Abstract
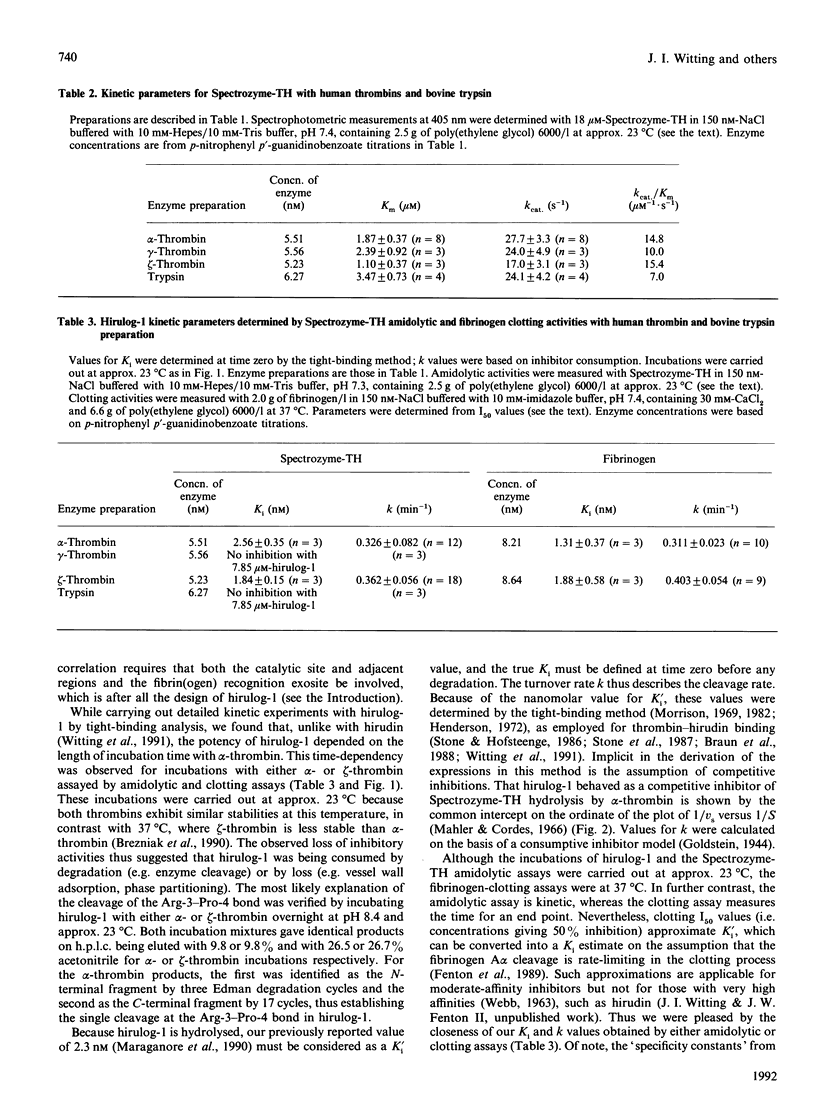
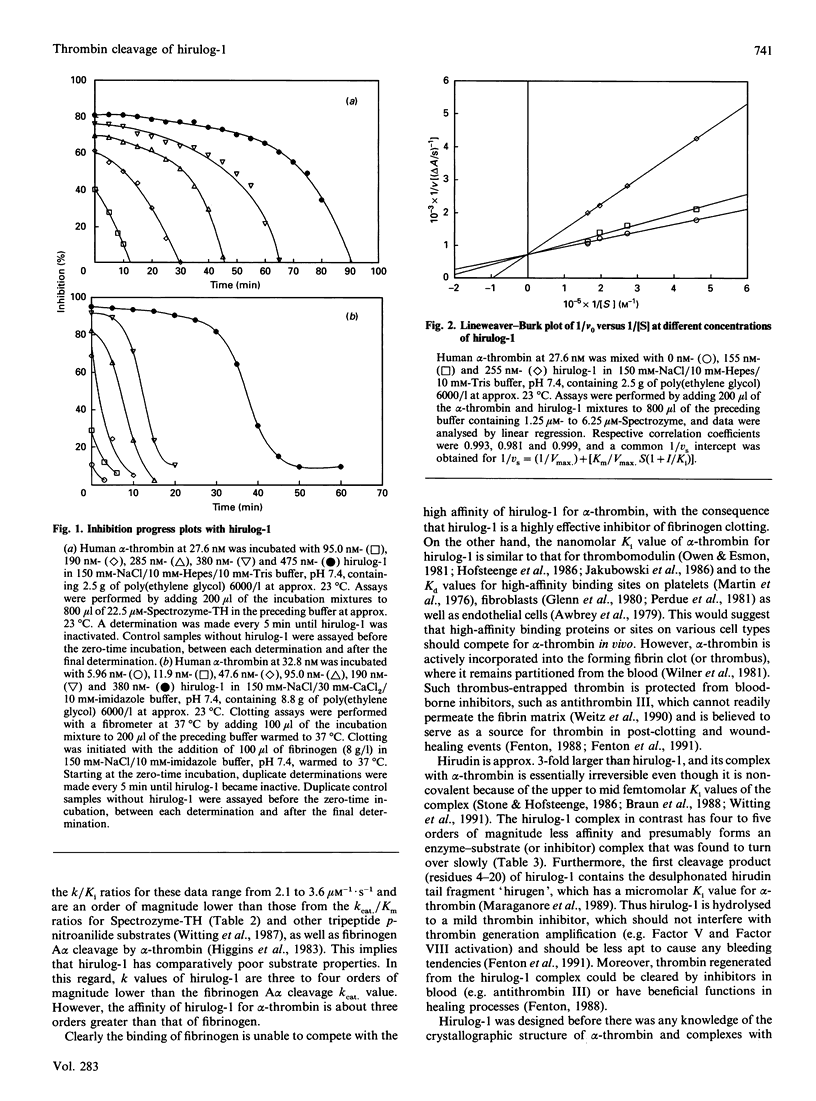
Hirulog-1 [D-Phe-Pro-Arg-Pro-[Gly]4-desulphohirudin-(53-64) (HV1)] was designed to bind by its first four and last 12 residues to the alpha-thrombin catalytic site and anion-binding exosite for fibrin(ogen) recognition respectively, with a [Gly]4 bridge and an Arg-Pro bond at the scissional position. Human alpha-, gamma- and zeta-thrombins, as well as bovine trypsin, readily hydrolyse Spectrozyme-TH (D-hexahydrotyrosyl-Ala-Arg p-nitroanilide) at pH 7.4 and approx. 23 degrees C. Both alpha- and zeta-thrombins, which have high fibrinogen-clotting activities (greater than 3000 kunits/g), were inhibited with this substrate by hirulog-1 [Ki = 2.56 +/- 0.35 nM (n = 3) and 1.84 +/- 0.15 nM (n = 3) respectively] and slowly cleaved the inhibitor [k = 0.326 +/- 0.082 min-1 (n = 12) and 0.362 +/- 0.056 min-1 (n = 18) respectively], whereas gamma-thrombin, which has essentially no clotting activity (approx. 4 kunits/g), and trypsin were not inhibited with greater than 1000-fold molar excess of hirulog-1. Similar inhibition parameters were also obtained for hirulog-1 incubated with alpha-thrombin or zeta-thrombin at approx. 23 degrees C and by measuring thrombin activity with fibrinogen in the clotting assay at 37 degrees C. Cleavage of the Arg-3-Pro-4 bond in hirulog-1 by either alpha- or zeta-thrombin was shown by identical cleavage products of either thrombin on h.p.l.c. and by sequence analysis of the alpha-thrombin products. These data demonstrate that hirulog-1 is a specific inhibitor of thrombin forms with high fibrinogen-procoagulant activities and that its Arg-3-Pro-4 bond is slowly cleaved by these thrombin forms.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awbrey B. J., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of human thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4092–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdy D., Barabas E., Gráf L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Hirudin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:669–678. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajusz S., Barabás E., Tolnay P., Széll E., Bagdy D. Inhibition of thrombin and trypsin by tripeptide aldehydes. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Oct;12(4):217–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Cory M., Fenton J. W., 2nd Exo-site affinity labeling of human thrombins. Similar labeling on the A chain and B chain/fragments of clotting alpha- and nonclotting gamma/beta-thrombins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8027–8034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Mayr I., Baumann U., Huber R., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467–3475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon P., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Maraganore J. M. Affinity labeling of lysine-149 in the anion-binding exosite of human alpha-thrombin with an N alpha-(dinitrofluorobenzyl)hirudin C-terminal peptide. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6379–6384. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun P. J., Dennis S., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to investigate the basis for the specificity of hirudin. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6517–6522. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezniak D. V., Brower M. S., Witting J. I., Walz D. A., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha- to zeta-thrombin cleavage occurs with neutrophil cathepsin G or chymotrypsin while fibrinogen clotting activity is retained. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3536–3542. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Walz D. A., Garry K. E., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human neutrophil elastase alters human alpha-thrombin function: limited proteolysis near the gamma-cleavage site results in decreased fibrinogen clotting and platelet-stimulatory activity. Blood. 1987 Mar;69(3):813–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Feinman R. D., Landis B. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd Antithrombin reactions with alpha- and gamma-thrombins. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):113–119. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church F. C., Pratt C. W., Noyes C. M., Kalayanamit T., Sherrill G. B., Tobin R. B., Meade J. B. Structural and functional properties of human alpha-thrombin, phosphopyridoxylated alpha-thrombin, and gamma T-thrombin. Identification of lysyl residues in alpha-thrombin that are critical for heparin and fibrin(ogen) interactions. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18419–18425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degryse E., Acker M., Defreyn G., Bernat A., Maffrand J. P., Roitsch C., Courtney M. Point mutations modifying the thrombin inhibition kinetics and antithrombotic activity in vivo of recombinant hirudin. Protein Eng. 1989 Mar;2(6):459–465. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.6.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio J., Gibbs B., Munn D., Lefebvre J., Ni F., Konishi Y. Bifunctional thrombin inhibitors based on the sequence of hirudin45-65. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21698–21703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio J., Ni F., Gibbs B., Konishi Y. A new class of potent thrombin inhibitors that incorporates a scissile pseudopeptide bond. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodt J., Köhler S., Baici A. Interaction of site specific hirudin variants with alpha-thrombin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80803-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodt J., Köhler S., Schmitz T., Wilhelm B. Distinct binding sites of Ala48-hirudin1-47 and Ala48-hirudin48-65 on alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):713–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Bing D. H. Thrombin active-site regions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1986 Jul;12(3):200–208. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J. Polyethylene glycol 6,000 enhancement of the clotting of fibrinogen solutions in visual and mechanical assays. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Ofosu F. A., Moon D. G., Maraganore J. M. Thrombin structure and function: why thrombin is the primary target for antithrombotics. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1991 Feb;2(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Olson T. A., Zabinski M. P., Wilner G. D. Anion-binding exosite of human alpha-thrombin and fibrin(ogen) recognition. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7106–7112. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Regulation of thrombin generation and functions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1988 Jul;14(3):234–240. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin interactions with hirudin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1989 Jul;15(3):265–268. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;485:5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Wideman C. S., Evatt B. L. Thrombin clotting activity measurement and standardization with lyophilized plasma. Clin Chem. 1986 Feb;32(2):320–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Witting J. I., Pouliott C., Fareed J. Thrombin anion-binding exosite interactions with heparin and various polyanions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;556:158–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K. C., Carney D. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Cunningham D. D. Thrombin active site regions required for fibroblast receptor binding and initiation of cell division. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6609–6616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grütter M. G., Priestle J. P., Rahuel J., Grossenbacher H., Bode W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Crystal structure of the thrombin-hirudin complex: a novel mode of serine protease inhibition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2361–2365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Degryse E., Stefani L., Schamber F., Cazenave J. P., Courtney M., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the anticoagulant hirudin from the bloodsucking leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1084–1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. A linear equation that describes the steady-state kinetics of enzymes and subcellular particles interacting with tightly bound inhibitors. