Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum identify polymorphic forms of the enzyme and indicate the presence in the enzyme of a classical high-affinity Ca2+ binding site. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1984 Dec;16(5-6):441–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00743238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


