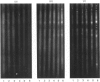
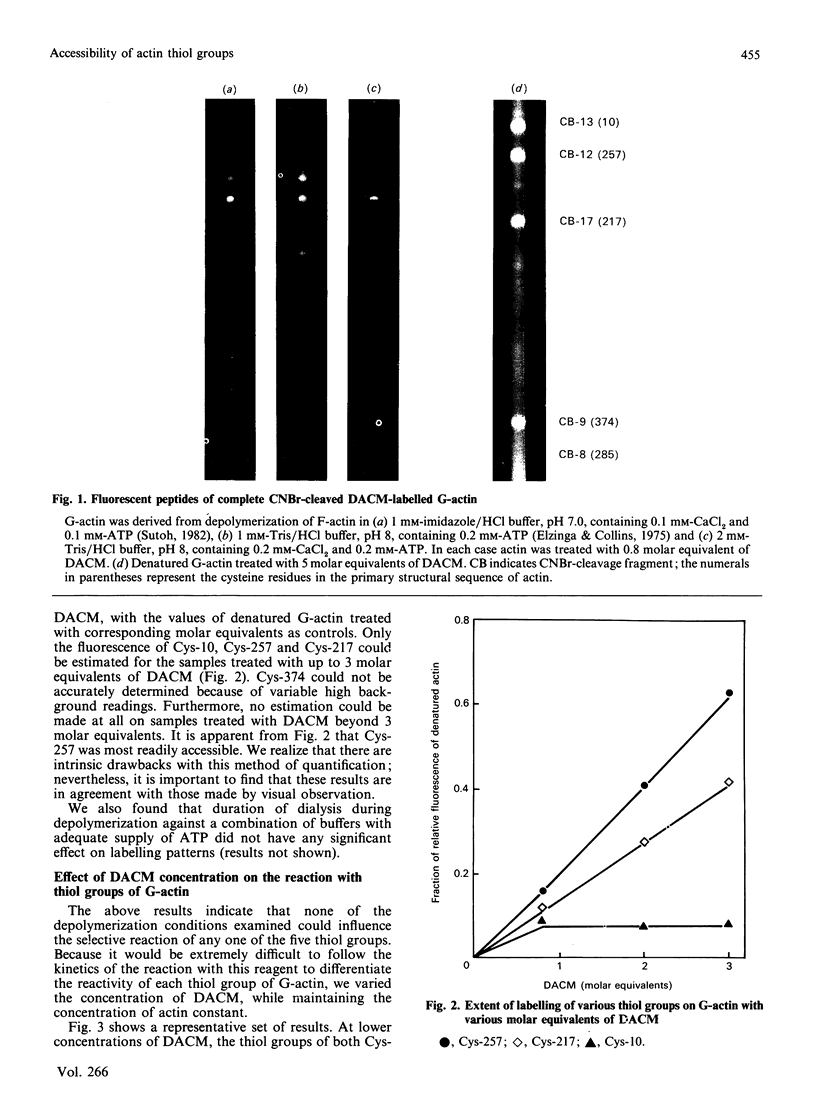
Abstract
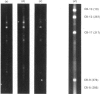
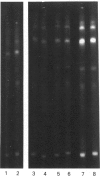
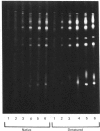
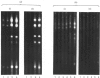
The accessibility of the cysteine residues of actin from rabbit muscles to the thiol-targeted reagent 7-dimethylamino-4-methyl-(N-maleimidyl)coumarin (DACM) was investigated. Under conditions where the actin is in the unpolymerized form (G-actin), the most reactive thiol group was Cys-257, suggesting that it was located on the surface of the actin molecule. The selective modification of Cys-374 for this reagent as reported by Sutoh [(1982) Biochemistry 21, 3654-3661] was not observed. Cys-10, Cys-217 and Cys-374 were much less reactive and only gradually became extensively modified when the concentration of DACM approached 5 molar equivalents of actin. Presumably these thiol groups were located further inward away from the surface or situated in a different environment that rendered them less reactive. On the other hand, Cys-285 was completely inaccessible and presumably was buried. The lack of preferential labelling of Cys-374 by DACM is incompatible with the finding with iodoacetic acid as the reagent as reported by Elzinga & Collins [(1975) J. Biol. Chem. 250, 5897-5905]. This discrepancy, however, might well be due to the different reagents employed. The DACM-G-actin largely retained its competence for polymerization. Upon polymerization of G-actin, practically all the thiol groups became inaccessible to DACM, suggesting that a drastic change occurred in the conformation of actin units in the transition of monomers to filamentous actin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender N., Fasold H., Kenmoku A., Middelhoff G., Volk K. E. The selective blocking of the polymerization reaction of striated muscle actin leading to a derivative suitable for crystallization. Modification of Tyr-53 by 5-diazonium-(1H)tetrazole. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):215–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Elzinga M. The primary structure of actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Completion and analysis of the amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5915–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Collins J. H., Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Complete amino-acid sequence of actin of rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Collins J. H. The primary structure of actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Five cyanogen bromide peptides, including the NH2 and COOH termini. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5897–5905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulstich H., Merkler I., Blackholm H., Stournaras C. Nucleotide in monomeric actin regulates the reactivity of the thiol groups. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1608–1612. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C., Lieberman D., Gilbert H. R. A fluorescent probe for conformational changes in skeletal muscle G-actin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):8991–8993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Yang Y. Z., Korn E. D. Polymerization of Acanthamoeba actin. Kinetics, thermodynamics, and co-polymerization with muscle actin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7474–7479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. ATP binding to a protease-resistant core of actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2742–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASAI M., OOSAWA F. REMOVAL OF NUCLEOTIDES FROM F-ACTIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:223–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno K., Morales M. F. Exposure of actin thiols by the removal of tightly held calcium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7904–7908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Actin polymerization and its regulation by proteins from nonmuscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):672–737. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):588–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Fluorimetry study of N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide-labelled F-actin. Local structural change of actin protomer both on polymerization and on binding of heavy meromyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Conti M. A., Adelstein R. S. Structural studies on rabbit skeletal muscle actin. Ordering of the peptides produced by cleavage with cyanogen bromide. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5890–5896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. I. Fluorimetric studies of actin labeled with dansyl aziridine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 30;185(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu R. C., Elzinga M. Partial amino acid sequence of brain actin and its homology with muscle actin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5801–5806. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusty C. J., Fasold H. Characterization of sulfhydryl groups of actin. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2933–2939. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Ue K. Proteolysis and structure of skeletal muscle actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Identification of myosin-binding sites on the actin sequence. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3654–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Cho J. Fluorescence lifetime quenching studies on the accessibilities of actin sulfhydryl sites. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2759–2765. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Rotational dynamics of spin-labeled F-actin in the sub-millisecond time range. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin amino-acid sequences. Comparison of actins from calf thymus, bovine brain, and SV40-transformed mouse 3T3 cells with rabbit skeletal muscle actin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):783–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of Physarum actin. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):720–721. doi: 10.1038/276720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of actin from chicken skeletal muscle actin and chicken gizzard smooth muscle actin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takamitsu S., Kanaoka Y. Fluorescent thiol reagents. XII. Fluorescent tracer method for protein SH groups using N-(7-dimethylamino-4-methyl coumarinyl) maleimide. An application to the proteins separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90381-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]