Abstract
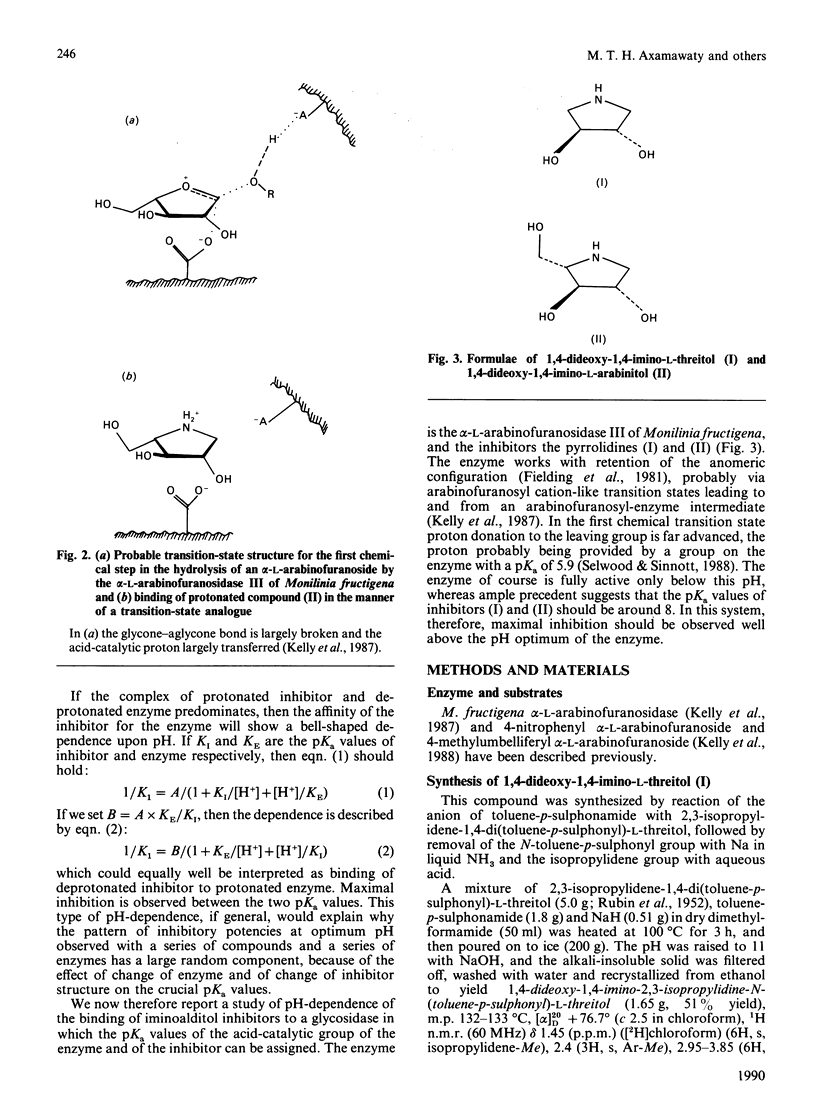
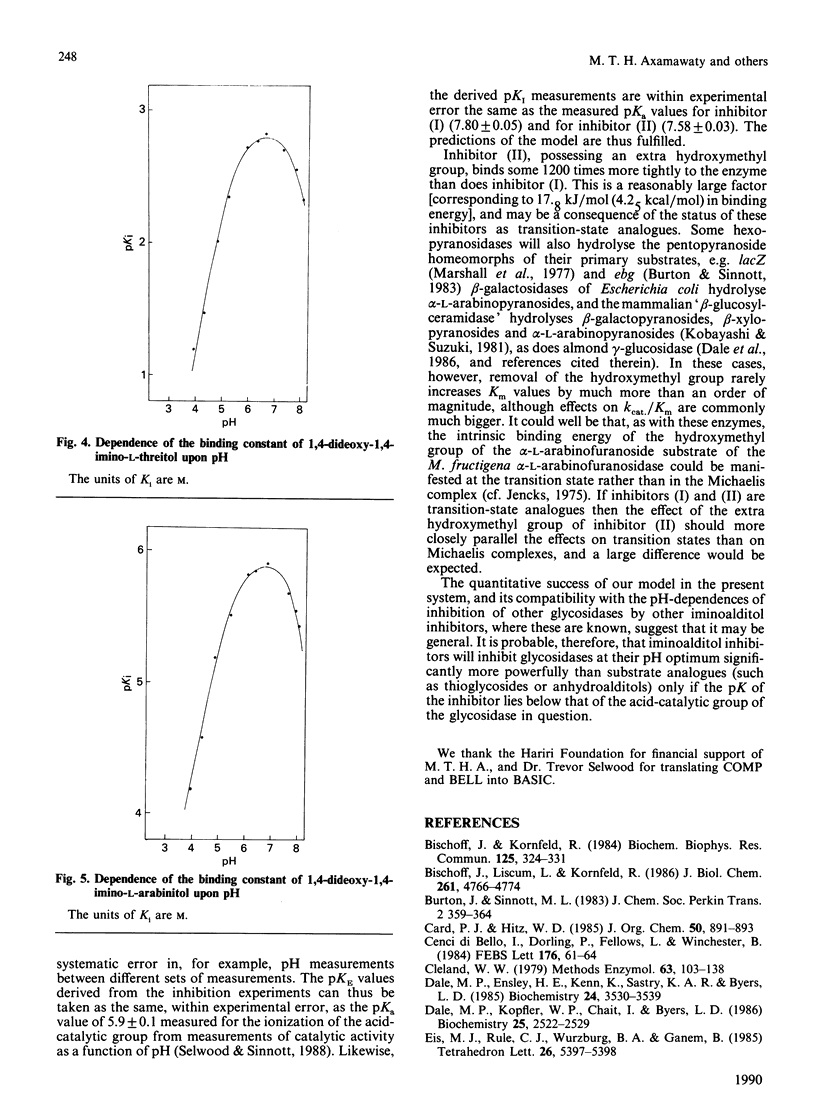
1. 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino-L-threitol was synthesized and the synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-L-arabinitol was improved. 2. Both compounds are competitive inhibitors of Monilinia fructigena alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase III, the additional hydroxymethyl group in the arabinitol contributing about 17.8 kj/mol (4.25 kcal/mol) to the Gibbs free energy of binding. 3. The affinities (1/Ki) of both compounds vary with pH in a classical bell-shaped way, the pKa value being that of the acid-catalytic group on the enzyme [5.9; Selwood & Sinnott (1988) Biochem. J. 254, 899-901] and the pKb values being those of the free inhibitors, 7.6 and 7.8 respectively. 4. On the basis of these and literature data we suggest that efficient inhibition of a glycosidase at its pH optimum by an appropriate iminoalditol will be found when the pKa of the iminoalditol is below that of the acid-catalytic group of the target enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bischoff J., Kornfeld R. The effect of 1-deoxymannojirimycin on rat liver alpha-mannosidases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):324–331. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J., Liscum L., Kornfeld R. The use of 1-deoxymannojirimycin to evaluate the role of various alpha-mannosidases in oligosaccharide processing in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4766–4774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenci di Bello I., Dorling P., Fellows L., Winchester B. Specific inhibition of human beta-D-glucuronidase and alpha-L-iduronidase by a trihydroxy pipecolic acid of plant origin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80911-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:103–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. P., Ensley H. E., Kern K., Sastry K. A., Byers L. D. Reversible inhibitors of beta-glucosidase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3530–3539. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. P., Kopfler W. P., Chait I., Byers L. D. Beta-glucosidase: substrate, solvent, and viscosity variation as probes of the rate-limiting steps. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2522–2529. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Szumilo T., Sanford B. A., Sharpless K. B., Adams C. Effect of isomers of swainsonine on glycosidase activity and glycoprotein processing. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2502–2510. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanozet G., Pircher H. P., Vanni P., Oesch B., Semenza G. An example of enzyme hysteresis. The slow and tight interaction of some fully competitive inhibitors with small intestinal sucrase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3703–3711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Tsuruoka T., Ito T., Niida T. Structure and synthesis of nojirimycin. Tetrahedron. 1968 Mar;24(5):2125–2144. doi: 10.1016/0040-4020(68)88115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama M., Takahashi T., Inokuchi N., Koyama T., Irie M. Inhibition of glucoamylases from a Rhizopus sp. and Aspergillus saitoi by aminoalcohol derivatives. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):341–347. