Abstract
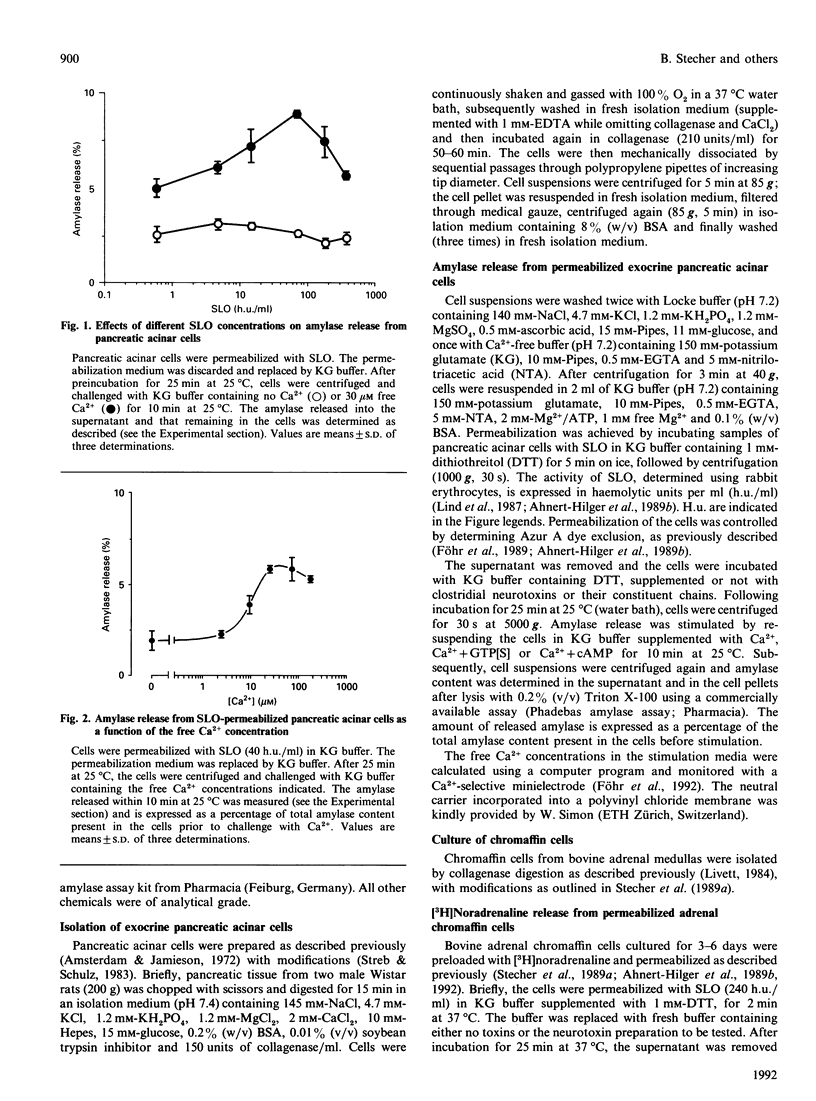
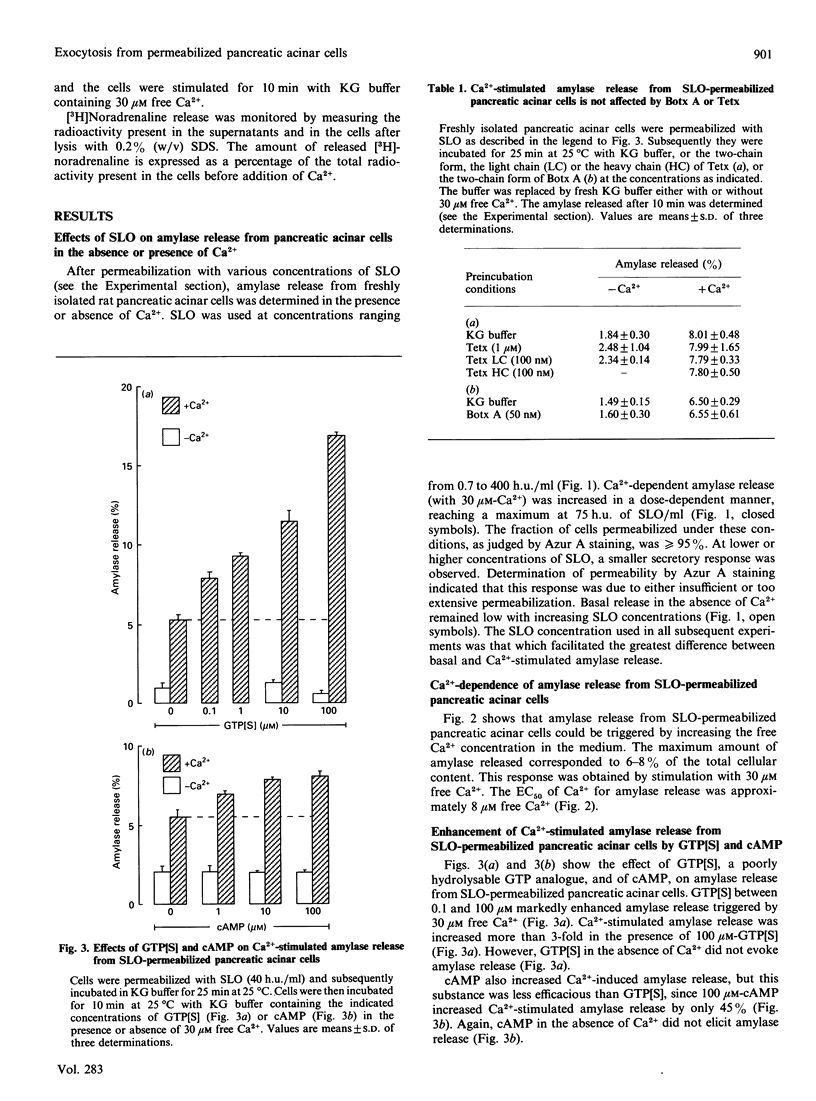
The molecular requirements for amylase release and the intracellular effects of botulinum A toxin and tetanus toxin on amylase release were investigated using rat pancreatic acinar cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Micromolar concentrations of free Ca2+ evoked amylase release from these cells. Maximal release was observed in the presence of 30 microM free Ca2+. Ca(2+)-stimulated, but not basal, amylase release was enhanced by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) (3-4 fold) or cyclic AMP (1.5-2 fold). Neither the two-chain forms of botulinum A toxin and tetanus toxin, under reducing conditions, nor the light chains of tetanus toxin, inhibited amylase release triggered by Ca2+, or combinations of Ca2+ + GTP[S] or Ca2+ + cAMP. The lack of inhibition was not due to inactivation of botulinum A toxin or tetanus toxin by pancreatic acinar cell proteolytic enzymes, as toxins previously incubated with permeabilized pancreatic acinar cells inhibited Ca(2+)-stimulated [3H]noradrenaline release from streptolysin O-permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. These data imply that clostridial neurotoxins inhibit a Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism which promotes exocytosis in neural and endocrine cells, but not in exocrine cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bader M. F., Bhakdi S., Gratzl M. Introduction of macromolecules into bovine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells and rat pheochromocytoma cells (PC12) by permeabilization with streptolysin O: inhibitory effect of tetanus toxin on catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1751–1758. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bräutigam M., Gratzl M. Ca2+-stimulated catecholamine release from alpha-toxin-permeabilized PC12 cells: biochemical evidence for exocytosis and its modulation by protein kinase C and G proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7842–7848. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Mach W., Föhr K. J., Gratzl M. Poration by alpha-toxin and streptolysin O: an approach to analyze intracellular processes. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:63–90. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Weller U., Dauzenroth M. E., Habermann E., Gratzl M. The tetanus toxin light chain inhibits exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80478-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam A., Jamieson J. D. Structural and functional characterization of isolated pancreatic exocrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3028–3032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Sontag J. M., Thiersé D., Aunis D. A reassessment of guanine nucleotide effects on catecholamine secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16426–16434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey G. K., Bigalke H., Nelson P. G. Differential effects of tetanus toxin on inhibitory and excitatory synaptic transmission in mammalian spinal cord neurons in culture: a presynaptic locus of action for tetanus toxin. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigalke H., Heller I., Bizzini B., Habermann E. Tetanus toxin and botulinum A toxin inhibit release and uptake of various transmitters, as studied with particulate preparations from rat brain and spinal cord. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;316(3):244–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00505657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz T., Kurazono H., Wille M., Frevert J., Wernars K., Niemann H. The complete sequence of botulinum neurotoxin type A and comparison with other clostridial neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9153–9158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., DasGupta B. R., Holz R. W. Isolated light chains of botulinum neurotoxins inhibit exocytosis. Studies in digitonin-permeabilized chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10354–10360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Habig W. H., Holz R. W. Isolated light chain of tetanus toxin inhibits exocytosis: studies in digitonin-permeabilized cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Sep;53(3):966–968. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb11800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. Effects of tetanus toxin on catecholamine release from intact and digitonin-permeabilized chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):451–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. Low molecular mass GTP-binding proteins of adrenal chromaffin cells are present on the secretory granule. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Two G-proteins act in series to control stimulus-secretion coupling in mast cells: use of neomycin to distinguish between G-proteins controlling polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2745–2750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darchen F., Zahraoui A., Hammel F., Monteils M. P., Tavitian A., Scherman D. Association of the GTP-binding protein Rab3A with bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5692–5696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayanithi G., Ahnert-Hilger G., Weller U., Nordmann J. J., Gratzl M. Release of vasopressin from isolated permeabilized neurosecretory nerve terminals is blocked by the light chain of botulinum A toxin. Neuroscience. 1990;39(3):711–715. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayanithi G., Weller U., Ahnert-Hilger G., Link H., Nordmann J. J., Gratzl M. The light chain of tetanus toxin inhibits calcium-dependent vasopressin release from permeabilized nerve endings. Neuroscience. 1992;46(2):489–493. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90068-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Fournier S., Parulekar M., Trifaró J. M. Detection of low molecular mass GTP-binding proteins in chromaffin granules and other subcellular fractions of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardson J. M., Vickery C., Christy L. J. Rat pancreatic acini permeabilised with streptolysin O secrete amylase at Ca2+ concentrations in the micromolar range, when provided with ATP and GTP gamma S. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 12;1053(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisel U., Jarausch W., Goretzki K., Henschen A., Engels J., Weller U., Hudel M., Habermann E., Niemann H. Tetanus toxin: primary structure, expression in E. coli, and homology with botulinum toxins. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2495–2502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Föhr K. J., Scott J., Ahnert-Hilger G., Gratzl M. Characterization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release from permeabilized endocrine cells and its inhibition by decavanadate and p-hydroxymercuribenzoate. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):83–89. doi: 10.1042/bj2620083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Dreyer F. Clostridial neurotoxins: handling and action at the cellular and molecular level. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;129:93–179. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71399-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Guanine nucleotides decrease the free [Ca2+] required for secretion of serotonin from permeabilized blood platelets. Evidence of a role for a GTP-binding protein in platelet activation. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Rat mast cells permeabilised with streptolysin O secrete histamine in response to Ca2+ at concentrations buffered in the micromolar range. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 18;927(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Imamura K., Eckhardt L., Schulz I. Ca2+-, phorbol ester-, and cAMP-stimulated enzyme secretion from permeabilized rat pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):G698–G708. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.5.G698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Williams J. A., De Lisle R. C. Amylase release from streptolysin O-permeabilized pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):G157–G164. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.2.G157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Guanine nucleotides and Ca-dependent exocytosis. Studies on two adrenal cell preparations. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):345–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Koh E. Ca2+ and cyclic nucleotide dependence of amylase release from isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells rendered permeable by intense electric fields. Cell Calcium. 1984 Aug;5(4):401–418. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(84)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M., Bui N. D., Christophe J. Novel GTP-binding proteins in plasma membranes and zymogen granule membranes from rat pancreas and in pancreatic AR 4-2J cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80362-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I., Ahnert-Hilger G., Fuchs G., Gratzl M. Purification of alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus and application to cell permeabilization. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jul;164(1):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G. Adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in vitro. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1103–1161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisey E. A., Wadsworth J. D., Poulain B., Shone C. C., Melling J., Gibbs P., Tauc L., Dolly J. O. Involvement of the constituent chains of botulinum neurotoxins A and B in the blockade of neurotransmitter release. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):683–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y. Agonist-induced changes in cell membrane capacitance and conductance in dialysed pancreatic acinar cells of rats. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:299–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka I., Dolly J. O. Identification and localization of low-molecular-mass GTP-binding proteins associated with synaptic vesicles and other membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 9;1026(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90338-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes C., Dolly J. O. Ca2(+)-dependent noradrenaline release from permeabilised PC12 cells is blocked by botulinum neurotoxin A or its light chain. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80582-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E., Dreyer F. Intracellularly injected tetanus toxin inhibits exocytosis in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):76–78. doi: 10.1038/324076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathyamoorthy V., DasGupta B. R. Separation, purification, partial characterization and comparison of the heavy and light chains of botulinum neurotoxin types A, B, and E. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10461–10466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher B., Gratzl M., Ahnert-Hilger G. Reductive chain separation of botulinum A toxin--a prerequisite to its inhibitory action on exocytosis in chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher B., Weller U., Habermann E., Gratzl M., Ahnert-Hilger G. The light chain but not the heavy chain of botulinum A toxin inhibits exocytosis from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 25;255(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Schulz I. Regulation of cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in acinar cells of rat pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):G347–G357. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.3.G347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Aunis D., Bockaert J., Homburger V., Rouot B. Presence of three pertussis toxin substrates and Go alpha immunoreactivity in both plasma and granule membranes of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller U., Dauzenroth M. E., Meyer zu Heringdorf D., Habermann E. Chains and fragments of tetanus toxin. Separation, reassociation and pharmacological properties. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 1;182(3):649–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller U., Mauler F., Habermann E. Tetanus toxin: biochemical and pharmacological comparison between its protoxin and some isotoxins obtained by limited proteolysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;338(2):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00174855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


