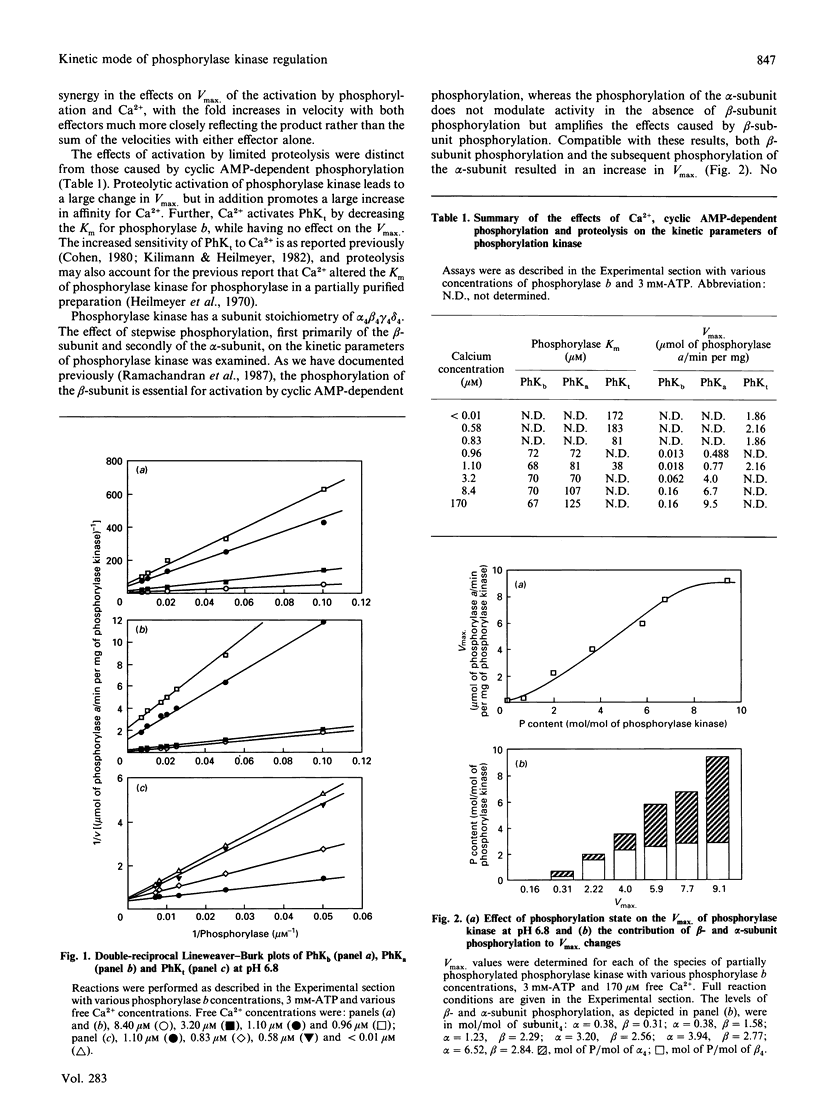
Abstract
The regulation of phosphorylase kinase has been proposed to occur physiologically under conditions of zero-order ultrasensitivity [Meinke & Edstrom (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 2259-2266]. This is also one of the conditions that recent theoretical approaches have indicated to be essential in order for an interconvertible enzyme cascade to generate a sensitive response to an effector [Cardenas & Cornish-Bowden (1989) Biochem. J. 257, 339-345]. In contrast, all published kinetic data to date have strongly suggested that activation of phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+ or phosphorylation is attributable solely to a change in affinity for phosphorylase, with no effect on the Vmax. of the reaction. In this study an attempt is made to resolve this conflict. Findings suggest that changes in Vmax. can fully account for the activation of phosphorylase kinase by the physiological mechanisms of cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation and increase in Ca2+ concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelos K. L., Ramachandran C., Walsh D. A. Subunit phosphorylation and activation of phosphorylase kinase in perfused rat hearts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3219–3226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger D., Cox J. A., Fischer E. H., Stein E. A. The activation of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase requires the binding of 3 Ca2+ per delta subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):632–638. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91481-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson G. M., Bechtel P. J., Graves D. J. Chemical and regulatory properties of phosphorylase kinase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;50:41–115. doi: 10.1002/9780470122952.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. F., Graves D. J. Rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Catalytic and regulatory properties of the active alpha gamma delta and gamma delta complexes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5948–5955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B., Rhee S. G., Stadtman E. R. Interconvertible enzyme cascades in cellular regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:813–843. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B., Stadtman E. R. Superiority of interconvertible enzyme cascades in metabolite regulation: analysis of multicyclic systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B., Stadtman E. R. Superiority of interconvertible enzyme cascades in metabolite regulation: analysis of multicyclic systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of calcium ions, calmodulin and troponin in the regulation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):563–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Sul H. S., McCullough T. E., Walsh D. A. Purification and properties of the cardiac isoenzyme of phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11794–11801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas M. L., Cornish-Bowden A. Characteristics necessary for an interconvertible enzyme cascade to generate a highly sensitive response to an effector. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):339–345. doi: 10.1042/bj2570339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher W. H., Van Patten S. M., Cheng H. C., Walsh D. A. Cytochemical identification of the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase by use of fluorescently labeled catalytic subunit. Examination of protein kinase dissociation in hepatoma cells responding to 8-Br-cAMP stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5504–5513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Koshland D. E., Jr An amplified sensitivity arising from covalent modification in biological systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6840–6844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Meyer F., Haschke R. H., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. II. Activation by calcium. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6649–6656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen L. Effect of metabolic changes on force generation in skeletal muscle during maximal exercise. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;82:75–88. doi: 10.1002/9780470715420.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., LOVE D. S., BRATVOLD G. E., TRAYSER K. A., MEYER W. L., FISCHER E. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHORYLASE B KINASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1022–1033. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Multiple activities on phosphorylase kinase. 1. Characterization of three partial activities by their response to calcium ion, magnesium ion, pH, and ammonium chloride and effect of activation by phosphorylation and proteolysis. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1727–1734. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Phosphorylation of isocitrate dehydrogenase as a demonstration of enhanced sensitivity in covalent regulation. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):286–290. doi: 10.1038/305286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke M. H., Bishop J. S., Edstrom R. D. Zero-order ultrasensitivity in the regulation of glycogen phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2865–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke M. H., Edstrom R. D. Muscle glycogenolysis. Regulation of the cyclic interconversion of phosphorylase a and phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2259–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett-Gies C. A., Carlsen R. C., Anderson L. J., Angelos K. L., Walsh D. A. Characterization of the isolated rat flexor digitorum brevis for the study of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3227–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett-Gies C. A., Walsh D. A. Subunit phosphorylation and activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Divalent metal ion, ATP, and protein concentration dependence. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2046–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran C., Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W., Walsh D. A. The interrelationship between cAMP-dependent alpha and beta subunit phosphorylation in the regulation of phosphorylase kinase activity. Studies using subunit specific phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3210–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahlin K. Intracellular pH and energy metabolism in skeletal muscle of man. With special reference to exercise. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1978;455:1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Chock P. B. Interconvertible enzyme cascades in metabolic regulation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;13:53–95. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152813-3.50007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sul H. S., Dirden B., Angelos K. L., Hallenbeck P., Walsh D. A. Cardiac phosphorylase kinase: preparation and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:250–259. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Feramisco J. R., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G., Walsh D. A. Studies on the kinetic mechanism of the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3693–3701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