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jencks W. P. Binding energy, specificity, and enzymic catalysis: the circe effect. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:219–410. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. A., Sinnott M. L., Herrchen M. Purification and mechanistic properties of an extracellular alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from Monilinia fructigena. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj2450843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby A. J. Mechanism and stereoelectronic effects in the lysozyme reaction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(4):283–315. doi: 10.3109/10409238709086959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Suzuki K. The glycosylceramidase in the murine intestine. Purification and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7768–7773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuszmann J., Kiss L. Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-glucitol, a glucosidase inhibitor. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Sep 15;153(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalégerie P., Legler G., Yon J. M. The use of inhibitors in the study of glycosidases. Biochimie. 1982 Nov-Dec;64(11-12):977–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Jülich E. Synthesis of 5-amino-5-deoxy-D-mannopyranose and 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-D-mannitol, and inhibition of alpha- and beta-D-mannosidases. Carbohydr Res. 1984 May 15;128(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Pohl S. Synthesis of 5-amino-5-deoxy-D-galactopyranose and 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-D-galactitol, and their inhibition of alpha- and beta-D-galactosidases. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Nov 1;155:119–129. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molyneux R. J., Roitman J. N., Dunnheim G., Szumilo T., Elbein A. D. 6-Epicastanospermine, a novel indolizidine alkaloid that inhibits alpha-glucosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Dec;251(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul R., Chambers J. P., Molyneux R. J., Elbein A. D. Castanospermine, a tetrahydroxylated alkaloid that inhibits beta-glucosidase and beta-glucocerebrosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):593–597. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul R., Molyneux R. J., Elbein A. D. Studies on the mechanism of castanospermine inhibition of alpha- and beta-glucosidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):668–675. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwood T., Sinnott M. L. One-proton catalysis by the alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase III of Monilinia fructigena. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):899–901. doi: 10.1042/bj2540899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Broquist H. P., Touster O. Marked differences in the swainsonine inhibition of rat liver lysosomal alpha-D-mannosidase, rat liver Golgi mannosidase II, and jack bean alpha-D-mannosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90643-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Harris T. M., Touster O. Swainsonine inhibits the biosynthesis of complex glycoproteins by inhibition of Golgi mannosidase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7936–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


