Abstract
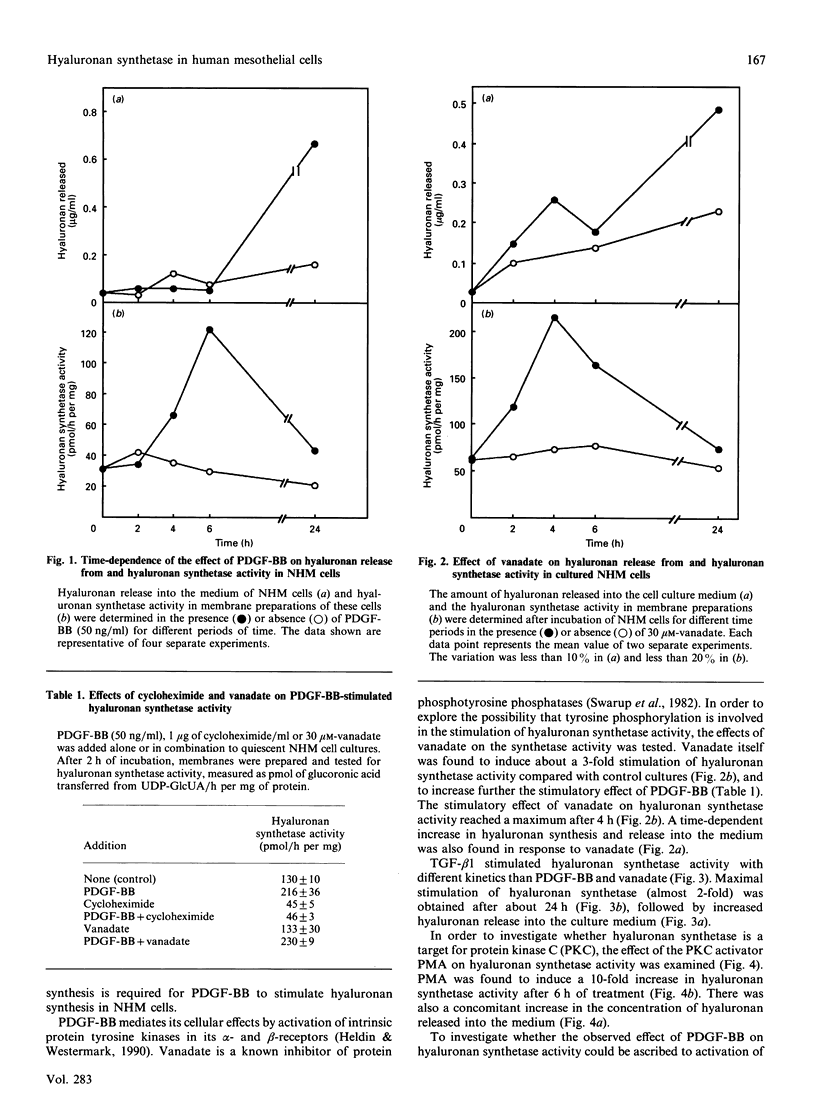
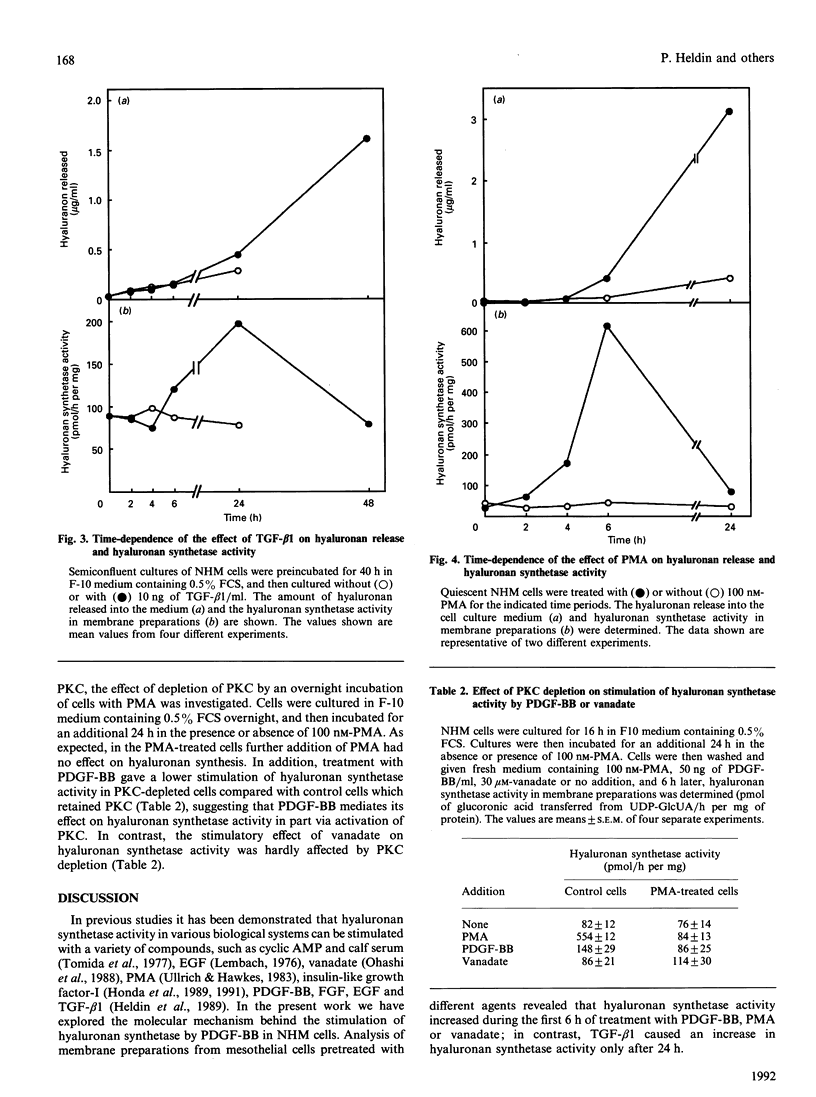
The molecular mechanism involved in the stimulation of hyaluronan synthetase in normal human mesothelial cells was investigated. Exposure of mesothelial cells to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB stimulated hyaluronan synthetase activity, measured in isolated membrane preparations, as well as hyaluronan secretion into the medium. The effect on hyaluronan synthetase was maximal after 6 h of treatment. In contrast, the stimulatory effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 reached a maximum after 24 h. The stimulatory effect of PDGF-BB was inhibited by cycloheximide. The phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor vanadate was found to stimulate hyaluronan synthetase activity, and to potentiate the effect of PDGF-BB. The protein kinase C (PKC) stimulator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) also stimulated hyaluronan synthetase; furthermore, depletion of PKC by preincubation of the cells with PMA led to an inhibition of the PDGF-BB-induced stimulation of hyaluronan synthetase activity. Thus the PDGF-BB-induced stimulation of hyaluronan synthetase activity is dependent on protein synthesis and involves tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of PKC.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Kang K. Y., Sato H., Satoh K., Nagai H., Motomiya M., Konno K. Significance of the quantification and demonstration of hyaluronic acid in tissue specimens for the diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Sep;120(3):529–532. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal M. K., Mason R. M. Evidence for rapid metabolic turnover of hyaluronate synthetase in Swarm rat chondrosarcoma chondrocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):515–519. doi: 10.1042/bj2360515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecht M., Mayer U., Schlosser E., Prehm P. Increased hyaluronate synthesis is required for fibroblast detachment and mitosis. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):445–450. doi: 10.1042/bj2390445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N. D., Rheinwald J. G. Regulation of the cytoskeleton in mesothelial cells: reversible loss of keratin and increase in vimentin during rapid growth in culture. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl I. M., Laurent T. C. Concentration of hyaluronan in the serum of untreated cancer patients with special reference to patients with mesothelioma. Cancer. 1988 Jul 15;62(2):326–330. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880715)62:2<326::aid-cncr2820620217>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl I. M., Solheim O. P., Erikstein B., Müller E. A longitudinal study of the hyaluronan level in the serum of patients with malignant mesothelioma under treatment. Hyaluronan as an indicator of progressive disease. Cancer. 1989 Jul 1;64(1):68–73. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890701)64:1<68::aid-cncr2820640112>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. O., Gibbs V. C., Milfay D. F., Williams L. T. Agents that increase cAMP accumulation block endothelial c-sis induction by thrombin and transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11893–11896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A., Feltelius N., Hällgren R., Wasteson A. Raised serum hyaluronate levels in scleroderma: an effect of growth factor induced activation of connective tissue cells? Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Sep;44(9):614–620. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.9.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielson E. W., Gerwin B. I., Harris C. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Lechner J. F. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in cultured primary human mesothelial cells by specific growth factors. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2717–2721. