Abstract
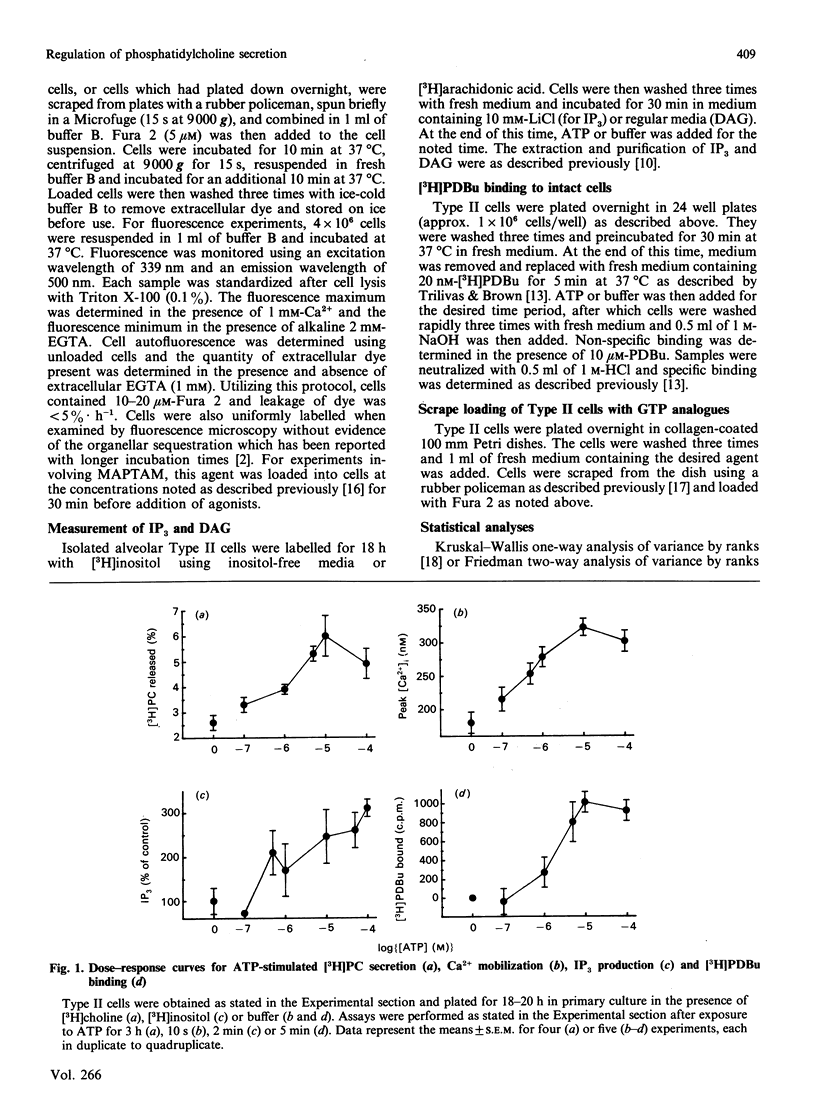
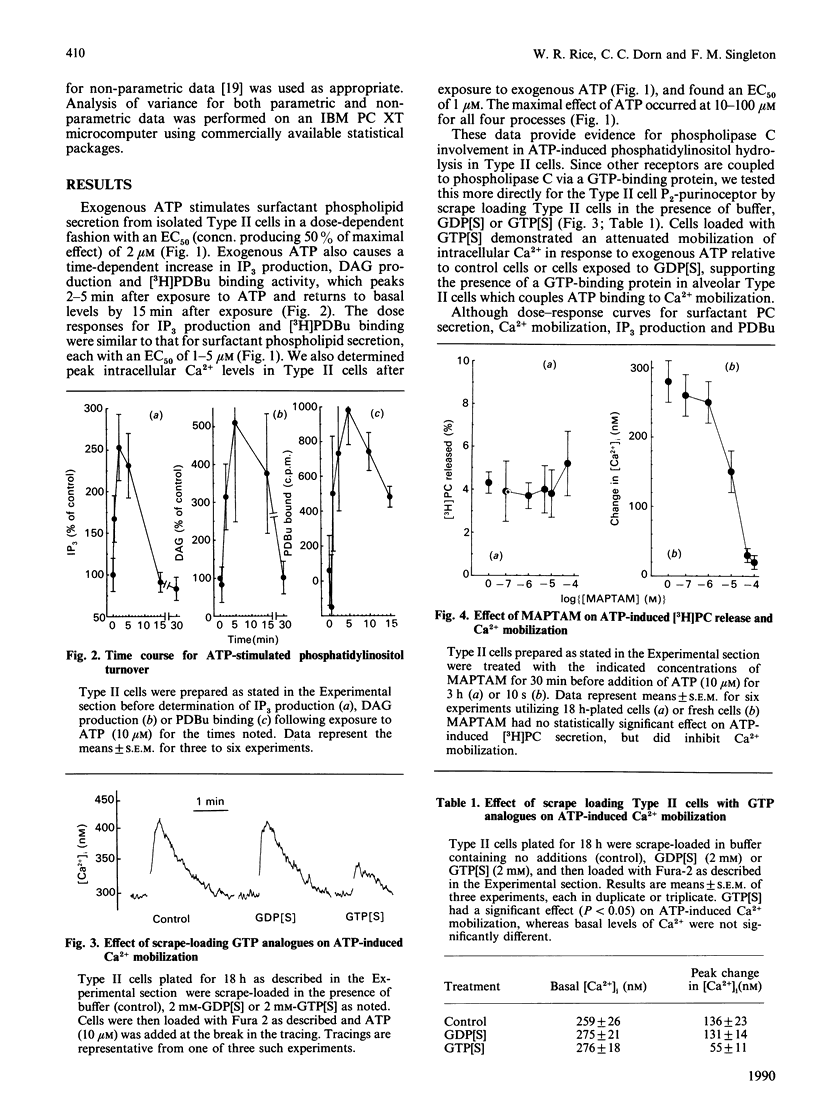
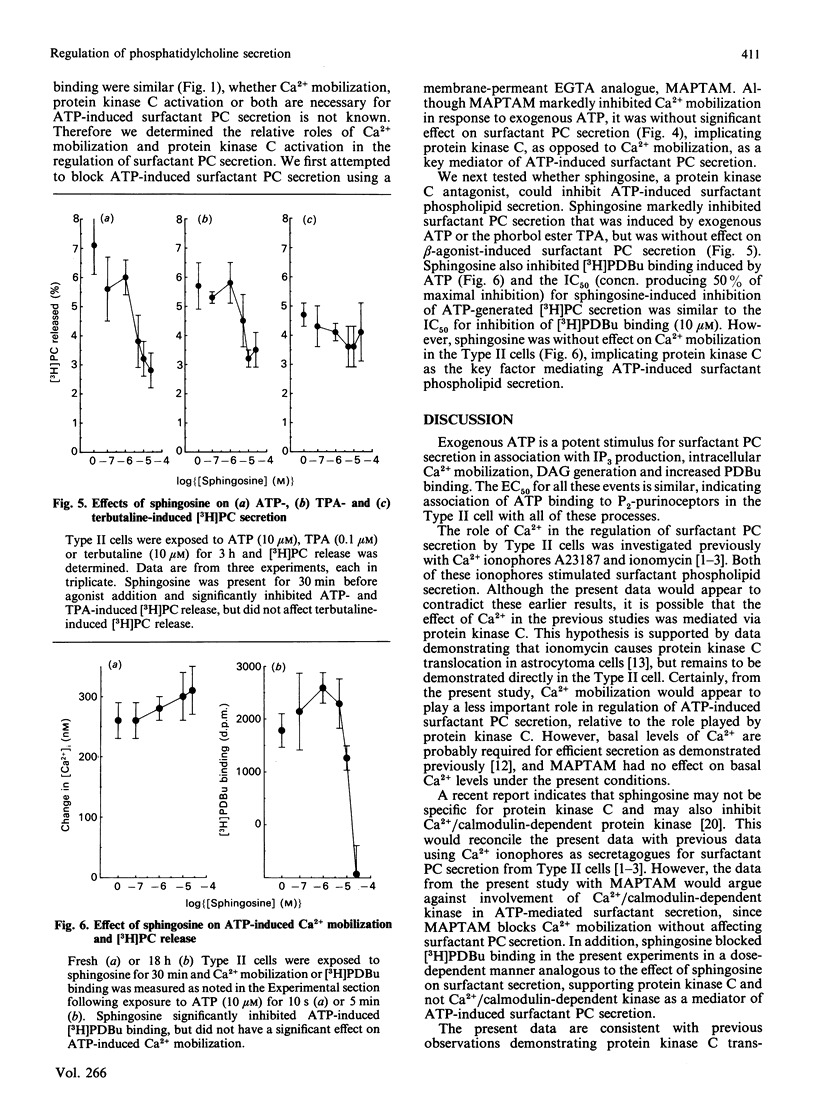
Ca2+ and protein kinase C have both been proposed as intracellular signals for subsequent phosphatidylcholine secretion by alveolar Type II cells. We have determined the relative roles of Ca2+ and protein kinase C in regulating surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion by utilizing exogenous ATP and the phorbol ester TPA (12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate) as secretagogues, along with MAPTAM to chelate intracellular Ca2+ and sphingosine to inhibit endogenous protein kinase C. Exposure of Type II cells to the P2-purinoceptor agonist, ATP, results in a dose-dependent increase in surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion from isolated alveolar Type II cells with an EC50 (concn. producing 50% of maximal response) of 2 microM. Administration of exogenous ATP to Type II cells also results in a dose-dependent increase in inositol trisphosphate production, Ca2+ mobilization and [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate ([3H]PDBu) binding as a measure of protein kinase C translocation. The EC50 in each case is 1-5 microM, indicating association of these events with surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion. Loading Type II cells with non-hydrolysable GTP analogue (GTP[S]) inhibited ATP-induced Ca2+ mobilization, supporting the hypothesis that Type II cell P2-purinoceptors are coupled to phospholipase C via a GTP-binding protein. The ATP-induced elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ was also inhibited by MAPTAM (a cell-permeant EGTA analogue) by 90%, but MAPTAM was without effect on surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion induced by ATP. Sphingosine inhibited both ATP- and TPA-induced surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion as well as [3H]PDBu binding with a similar IC50 (concn. producing 50% of maximal inhibition) (10 microM). Sphingosine did not affect surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion induced by terbutaline and did not have a significant effect on Ca2+ mobilization induced by exogenous ATP. These results are consistent with a prominent role for protein kinase C in regulation of P2-purinoceptor-induced surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion, and indicate that Ca2+ mobilization is not a necessary step for ATP-induced surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer J. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Kinetics of activation of phospholipase C by P2Y purinergic receptor agonists and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Dennis P. A., Griendling K. K., Diehl T. S., Davies P. F. GTP gamma S loading of endothelial cells stimulates phospholipase C and uncouples ATP receptors. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):C667–C673. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.5.C667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Gonzalez R. F., Marinari L. A., Mescher E. J., Hawgood S. The role of calcium in the secretion of surfactant by rat alveolar type II cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 27;877(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Gonzalez R., Williams M. C. An improved method for isolating type II cells in high yield and purity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):141–145. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., Cowen D. S., Meuller L. M. Activation of inositol phospholipid breakdown in HL60 cells by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Evidence for mediation by both pertussis toxin-sensitive and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18108–18117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R. Extracellular ATP activates polyphosphoinositide breakdown and Ca2+ mobilization in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 15;245(1):84–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan A. M., Rooney S. A. Purinoceptor agonists stimulate phosphatidylcholine secretion in primary cultures of adult rat type II pneumocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 13;917(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Schulman H. Sphingosine inhibits calmodulin-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15241–15244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Vosshall L. B., Haines K. A., Wilkenfeld C., Lundquist K. F., Weissmann G. Activation of the human neutrophil by calcium-mobilizing ligands. II. Correlation of calcium, diacyl glycerol, and phosphatidic acid generation with superoxide anion generation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11098–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson E. A., Goldstein D., Brown J. H. Muscarinic receptor activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Relationship to phosphoinositide hydrolysis and diacylglycerol metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14748–14754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Williams J. A. Multiple sources of 1,2-diacylglycerol in isolated rat pancreatic acini stimulated by cholecystokinin. Involvement of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate and phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14729–14734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Murphy R. F., Lanni F., Taylor D. L. A method for incorporating macromolecules into adherent cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1556–1564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. A., Fujiki T., Rossi M. W., Korchak H. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Influence of calcium on the subcellular distribution of protein kinase C in human neutrophils. Extraction conditions determine partitioning of histone-phosphorylating activity and immunoreactivity between cytosol and particulate fractions. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8361–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pian M. S., Dobbs L. G., Düzgünes N. Positive correlation between cytosolic free calcium and surfactant secretion in cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 2;960(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Burhans M., Wispé J. R. Effect of oxygen exposure on ATP content of rat bronchoalveolar lavage. Pediatr Res. 1989 Apr;25(4):396–398. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198904000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Singleton F. M. P2-purinoceptors regulate surfactant secretion from rat isolated alveolar type II cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Singleton F. M. P2Y-purinoceptor regulation of surfactant secretion from rat isolated alveolar type II cells is associated with mobilization of intracellular calcium. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;91(4):833–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Effect of secretagogues on cytoplasmic free calcium in alveolar type II epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):C679–C686. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.5.C679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Involvement of protein kinase C in pulmonary surfactant secretion from alveolar type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12725–12729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trilivas I., Brown J. H. Increases in intracellular Ca2+ regulate the binding of [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate to intact 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3102–3107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D., Buckley S., Cosico L. P1 and P2 purinergic receptor signal transduction in rat type II pneumocytes. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Feb;66(2):901–905. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.2.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


