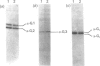
Abstract
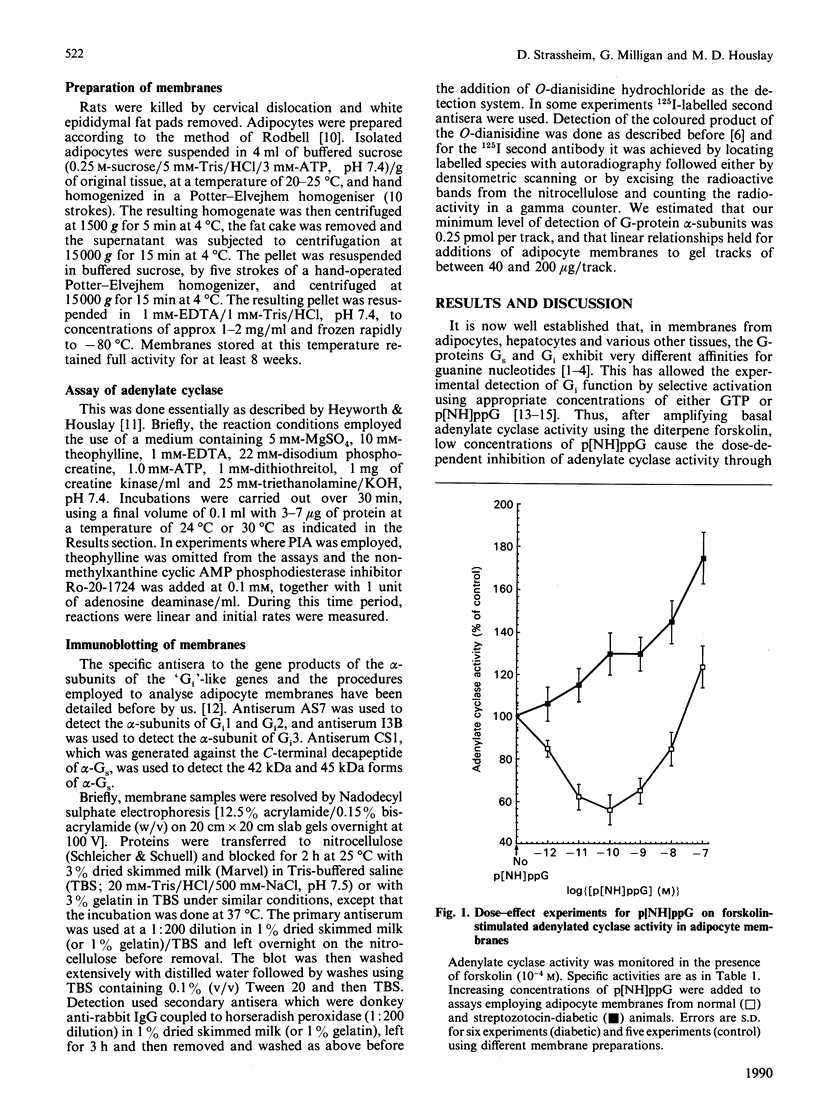
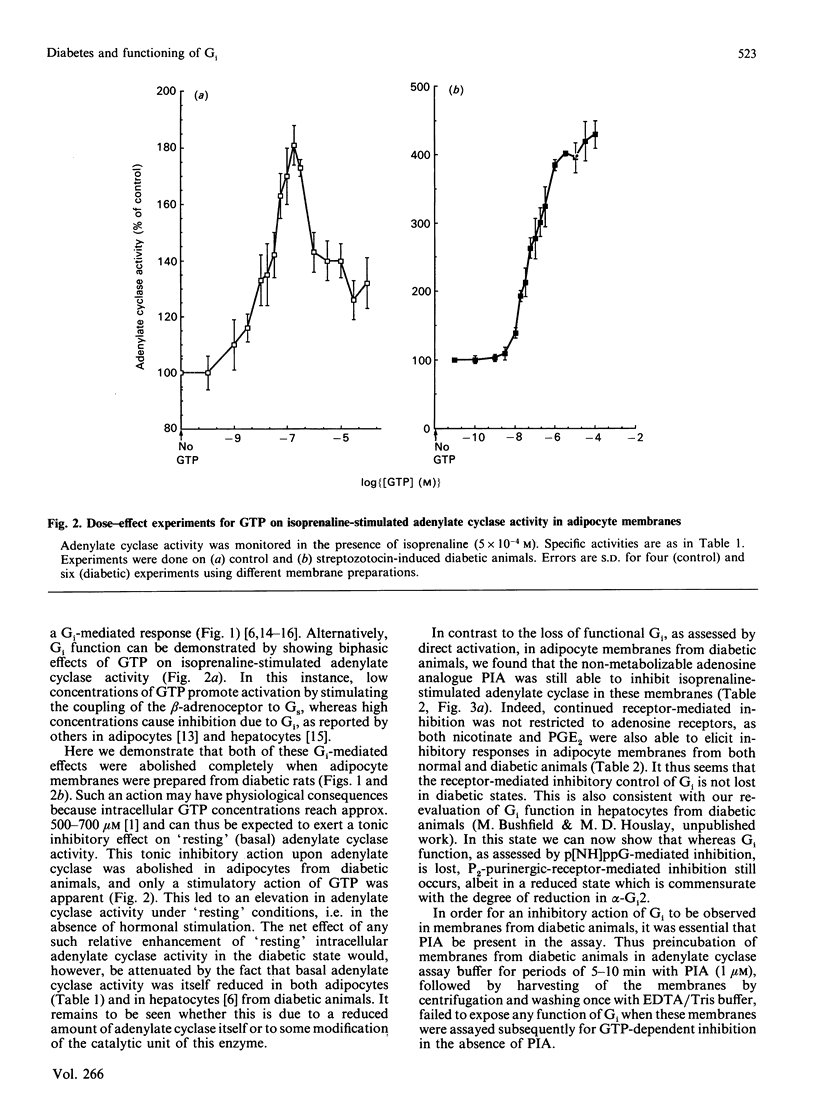
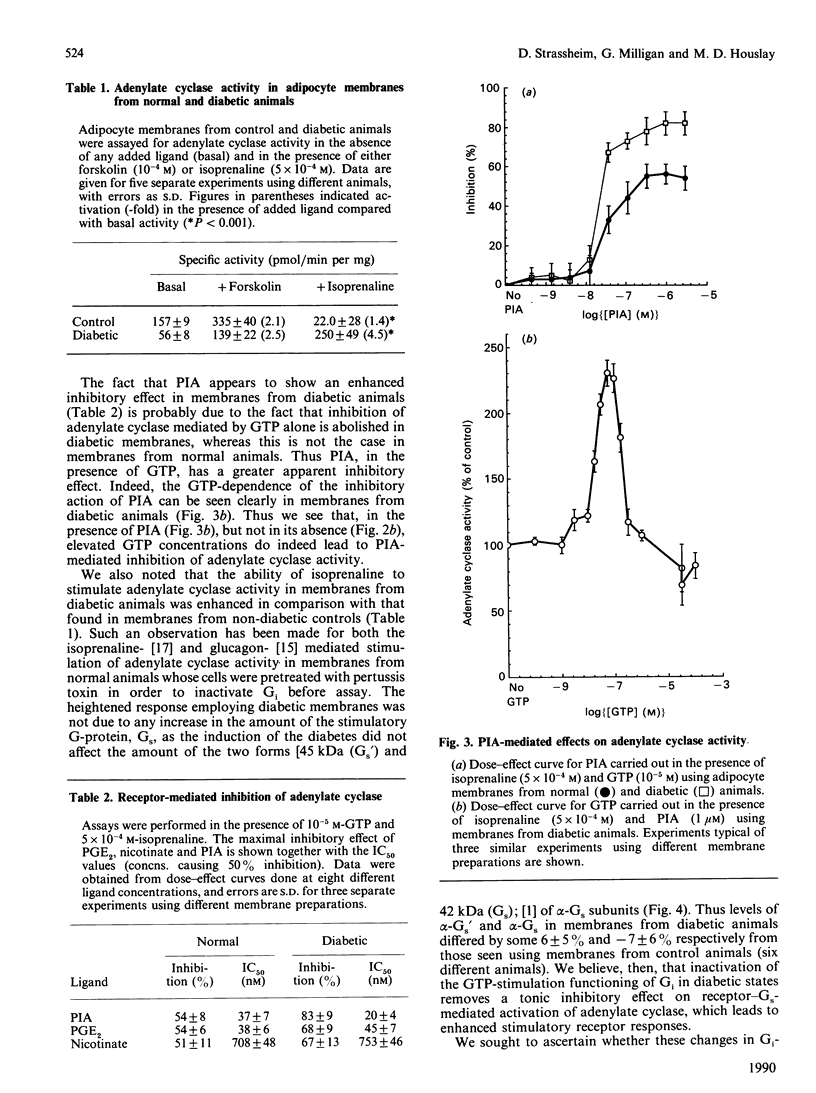
Adipocyte membranes from control rats exhibited a functional Gi (inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein) activity which could be assessed either by the inhibitory action of low concentrations of guanosine 5-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate (p[NH]ppG) upon forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity or by the inhibitory action of high concentrations of GTP upon isoprenaline-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. When membranes from animals made diabetic with streptozotocin were used, then both such inhibitory functions of Gi were abolished. In contrast, receptor-mediated inhibitory responses of Gi, effected by N6-phenylisopropyl (adenosine), prostaglandin E2 or nicotinate, were either unchanged or even apparently more effective in membranes from diabetic animals. Induction of diabetes did not cause any change in the adipocyte plasma membrane levels of the alpha, GTP-binding subunits of either Gi1 or Gi2 or of Gs (stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein), but elicited an increase in the level of alpha-Gi3. The induction of diabetes reduced the specific activity of adenylate cyclase in adipocyte membranes and enhanced the stimulatory effect of isoprenaline. It is suggested that diabetes causes selective changes in the functioning of Gi in adipocyte membranes which removes the tonic GTP-dependent inhibitory function of this G-protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bégin-Heick N. Absence of the inhibitory effect of guanine nucleotides on adenylate cyclase activity in white adipocyte membranes of the ob/ob mouse. Effect of the ob gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6187–6193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin-Heick N., Welsh J. The regulation of adenylate cyclase in liver membranes of lean and obese mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;59(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Olate