Full text
PDF
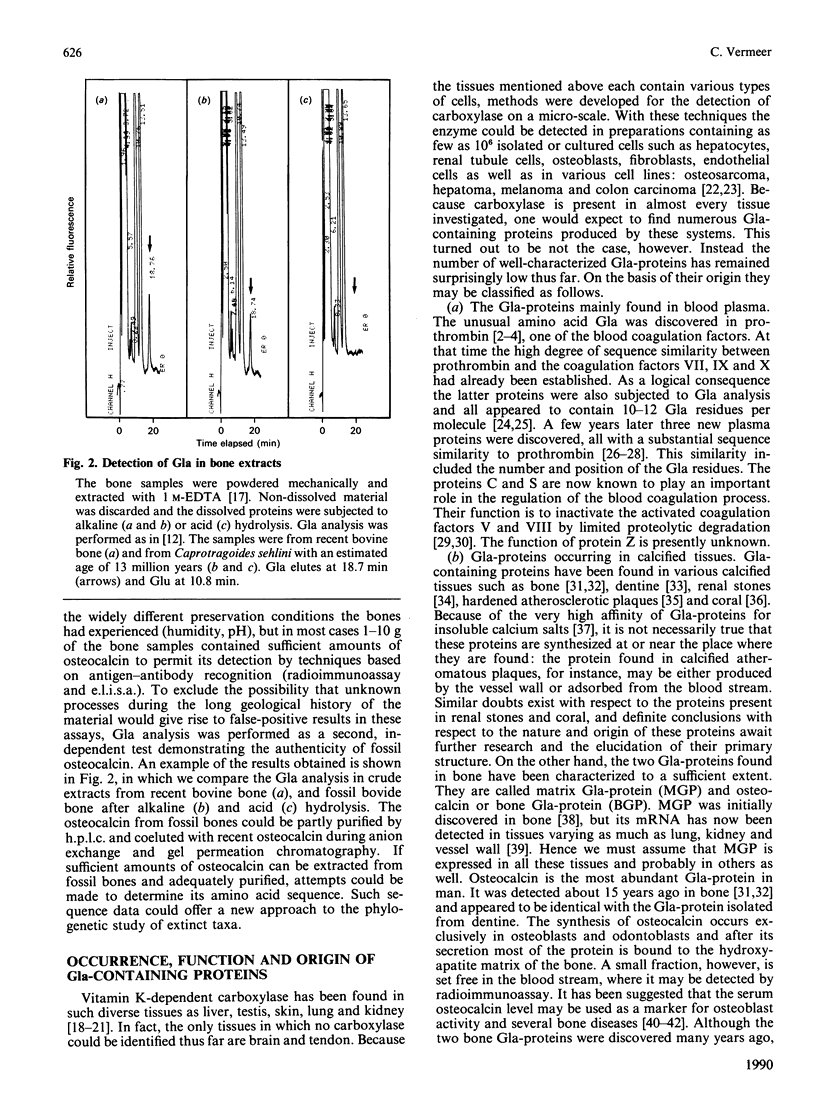



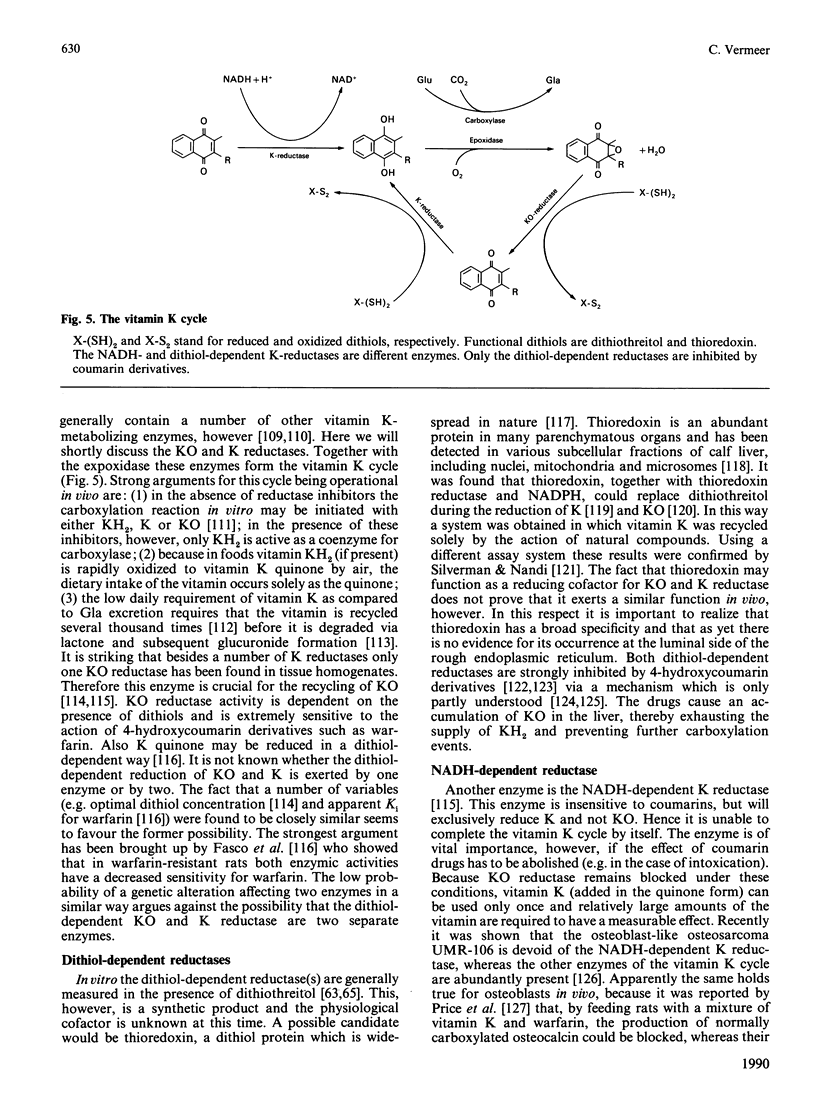






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew M., Paes B., Milner R., Johnston M., Mitchell L., Tollefsen D. M., Powers P. Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anson D. S., Austen D. E., Brownlee G. G. Expression of active human clotting factor IX from recombinant DNA clones in mammalian cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):683–685. doi: 10.1038/315683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balland A., Faure T., Carvallo D., Cordier P., Ulrich P., Fournet B., de la Salle H., Lecocq J. P. Characterisation of two differently processed forms of human recombinant factor IX synthesised in CHO cells transformed with a polycistronic vector. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):565–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal S. D., Bell R. G. Vitamin K dependent carboxylation of glutamate residues to gamma-carboxyglutamate in microsomes from spleen and testes: comparison with liver, lung, and kidney. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1077–1082. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Kumar A., Joseph M., Halfpap L., Insley M., Berkner K., Kurachi K., Woodbury R. Expression of active human factor IX in transfected cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):271–273. doi: 10.1038/316271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celeste A. J., Rosen V., Buecker J. L., Kriz R., Wang E. A., Wozney J. M. Isolation of the human gene for bone gla protein utilizing mouse and rat cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1885–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. L., Chau W. K., Ho C. H. A case of 'superwarfarin' poisoning. Scand J Haematol. 1986 Mar;36(3):314–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Primary structure of bovine vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam H. The antihaemorrhagic vitamin of the chick. Biochem J. 1935 Jun;29(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1042/bj0291273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K. Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799–829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Metz M., Soute B. A., Hemker H. C., Vermeer C. The inhibition of vitamin K-dependent carboxylase by cyanide. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 25;137(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80361-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid and gene coding for human prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2087–2097. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas P. D., Demiaux B., Malaval L., Chapuy M. C., Edouard C., Meunier P. J. Serum bone gamma carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein in primary hyperparathyroidism and in malignant hypercalcemia. Comparison with bone histomorphometry. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):985–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI112400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diuguid D. L., Rabiet M. J., Furie B. C., Liebman H. A., Furie B. Molecular basis of hemophilia B: a defective enzyme due to an unprocessed propeptide is caused by a point mutation in the factor IX precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5803–5807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J., Gaudry M., Bory S., Azerad R., Marquet A. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Study of the hydrogen abstraction stereochemistry with gamma-fluoroglutamic acid-containing peptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7897–7899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Sadowski J. A., Suttie J. W. A new carboxylation reaction. The vitamin K-dependent incorporation of H-14-CO3- into prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4744–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Solubilization and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6238–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasco M. J., Hildebrandt E. F., Suttie J. W. Evidence that warfarin anticoagulant action involves two distinct reductase activities. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11210–11212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasco M. J., Principe L. M. R- and S-Warfarin inhibition of vitamin K and vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase activities in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4894–4901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Rudinski M. S., Schach B. G., Berkner K. L., Kumar A. A., Hagen F. S., Sprecher C. A., Insley M. Y., Davie E. W. Propeptide of human protein C is necessary for gamma-carboxylation. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):7003–7011. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Yoshitake S., Davie E. W. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4673–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Price P. A. Lung, heart, and kidney express high levels of mRNA for the vitamin K-dependent matrix Gla protein. Implications for the possible functions of matrix Gla protein and for the tissue distribution of the gamma-carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11033–11036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B., Brockway B. E., Lambert N. Protein disulphide-isomerase and the formation of native disulphide bonds. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Dec;12(6):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bst0120929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Shia M. A., Gallop P. M., Griep A. E. Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carbon-hydrogen bond cleavage and nonmandatory concurrent carboxylation of peptide-bound glutamic acid residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3126–3129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Campbell R. M., MacGillivray R. T. Blood coagulation factor X mRNA encodes a single polypeptide chain containing a prepro leader sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4481–4492. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Hay C. W., MacGillivray R. T. Characterization of an almost full-length cDNA coding for human blood coagulation factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3591–3595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallop P. M., Lian J. B., Hauschka P. V. Carboxylated calcium-binding proteins and vitamin K. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 26;302(26):1460–1466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006263022608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardot J. M., Johnson B. C. A new detergent for the solubilization of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation system from liver microsomes: comparison with triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90486-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundberg C. M., Lian J. B., Gallop P. M., Steinberg J. J. Urinary gamma-carboxyglutamic acid and serum osteocalcin as bone markers: studies in osteoporosis and Paget's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1221–1225. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler M. R., Shadbolt R. S. Novel 4-hydroxycoumarin anticoagulants active against resistant rats. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):275–277. doi: 10.1038/253275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. E., King G., Tesch D., Riddles P. W., Keough D. T., Jell J., Zerner B. gamma-Carboxyglutamic acid in invertebrates: its identification in hermatypic corals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):610–613. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamulyák K., de Boer-van den Berg M. A., Thijssen H. H., Hemker H. C., Vermeer C. The placental transport of [3H]vitamin K1 in rats. Br J Haematol. 