Abstract
Two glycoforms of a secretable human thrombomodulin mutant [TMD1-105 and TMD1-75; Parkinson, Grinnell, Moore, Hoskins, Vlahos & Bang (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 12602-12610] were expressed in human 293 cells and used to study the role of glycosylation in the functions of this endothelial-cell thrombin receptor. Carbohydrate content analysis and intrinsic labelling with [3H]glucosamine and [35S]sulphate showed that TMD1-105 contained a chondroitin sulphate whereas TMD1-75 did not. Other than chondroitin sulphate, the carbohydrate contents of the two glycoforms were identical, indicating similar glycosylation patterns at other O-linked and N-linked sites in the two glycoforms. The properties of TMD1-105 were converted into those of TMD1-75 by chondroitin ABC lyase digestion. Trypsin digestion of labelled TMD1-105 permitted isolation of two overlapping peptides that contained chondroitin sulphate, spanned the entire O-glycosylation domain and had O-glycosylation sites at Ser-492, Ser-498, Thr-500, Thr-504 and Thr-506. The chondroitin sulphate-attachment site was assigned to Ser-492 as this residue is conserved in mouse and bovine thrombomodulin and lies within a sequence Ser-Gly-Ser-492-Gly-Glu-Pro, which has strong similarity to chondroitin sulphate attachment sites in other proteoglycans. Five peptides with N-linked carbohydrate were also isolated and contained glycosylation sites in the lectin-like domain (Asn-47, Asn-115, Asn-116) and in the fourth (Asn-382) and fifth (Asn-409) epidermal growth factor domains. The role of N-linked and simple O-linked carbohydrates in the functions of human thrombomodulin remain unclear. The present studies demonstrate, however, that the presence of chondroitin sulphate in human thrombomodulin has profound effects on all of the anticoagulant properties of this important anticoagulant thrombin receptor.
Full text
PDF



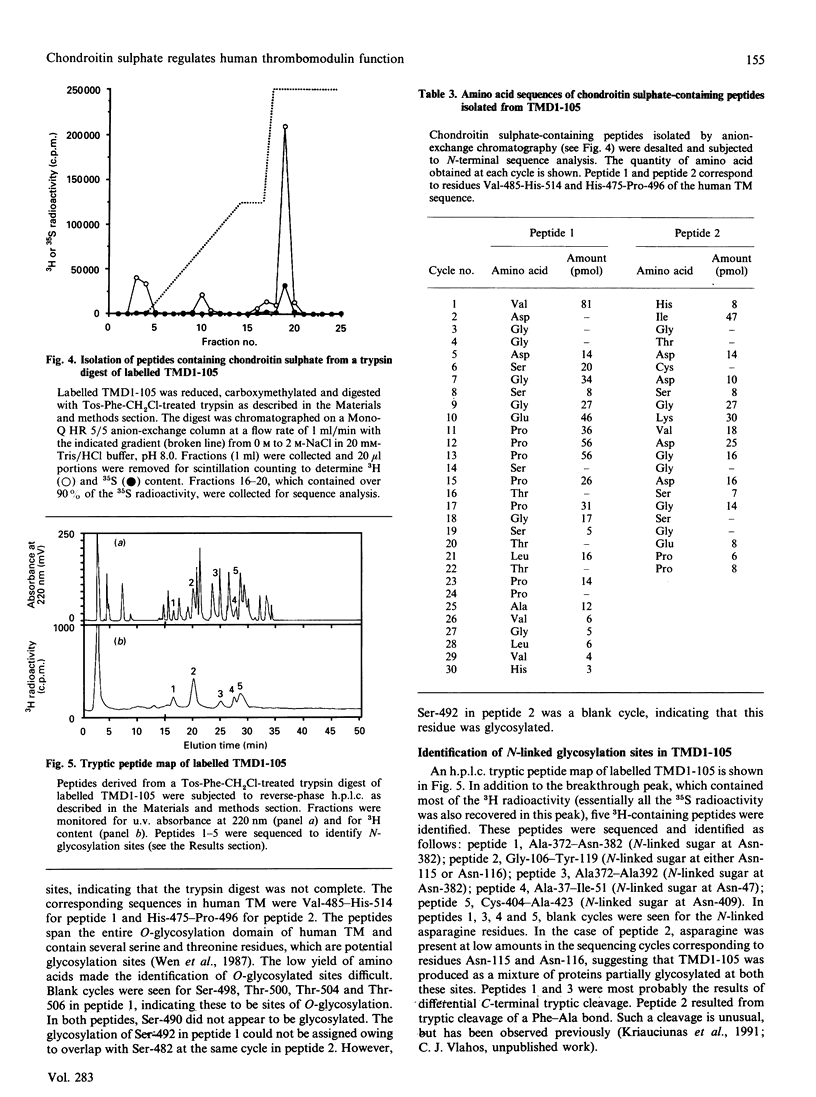


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode W., Mayr I., Baumann U., Huber R., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467–3475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Krusius T., Campbell S., Schwartz N. B., Ruoslahti E. Identification and synthesis of a recognition signal for the attachment of glycosaminoglycans to proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourin M. C. Effect of rabbit thrombomodulin on thrombin inhibition by antithrombin in the presence of heparin. Thromb Res. 1989 Apr 1;54(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourin M. C., Lindahl U. Functional role of the polysaccharide component of rabbit thrombomodulin proteoglycan. Effects on inactivation of thrombin by antithrombin, cleavage of fibrinogen by thrombin and thrombin-catalysed activation of factor V. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):419–425. doi: 10.1042/bj2700419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourin M. C., Lundgren-Akerlund E., Lindahl U. Isolation and characterization of the glycosaminoglycan component of rabbit thrombomodulin proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15424–15431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourin M. C., Ohlin A. K., Lane D. A., Stenflo J., Lindahl U. Relationship between anticoagulant activities and polyanionic properties of rabbit thrombomodulin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8044–8052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad H. E. Structure of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;556:18–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Kumada T., Sadler J. E., Majerus P. W. The structure and function of mouse thrombomodulin. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates degradation and synthesis of thrombomodulin without affecting mRNA levels in hemangioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15815–15822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Majerus P. W. Structure and function of thrombomodulin: a natural anticoagulant. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Carroll R. C., Esmon C. T. Thrombomodulin blocks the ability of thrombin to activate platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12238–12242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada S., Yamaguchi H., Nagumo M., Katayanagi S., Iwasaki H., Imada M. Identification of fetomodulin, a surface marker protein of fetal development, as thrombomodulin by gene cloning and functional assays. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90058-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman R. W., Beeler D. L., VanDeWater L., Rosenberg R. D. Characterization of a thrombomodulin cDNA reveals structural similarity to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriauciunas A., Frolik C. A., Hassell T. C., Skatrud P. L., Johnson M. G., Holbrook N. L., Chen V. J. The functional role of cysteines in isopenicillin N synthase. Correlation of cysteine reactivities toward sulfhydryl reagents with kinetic properties of cysteine mutants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11779–11788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa S., Galvin J. B., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T. Proteolytic formation and properties of functional domains of thrombomodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2206–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Salem H. H., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Human thrombomodulin is not an efficient inhibitor of the procoagulant activity of thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):987–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI111800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa K., Sakano K., Fujiwara H., Sato Y., Sugiyama N., Teruuchi T., Iwamoto M., Marumoto Y. Presence and function of chondroitin-4-sulfate on recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. F., Garcia J. G., Bang N. U. Decreased thrombin affinity of cell-surface thrombomodulin following treatment of cultured endothelial cells with beta-D-xyloside. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 31;169(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91451-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. F., Grinnell B. W., Moore R. E., Hoskins J., Vlahos C. J., Bang N. U. Stable expression of a secretable deletion mutant of recombinant human thrombomodulin in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12602–12610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Detecting distant homologies of mosaic proteins. Analysis of the sequences of thrombomodulin, thrombospondin complement components C9, C8 alpha and C8 beta, vitronectin and plasma cell membrane glycoprotein PC-1. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90550-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Delvos U., Müller-Berghaus G. Binding of thrombin to thrombomodulin accelerates inhibition of the enzyme by antithrombin III. Evidence for a heparin-independent mechanism. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2521–2528. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Koyama T., Müller D., Tschopp J., Müller-Berghaus G. Domain structure of the endothelial cell receptor thrombomodulin as deduced from modulation of its anticoagulant functions. Evidence for a glycosaminoglycan-dependent secondary binding site for thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4915–4922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Roitsch C., Fenton J. W., 2nd The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):277–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2374926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Maruyama I., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of thrombomodulin from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns D. J., Kurosawa S., Esmon C. T. Microthrombomodulin. Residues 310-486 from the epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain of thrombomodulin will accelerate protein C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3352–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Z., Dittman W. A., Ye R. D., Deaven L. L., Majerus P. W., Sadler J. E. Human thrombomodulin: complete cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4350–4357. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. C., Razzano P., Chao Y. B., Walls J. D., Berg D. T., McClure D. B., Grinnell B. W. Characterization and novel purification of recombinant human protein C from three mammalian cell lines. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Jul;8(7):655–661. doi: 10.1038/nbt0790-655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




