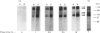Abstract
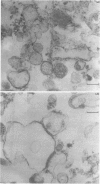
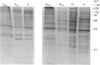
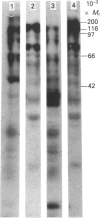
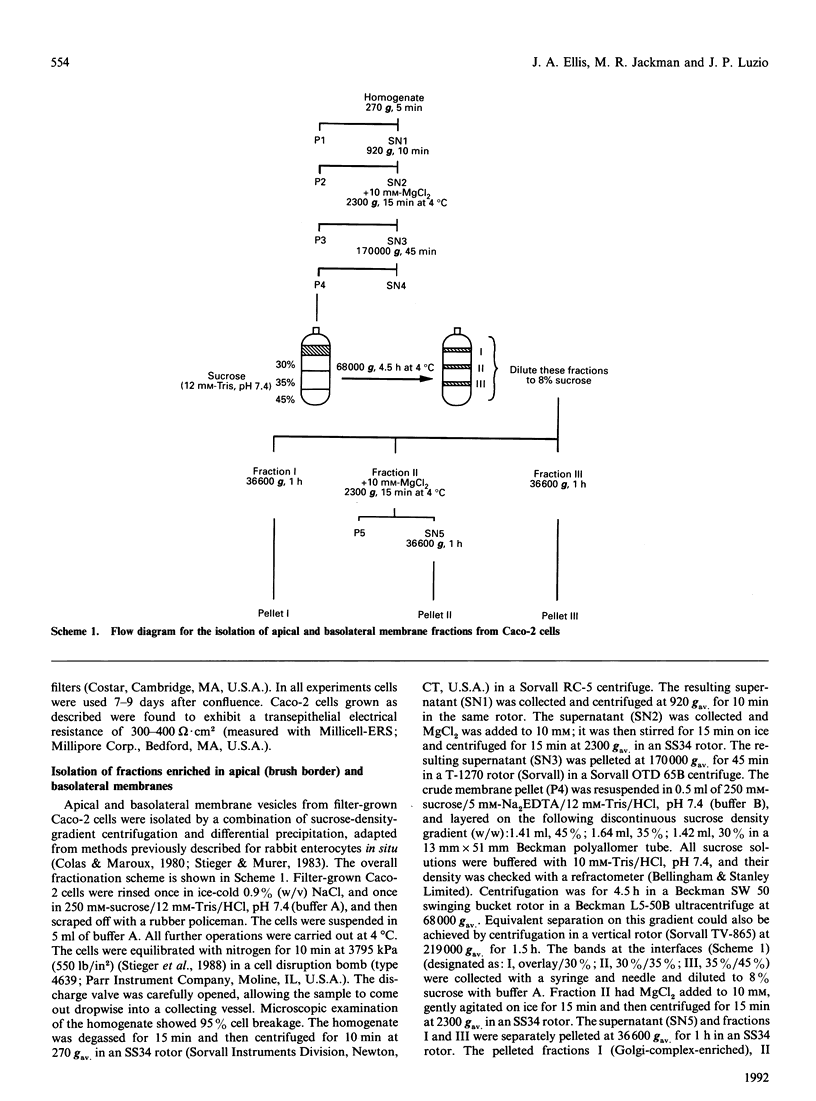
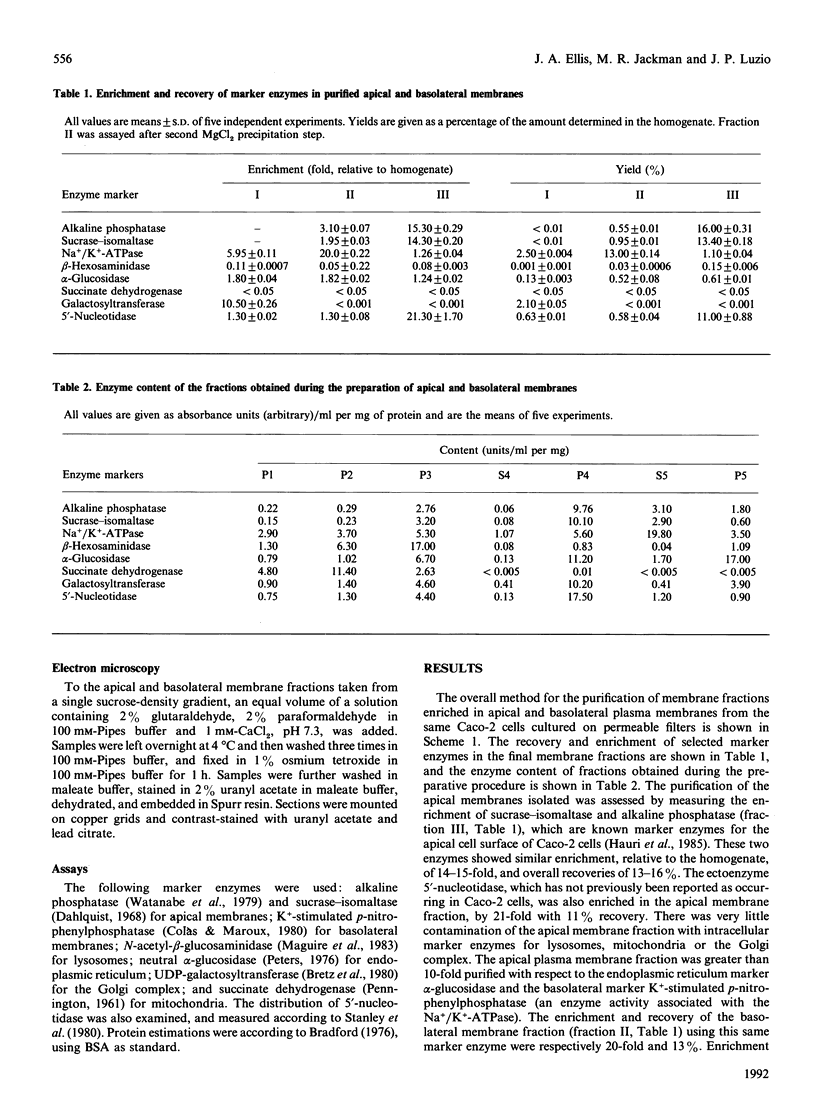
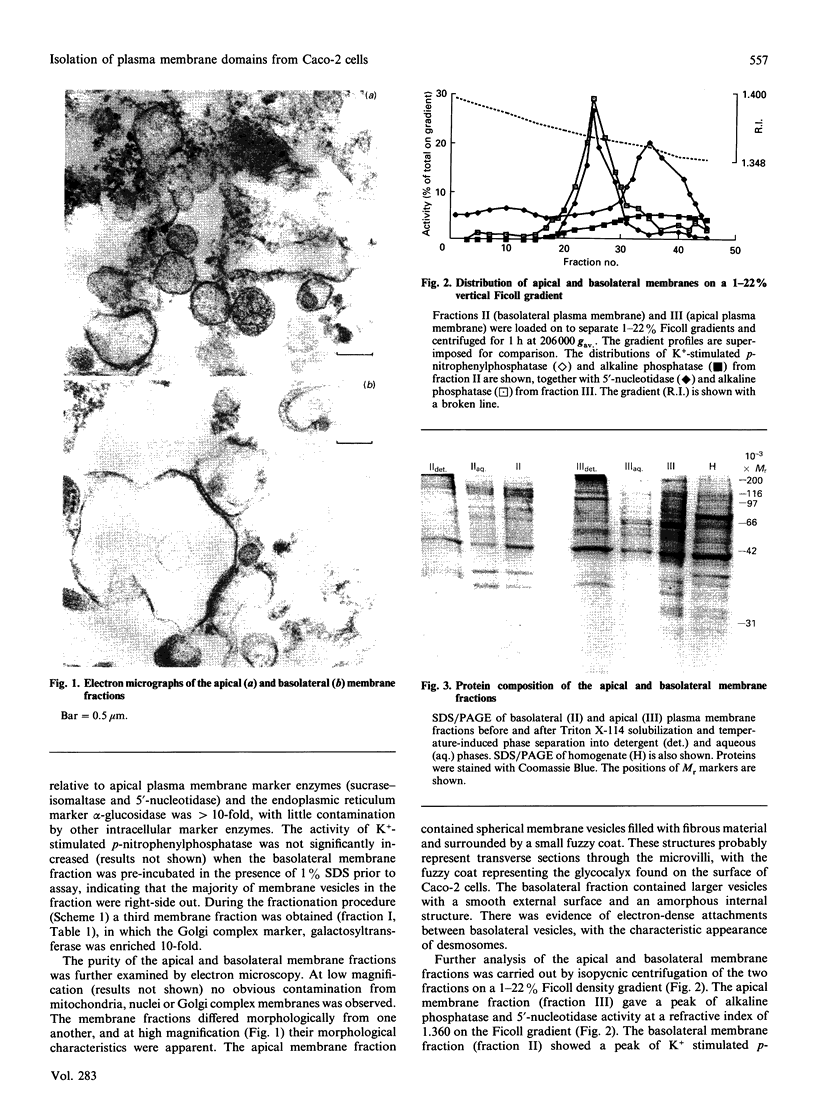
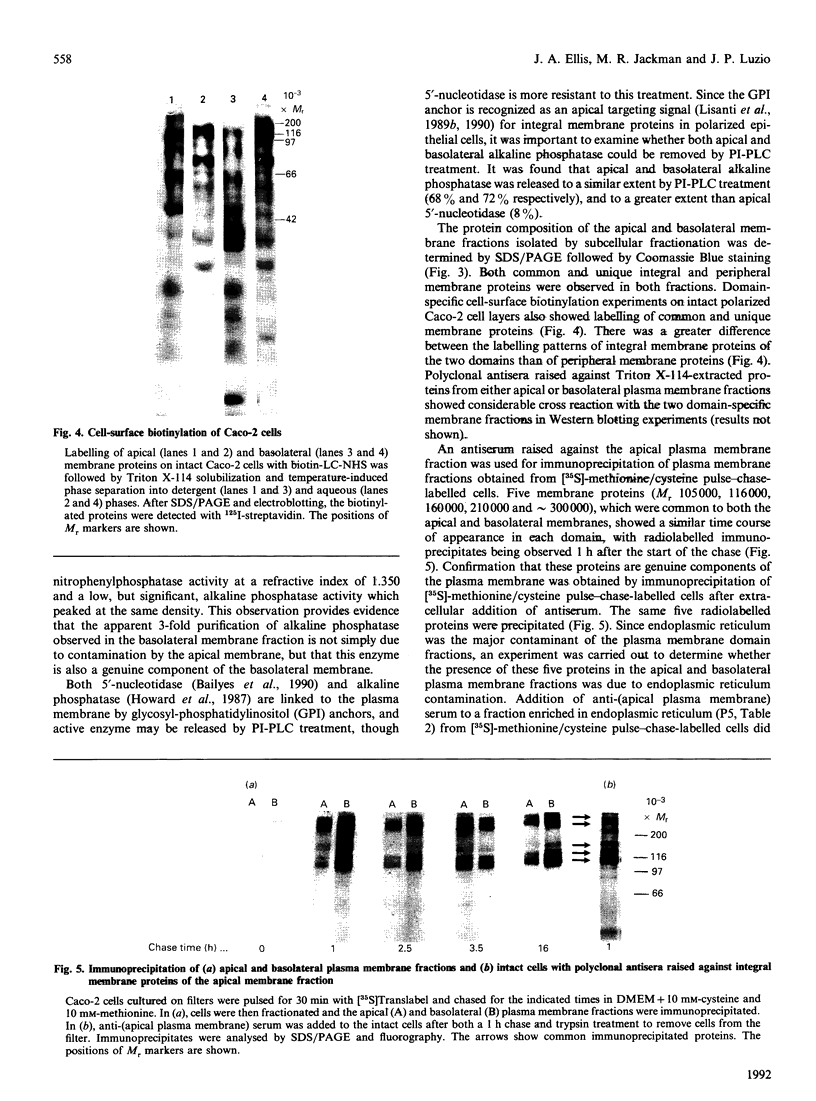
A subcellular fractionation method to isolate simultaneously apical and basolateral plasma membrane fractions from the human adenocarcinoma cell line Caco-2, grown on filter supports, is described. The method employs sucrose-density-gradient centrifugation and differential precipitation. The apical membrane fraction was enriched 14-fold in sucrase-isomaltase and 21-fold in 5'-nucleotidase compared with the homogenate. The basolateral membrane fraction was enriched 20-fold relative to the homogenate in K(+)-stimulated p-nitrophenylphosphatase. Alkaline phosphatase was enriched 15-fold in the apical membrane fraction and 3-fold in the basolateral membrane fraction. Analytical density-gradient centrifugation showed that this enzyme was a true constituent of both fractions, and experiments measuring alkaline phosphatase release following treatment with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C showed that in both membrane fractions the enzyme was glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked. There was very little contamination of either membrane fraction by marker enzymes of the Golgi complex, mitochondria or lysosomes. Both membrane fractions were greater than 10-fold purified with respect to the endoplasmic reticulum marker enzyme alpha-glucosidase. Protein composition analysis of purified plasma membrane fractions together with domain-specific cell surface biotinylation experiments revealed the presence of both common and unique integral membrane proteins in each plasma membrane domain. The post-synthetic transport of endogenous integral plasma membrane proteins was examined using the devised subcellular fractionation procedure in conjunction with pulse-chase labelling experiments and immunoprecipitation. Five common integral membrane proteins immunoprecipitated by an antiserum raised against a detergent extract of the apical plasma membrane fraction were delivered with the same time course to each cell-surface domain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnen D. J., Mircheff A. K., Santiago N. A., Yoshioka C., Gray G. M. Intestinal surface aminooligopeptidase. Distinct molecular forms during assembly on intracellular membranes in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5960–5966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailyes E. M., Ferguson M. A., Colaco C. A., Luzio J. P. Inositol is a constituent of detergent-solubilized immunoaffinity-purified rat liver 5'-nucleotidase. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):907–909. doi: 10.1042/bj2650907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Feracci H. M., Stieger B., Hubbard A. L. Biogenesis of the rat hepatocyte plasma membrane in vivo: comparison of the pathways taken by apical and basolateral proteins using subcellular fractionation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1241–1251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Hubbard A. L. Plasma membrane protein sorting in epithelial cells: do secretory pathways hold the key? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 May;13(5):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch W. J., Mullock B. M., Luzio J. P. Rapid subcellular fractionation of the rat liver endocytic compartments involved in transcytosis of polymeric immunoglobulin A and endocytosis of asialofetuin. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):311–315. doi: 10.1042/bj2440311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretz R., Bretz H., Palade G. E. Distribution of terminal glycosyltransferases in hepatic Golgi fractions. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):87–101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändli A. W., Parton R. G., Simons K. Transcytosis in MDCK cells: identification of glycoproteins transported bidirectionally between both plasma membrane domains. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2909–2921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colas B., Maroux S. Simultaneous isolation of brush border and basolateral membrane from rabbit enterocytes. Presence of brush border hydrolases in the basolateral membrane of rabbit enterocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 4;600(2):406–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh J. M., Orfeo T. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):221–226. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. D., Berger J., Gerber L., Familletti P., Udenfriend S. Characterization of the phosphatidylinositol-glycan membrane anchor of human placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6055–6059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Devaney E., Gruenberg J. Subcellular fractionation of tissue culture cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):44–47. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Quaroni A., Nichols B., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenetic pathways of plasma membrane proteins in Caco-2, a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Caras I. W., Davitz M. A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. A glycophospholipid membrane anchor acts as an apical targeting signal in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2145–2156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Le Bivic A., Sargiacomo M., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Steady-state distribution and biogenesis of endogenous Madin-Darby canine kidney glycoproteins: evidence for intracellular sorting and polarized cell surface delivery. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2117–2127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Saltiel A. R. Emerging functional roles for the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchor. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jul;117(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01871561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire G. A., Docherty K., Hales C. N. Sugar transport in rat liver lysosomes. Direct demonstration by using labelled sugars. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 15;212(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2120211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Brauchbar M., Bucher K., Hauri H. P. Sorting of endogenous plasma membrane proteins occurs from two sites in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Stieger B., Klumperman J., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Endocytosis, recycling, and lysosomal delivery of brush border hydrolases in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3503–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moktari S., Feracci H., Gorvel J. P., Mishal Z., Rigal A., Maroux S. Subcellular fractionation and subcellular localization of aminopeptidase N in the rabbit enterocytes. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(1):53–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01870895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J. Analytical subcellular fractionation of jejunal biopsy specimens: methodology and characterization of the organelles in normal tissue. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Dec;51(6):557–574. doi: 10.1042/cs0510557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Lisanti M., Graeve L., Le Bivic A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Integral and peripheral protein composition of the apical and basolateral membrane domains in MDCK cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Mar;107(3):277–286. doi: 10.1007/BF01871942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalera V., Storelli C., Storelli-Joss C., Haase W., Murer H. A simple and fast method for the isolation of basolateral plasma membranes from rat small-intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):177–181. doi: 10.1042/bj1860177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Wandinger-Ness A. Polarized sorting in epithelia. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90357-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Edwards M. R., Luzio J. P. Subcellular distribution and movement of 5'-nucleotidase in rat cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):59–69. doi: 10.1042/bj1860059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Matter K., Baur B., Bucher K., Höchli M., Hauri H. P. Dissection of the asynchronous transport of intestinal microvillar hydrolases to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1853–1861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Murer H. Heterogeneity of brush-border-membrane vesicles from rat small intestine prepared by a precipitation method using Mg/EGTA. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe F., Takano M., Tanaka F., Amino N., Hayashi C., Miyai K. The analysis of alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme using 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate as substrate on a cellulose acetate membrane. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Feb 1;91(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M., Neumeier M. M., Quaroni A., Kirsch K. Synthesis of plasmalemmal glycoproteins in intestinal epithelial cells. Separation of Golgi membranes from villus and crypt cell surface membranes; glycosyltransferase activity of surface membrane. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):722–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener H., Turnheim K., van Os C. H. Rabbit distal colon epithelium: I. Isolation and characterization of basolateral plasma membrane vesicles from surface and crypt cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Sep;110(2):147–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01869470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcook S., Williamson I., Hassan I., Mackay M. Isolation and characterisation of clones from the Caco-2 cell line displaying increased taurocholic acid transport. J Cell Sci. 1991 Mar;98(Pt 3):323–332. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]