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.3260881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwin B. I., Lechner J. F., Reddel R. R., Roberts A. B., Robbins K. C., Gabrielson E. W., Harris C. C. Comparison of production of transforming growth factor-beta and platelet-derived growth factor by normal human mesothelial cells and mesothelioma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 1;47(23):6180–6184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty K. A., Smith G. N., Jr, Kang A. H. Studies on glycosaminoglycans of regenerating rabbit ear cartilage. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: mechanism of action and possible in vivo function. Cell Regul. 1990 Jul;1(8):555–566. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.8.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin P., Laurent T. C., Heldin C. H. Effect of growth factors on hyaluronan synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):919–922. doi: 10.1042/bj2580919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin P., Pertoft H., Nordlinder H., Heldin C. H., Laurent T. C. Differential expression of platelet-derived growth factor alpha- and beta- receptors on fat-storing cells and endothelial cells of rat liver. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Apr;193(2):364–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda A., Iwai T., Mori Y. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) enhances hyaluronic acid synthesis in rabbit pericardium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda A., Noguchi N., Takehara H., Ohashi Y., Asuwa N., Mori Y. Cooperative enhancement of hyaluronic acid synthesis by combined use of IGF-I and EGF, and inhibition by tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein, in cultured mesothelial cells from rabbit pericardial cavity. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jan;98(Pt 1):91–98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hronowski L., Anastassiades T. P. The effect of cell density on net rates of glycosaminoglycan synthesis and secretion by cultured rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10091–10099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson W., Biswas C., Li X. Q., Nemec R. E., Toole B. P. The role and regulation of tumour-associated hyaluronan. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:150-9; discussion 159-69, 281-5. doi: 10.1002/9780470513774.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laveck M. A., Somers A. N., Moore L. L., Gerwin B. I., Lechner J. F. Dissimilar peptide growth factors can induce normal human mesothelial cell multiplication. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;24(11):1077–1084. doi: 10.1007/BF02620808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembach K. J. Enhanced synthesis and extracellular accumulation of hyaluronic acid during stimulation of quiescent human fibroblasts by mouse epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Oct;89(2):277–288. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuoka K., Namba M., Mitsui Y. Hyaluronate synthetase inhibition by normal and transformed human fibroblasts during growth reduction. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1105–1115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian N. Analysis of cell-growth-phase-related variations in hyaluronate synthase activity of isolated plasma-membrane fractions of cultured human skin fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):333–342. doi: 10.1042/bj2370333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian N. Characterization of a high-Mr plasma-membrane-bound protein and assessment of its role as a constituent of hyaluronate synthase complex. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):343–357. doi: 10.1042/bj2370343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Honda A., Iwai T., Mori Y. Stimulatory effect of vanadate on hyaluronic acid synthesis in mesothelial cells from rabbit pericardium. Biochem Int. 1988 Feb;16(2):293–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostman A., Bäckström G., Fong N., Betsholtz C., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Westermark B., Valenzuela P., Heldin C. H. Expression of three recombinant homodimeric isoforms of PDGF in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for difference in receptor binding and functional activities. Growth Factors. 