Abstract
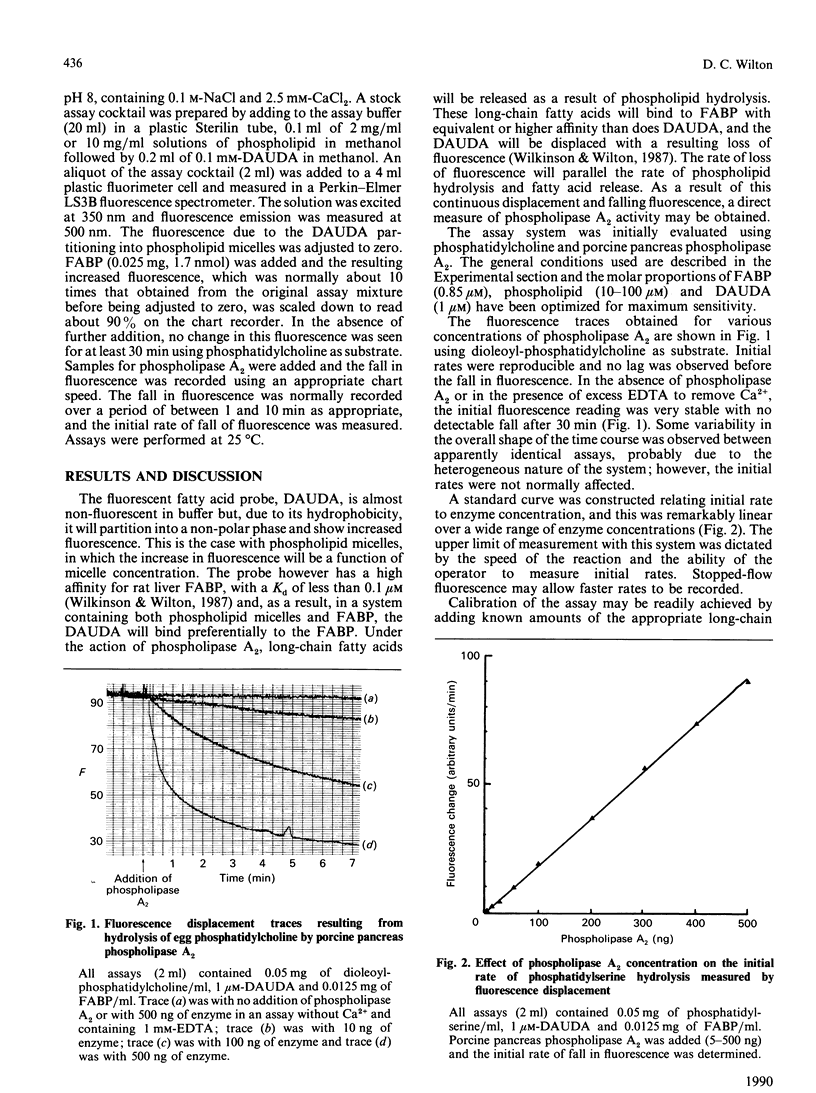
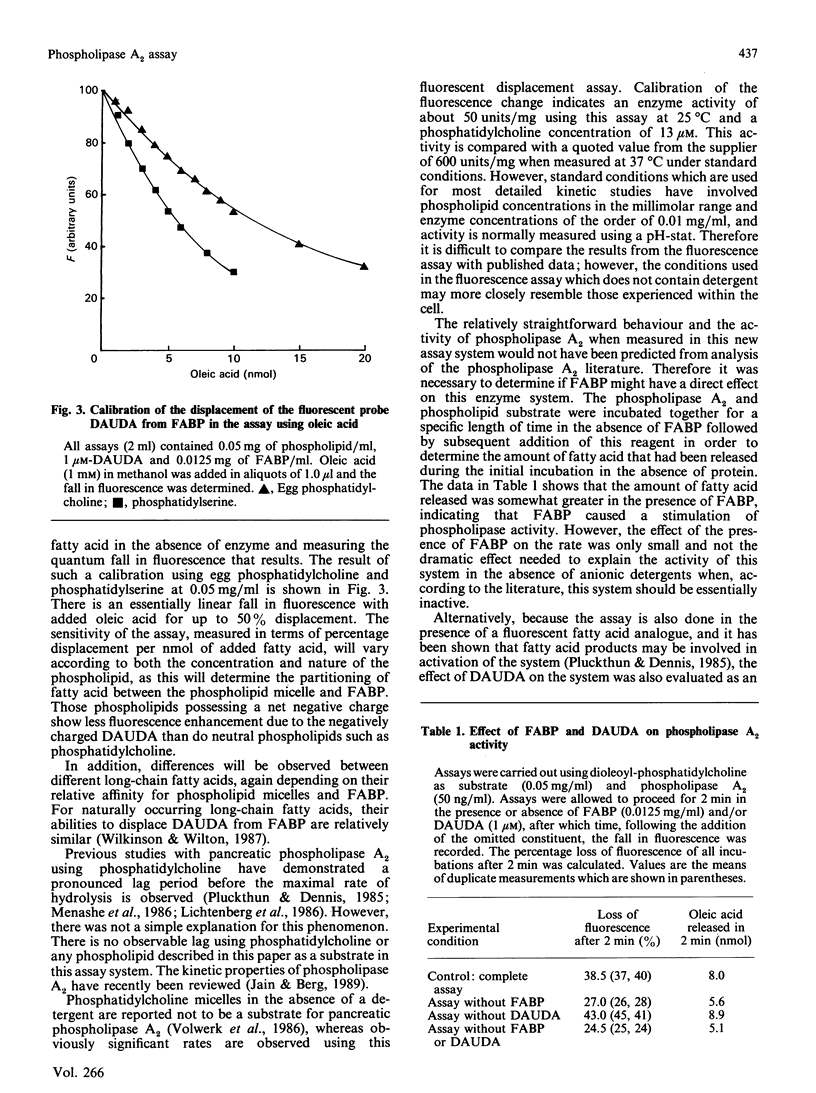
1. A new continuous fluorescence assay for phospholipase A2 is described which involves the displacement of the highly fluorescent fatty-acid probe 11-(dansylamino)undecanoic acid from rat liver fatty-acid-binding protein by long-chain fatty acids released as a result of phospholipase A2-catalysed hydrolysis of phospholipids. The initial rate of decrease in fluorescence is linearly related to enzyme activity. 2. The assay will detect enzyme activity down to about 10 pmol/min per ml and gives a linear response up to about 10 nmol/min per ml. 3. The assay will work with all phospholipids that have been tested including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylglycerol. Substrates carrying a net negative charge showed the highest rates of hydrolysis. 4. The assay will work, in principle, with an enzyme catalysing the release of long-chain fatty acids from a fatty-acylated substrate. This has been confirmed with pancreatic lipase and cholesterol esterase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crompton M. R., Moss S. E., Crumpton M. J. Diversity in the lipocortin/calpactin family. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A., Powell M., Glenney J. R., Jr Inhibition of phospholipase A2 by "lipocortins" and calpactins. An effect of binding to substrate phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1698–1705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Schlaepfer D. D., Burgess W. H. Characterization of lipocortin I and an immunologically unrelated 33-kDa protein as epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase substrates and phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6921–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Berg O. G. The kinetics of interfacial catalysis by phospholipase A2 and regulation of interfacial activation: hopping versus scooting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 3;1002(2):127–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B. Ca2+-dependent phospholipid- (and membrane-) binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6645–6653. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Swaisgood M. H., Ramos B. V., Steck T. L. Plasma membranes contain half the phospholipid and 90% of the cholesterol and sphingomyelin in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3786–3793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Romero G., Menashe M., Biltonen R. L. Hydrolysis of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine large unilamellar vesicles by porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5334–5340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menashe M., Romero G., Biltonen R. L., Lichtenberg D. Hydrolysis of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine small unilamellar vesicles by porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5328–5333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele L., Cordella-Miele E., Facchiano A., Mukherjee A. B. Novel anti-inflammatory peptides from the region of highest similarity between uteroglobin and lipocortin I. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):726–730. doi: 10.1038/335726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plückthun A., Dennis E. A. Activation, aggregation, and product inhibition of cobra venom phospholipase A2 and comparison with other phospholipases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11099–11106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait J. F., Gibson D., Fujikawa K. Phospholipid binding properties of human placental anticoagulant protein-I, a member of the lipocortin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7944–7949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volwerk J. J., Jost P. C., de Haas G. H., Griffith O. H. Activation of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2 by the presence of negative charges at the lipid-water interface. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1726–1733. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson T. C., Wilton D. C. Studies on fatty acid-binding proteins. The binding properties of rat liver fatty acid-binding protein. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):485–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2470485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson T. C., Wilton D. C. Studies on fatty acid-binding proteins. The detection and quantification of the protein from rat liver by using a fluorescent fatty acid analogue. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):419–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2380419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton D. C. Studies on fatty-acid-binding proteins. The purification of rat liver fatty-acid-binding protein and the role of cysteine-69 in fatty acid binding. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2610273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