J., Abramowitz J., Mattera R., Cook R. G., Birnbaumer L. Alpha i-3 cDNA encodes the alpha subunit of Gk, the stimulatory G protein of receptor-regulated K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6746–6750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M. Bimodal regulation of adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Londos C. GTP-dependent stimulation and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1982;6:309–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Houslay M. D. Treatment of streptozotocin-diabetic rats with metformin restores the ability of insulin to inhibit adenylate cyclase activity and demonstrates that insulin does not exert this action through the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):537–542. doi: 10.1042/bj2490537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. S., Taylor S. I., Londos C. Presence of a functional inhibitory GTP-binding regulatory component, Gi, linked to adenylate cyclase in adipocytes of ob/ob mice. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4564–4568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Hanski E., Houslay M. D. Islet-activating protein blocks glucagon desensitization in intact hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):189–194. doi: 10.1042/bj2220189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Houslay M. D. Challenge of hepatocytes by glucagon triggers a rapid modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in isolated membranes. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):93–98. doi: 10.1042/bj2140093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Hanoune J., Birnbaumer L. Guanine nucleotide inhibition of cyc- S49 mouse lymphoma cell membrane adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14723–14725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Gawler D. J., Milligan G., Wilson A. Multiple defects occur in the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein system in liver plasma membranes of obese (fa/fa) but not lean (Fa/Fa) Zucker rats: loss of functional Gi and abnormal Gs function. Cell Signal. 