1989;1(3):271–281. doi: 10.3109/08977198908998003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L. H., Schwartz N. B. Subcellular localization of hyaluronate synthetase in oligodendroglioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5017–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Hyaluronate is synthesized at plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):597–600. doi: 10.1042/bj2200597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Identification and regulation of the eukaryotic hyaluronate synthase. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:21-30; discussion 30-40, 281-5. doi: 10.1002/9780470513774.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Synthesis of hyaluronate in differentiated teratocarcinoma cells. Characterization of the synthase. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 1;211(1):181–189. doi: 10.1042/bj2110181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Synthesis of hyaluronate in differentiated teratocarcinoma cells. Mechanism of chain growth. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 1;211(1):191–198. doi: 10.1042/bj2110191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roboz J., Greaves J., Silides D., Chahinian A. P., Holland J. F. Hyaluronic acid content of effusions as a diagnostic aid for malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1850–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomida M., Koyama H., Ono T. Effects of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and serum on synthesis of hyaluronic acid in confluent rat fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):539–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1620539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomida M., Koyama H., Ono T. Induction of hyaluronic acid synthetase activity in rat fibroblasts by medium change of confluent cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Aug;86(1):121–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Biswas C., Gross J. Hyaluronate and invasiveness of the rabbit V2 carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6299–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Munaim S. I., Welles S., Knudson C. B. Hyaluronate-cell interactions and growth factor regulation of hyaluronate synthesis during limb development. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:138–285. doi: 10.1002/9780470513774.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S. J., Hawkes S. P. The effect of the tumor promoter, phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), on hyaluronic acid (HA) synthesis by chicken embryo fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Oct 15;148(2):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versnel M. A., Claesson-Welsh L., Hammacher A., Bouts M. J., van der Kwast T. H., Eriksson A., Willemsen R., Weima S. M., Hoogsteden H. C., Hagemeijer A. Human malignant mesothelioma cell lines express PDGF beta-receptors whereas cultured normal mesothelial cells express predominantly PDGF alpha-receptors. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):2005–2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versnel M. A., Hagemeijer A., Bouts M. J., van der Kwast T. H., Hoogsteden H. C. Expression of c-sis (PDGF B-chain) and PDGF A-chain genes in ten human malignant mesothelioma cell lines derived from primary and metastatic tumors. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):601–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxler B., Eisenstein R., Battifora H. Electrophoresis of tissue glycosaminoglycans as an aid in the diagnosis of mesotheliomas. Cancer. 1979 Jul;44(1):221–227. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197907)44:1<221::aid-cncr2820440136>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