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):321–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1270321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Lewis S. D., Shafer J. A. Steady state kinetic parameters for the thrombin-catalyzed conversion of human fibrinogen to fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9276–9282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Taguchi H., Stone S. R. Effect of thrombomodulin on the kinetics of the interaction of thrombin with substrates and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):243–251. doi: 10.1042/bj2370243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline T., Hammond C., Bourdon P., Maraganore J. M. Hirulog peptides with scissile bond replacements resistant to thrombin cleavage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1049–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90644-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krstenansky J. L., Mao S. J. Antithrombin properties of C-terminus of hirudin using synthetic unsulfated N alpha-acetyl-hirudin45-65. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 19;211(1):10–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81264-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. D., Lorand L., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Shafer J. A. Catalytic competence of human alpha- and gamma-thrombin in the activation of fibrinogen and factor XIII. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7597–7603. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao S. J., Yates M. T., Owen T. J., Krstenansky J. L. Interaction of hirudin with thrombin: identification of a minimal binding domain of hirudin that inhibits clotting activity. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8170–8173. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraganore J. M., Bourdon P., Jablonski J., Ramachandran K. L., Fenton J. W., 2nd Design and characterization of hirulogs: a novel class of bivalent peptide inhibitors of thrombin. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7095–7101. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraganore J. M., Chao B., Joseph M. L., Jablonski J., Ramachandran K. L. Anticoagulant activity of synthetic hirudin peptides. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8692–8698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. M., Wasiewski W. W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Detwiler T. C. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to platelets. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4886–4893. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):269–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue J. F., Lubenskyi W., Kivity E., Sonder S. A., Fenton J. W., 2nd Protease mitogenic response of chick embryo fibroblasts and receptor binding/processing of human alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2767–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Roitsch C., Fenton J. W., 2nd The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):277–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2374926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Braun P. J., Hofsteenge J. Identification of regions of alpha-thrombin involved in its interaction with hirudin. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4617–4624. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. Kinetics of the inhibition of thrombin by hirudin. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4622–4628. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz J. I., Hudoba M., Massel D., Maraganore J., Hirsh J. Clot-bound thrombin is protected from inhibition by heparin-antithrombin III but is susceptible to inactivation by antithrombin III-independent inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):385–391. doi: 10.1172/JCI114723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Danitz M. P., Mudd M. S., Hsieh K. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd Selective immobilization of alpha-thrombin by surface-bound fibrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Mar;97(3):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witting J. I., Brezniak D. V., Hayes J. R., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha- and zeta-thrombin inhibition by recombinant HV1 and HV2K47 hirudins. Thromb Res. 1991 Aug 15;63(4):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90235-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witting J. I., Miller T. M., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha- and gamma-thrombin specificity with tripeptide p-nitroanalide substrates under physiologically relevant conditions. Thromb Res. 1987 May 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witting J. I., Pouliott C., Catalfamo J. L., Fareed J., Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin inhibition with dipeptidyl argininals. Thromb Res. 1988 May 15;50(4):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