1989;1(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Siddle K. Molecular basis of insulin receptor function. Br Med Bull. 1989 Jan;45(1):264–284. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. Modulation by islet-activating protein of adenylate cyclase activity in C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3739–3746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Rajaram R., Lakonishok M., Benovic J. L., Cerione R. A. Insulin-dependent phosphorylation of GTP-binding proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12333–12341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Techniques used in the identification and analysis of function of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2550001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Griffiths S. L., Saggerson E. D., Houslay M. D., Knowler J. T., Milligan G. Guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins expressed in rat white adipose tissue. Identification of both mRNAs and proteins corresponding to Gi1, Gi2 and Gi3. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):403–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2620403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Houslay M. D., Milligan G., Siddle K. The insulin receptor tyrosyl kinase phosphorylates holomeric forms of the guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins Gi and Go. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 23;212(2):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyne N. J., Murphy G. J., Milligan G., Houslay M. D. Treatment of intact hepatocytes with either the phorbol ester TPA or glucagon elicits the phosphorylation and functional inactivation of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 16;243(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Imaizumi T., Misaki N., Iwakura K., Yoshida H. Effects of phosphorylation of inhibitory GTP-binding protein by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase on its ADP-ribosylation by pertussis toxin, islet-activating protein. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):372–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]