Abstract
NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase is known to be located on two distinct membranes, i.e. endoplasmic reticulum and outer mitochondrial membranes. The endoplasmic-reticulum-associated form of the enzyme contains myristic acid in an amide linkage to its N-terminal glycine [Ozols, Carr & Strittmatter (1984) J. Biol. Chem. 259, 13349-13354]. To investigate whether the dual subcellular localization of the reductase corresponds to a difference in fatty acylation, the enzyme was purified from well-characterized rat liver microsomal and mitochondrial fractions and analysed by a new quantitative analytical procedure. The purified reductases were run on SDS/polyacrylamide gels and blotted on to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. The reductase-containing bands were treated with hydroxylamine, and amide-linked fatty acids were then detached by acid hydrolysis. The detached fatty acids were extracted, derivatized and analysed as phenylacyl esters by reverse-phase h.p.l.c., and the protein content of the samples was determined by amino acid analysis of the acid hydrolysates. Myristic acid was found in both the microsomal and mitochondrial reductases in a molar ratio of 1:1 with protein. These results demonstrate for the first time the presence of a myristylated protein on outer mitochondrial membranes, and show that the microsomal and mitochondrial reductases are also identical in their fatty acylation.
Full text
PDF



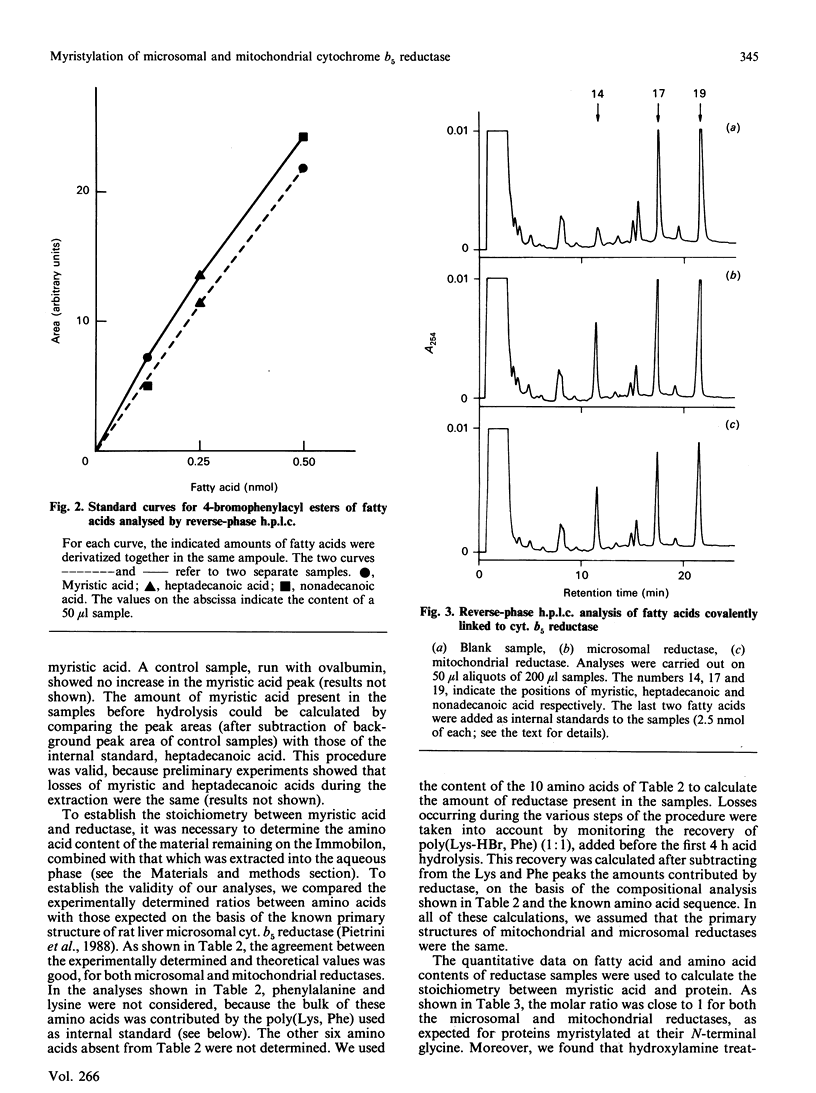
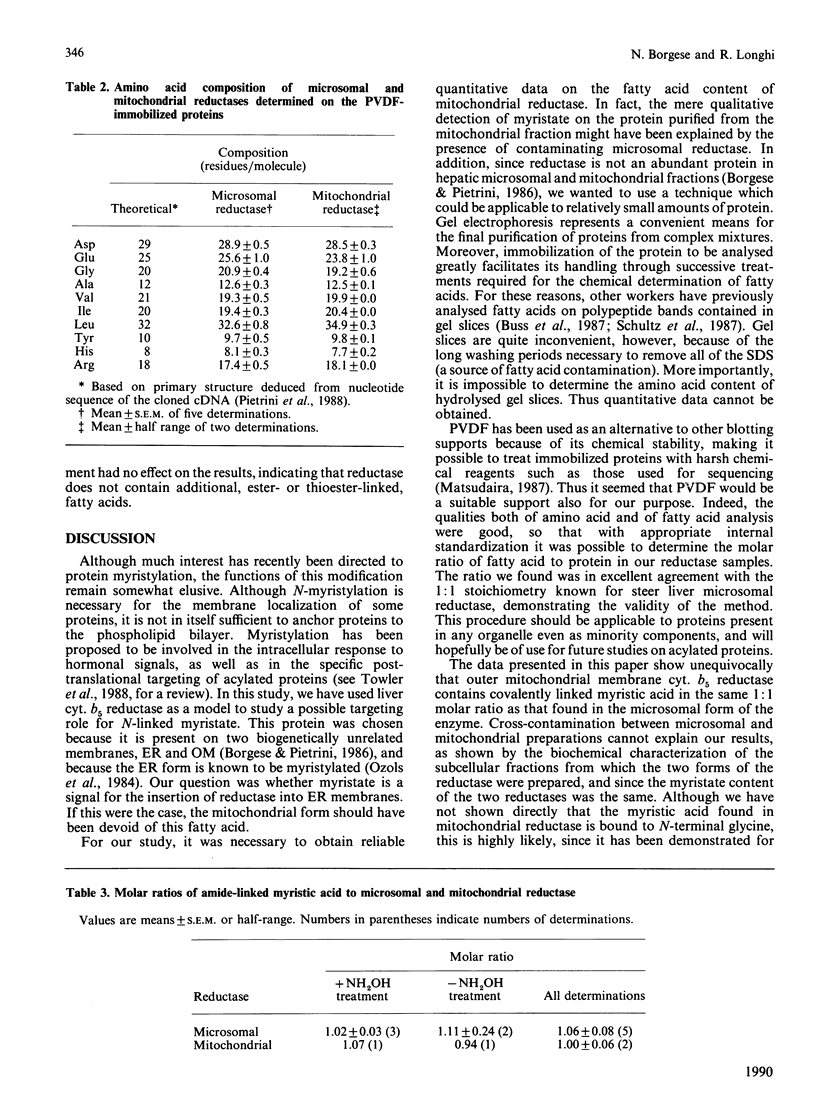

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews D. W., Lauffer L., Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Evidence for a two-step mechanism involved in assembly of functional signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):797–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese N., Gaetani S. In vitro synthesis and post-translational insertion into microsomes of the integral membrane protein, NADH-cytochrome b5 oxidoreductase. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1263–1269. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese N., Gaetani S. Site of synthesis of rat liver NADH--cytochrome b5 reductase, an integral membrane protein. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 7;112(2):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese N., Pietrini G. Distribution of the integral membrane protein NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase in rat liver cells, studied with a quantitative radioimmunoblotting assay. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):393–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2390393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese N., Pietrini G., Meldolesi J. Localization and biosynthesis of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase, an iontegral membrane protein, in rat liver cells. III. Evidence for the independent insertion and turnover the enzyme in various subcellular compartments. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):38–45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Der C. J., Solski P. A. The six amino-terminal amino acids of p60src are sufficient to cause myristylation of p21v-ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3960–3963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durst H. D., Milano M., Kikta E. J., Jr, Connelly S. A., Grushka E. Phenacyl esters of fatty acids via crown ether catalysts for enhanced ultraviolet detection in liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Sep;47(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1021/ac60361a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara S., Okada Y., Omura T. Evidence for molecular identity of microsomal and mitochondrial NADH-cytochrome b5 reductases of rat liver. J Biochem. 1978 Apr;83(4):1049–1059. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. M., Forde M. D., Lee M. C., Bucher D. J. Fluorometric microbore amino acid analyzer: the construction of an inexpensive, highly sensitive instrument using o-phthalaldehyde as a detection agent. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 15;96(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90585-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlhinney R. A., Pelly S. J., Chadwick J. K., Cowley G. P. Studies on the attachment of myristic and palmitic acid to cell proteins in human squamous carcinoma cell lines: evidence for two pathways. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1145–1152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Corte G., Pietrini G., Borgese N. Localization and biosynthesis of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase, an integral membrane protein, in rat liver cells. II. Evidence that a single enzyme accounts for the activity in its various subcellular locations. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):516–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Carr S. A., Strittmatter P. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase as myristic acid and the complete amino acid sequence of the membrane-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13349–13354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrini G., Carrera P., Borgese N. Two transcripts encode rat cytochrome b5 reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. A., Hultquist D. E. Purification of bovine liver microsomal NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase using affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 16;95(1):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90749-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Tsai S. C., Kung H. F., Oroszlan S., Moss J., Vaughan M. Hydroxylamine-stable covalent linkage of myristic acid in G0 alpha, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein of bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1234–1239. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90780-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz L., Strittmatter P. A form of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-cytochrome b 5 reductase containing both the catalytic site and an additional hydrophobic membrane-binding segment. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):793–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takesue S., Omura T. Solubilization of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase from liver microsomes by lysosomal digestion. J Biochem. 1970 Feb;67(2):259–266. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Acylation of proteins with myristic acid occurs cotranslationally. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1275–1278. doi: 10.1126/science.3685978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