1987 Mar;65(3):335–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb06863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haroon Y. Rapid assay for gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in urine and bone by precolumn derivatization and reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haroon Y., Shearer M. J., Rahim S., Gunn W. G., McEnery G., Barkhan P. The content of phylloquinone (vitamin K1) in human milk, cows' milk and infant formula foods determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Nutr. 1982 Jun;112(6):1105–1117. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.6.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart J. P., Catterall A., Dodds R. A., Klenerman L., Shearer M. J., Bitensky L., Chayen J. Circulating vitamin K1 levels in fractured neck of femur. Lancet. 1984 Aug 4;2(8397):283–283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Carr S. A. Calcium-dependent alpha-helical structure in osteocalcin. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2538–2547. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Friedman P. A., Traverso H. P., Gallop P. M. Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxyglutamic acid formation by kidney microsomes in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1207–1213. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Henson E. B., Gallop P. M. Quantitative analysis and comparative decarboxylation of aminomalonic acid, beta-carboxyaspartic acid, and gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Anal Biochem. 1980 Oct;108(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Reid M. L. Vitamin D dependence of a calcium-binding protein containing gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in chicken bone. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9063–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V. Specific tritium labeling of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in proteins. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4992–4999. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelett S. E., Preusch P. C. Tissue distribution and warfarin sensitivity of vitamin K epoxide reductase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):929–934. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland L. The submicrosomal site for the conversion of prothrombin precursor to biologically active prothrombin in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 29;499(2):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt E. F., Suttie J. W. Mechanism of coumarin action: sensitivity of vitamin K metabolizing enzymes of normal and warfarin-resistant rat liver. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2406–2411. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Luthman M. Tissue distrubution and subcellular localization of bovine thioredoxin determined by radioimmunoassay. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4071–4077. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:237–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser R. M., Carey D. J., Dus K. M., Marshall G. R., Olson R. E. Partial sequence of rat prothrombin and the activity of two related pentapeptides as substrates for the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase system. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):226–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard B. R., Jacobs M., Ulrich M. M., Walsh C., Furie B., Furie B. C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. In vitro modification of synthetic peptides containing the gamma-carboxylation recognition site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14145–14150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard B. R., Ulrich M. M., Jacobs M., Vermeer C., Walsh C., Furie B., Furie B. C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: affinity purification from bovine liver by using a synthetic propeptide containing the gamma-carboxylation recognition site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6893–6897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq N. L., Rambaud S. M., Teh L. C., Davies A. D., McCulloch B., Trotter M. M., Chapman G. E. Immunochemical detection and characterisation of osteocalcin from moa bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):714–720. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91950-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højrup P., Roepstorff P., Petersen T. E. Amino-acid sequence of the vitamin-K-dependent part of protein Z. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):343–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johan L., van Haarlem M., Soute B. A., Vermeer C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Possible role for thioredoxin in the reduction of vitamin K metabolites in liver. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen M. J., Cantor A. B., Furie B. C., Brown C. L., Shoemaker C. B., Furie B. Recognition site directing vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation resides on the propeptide of factor IX. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen M. J., Cantor A. B., Furie B. C., Furie B. Expression of completely gamma-carboxylated recombinant human prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6729–6734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Ericsson L. H., Enfield D. L., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W., Titani K. Comparison of amino acid sequence of bovine coagulation Factor IX (Christmas Factor) with that of other vitamin K-dependent plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Furie B. C., Furie B., Shoemaker C. B. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant gamma-carboxylated factor IX synthesized in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9622–9628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Furie B. C., Furie B., Shoemaker C. B. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant gamma-carboxylated factor IX synthesized in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9622–9628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapen M. H., Hamulyák K., Vermeer C. The effect of vitamin K supplementation on circulating osteocalcin (bone Gla protein) and urinary calcium excretion. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Dec 15;111(12):1001–1005. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-111-12-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J. E., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Control of enzyme activity by the "propeptide" region of factor X. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15334–15337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwada M., Katayama K. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid and glutamic acid in proteins, bone, and urine. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90720-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwada M., Katayama K. An improved method for the determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in proteins, bone, and urine. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N., Freedman R. B. The latency of rat liver microsomal protein disulphide-isomerase. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):635–645. doi: 10.1042/bj2280635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson A. E., Friedman P. A., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Stoichiometry of carboxylation and vitamin K 2,3-epoxide formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11032–11035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. B., Dunn K., Key L. L., Jr In vitro degradation of bone particles by human monocytes is decreased with the depletion of the vitamin K-dependent bone protein from the matrix. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1636–1642. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. B., Prien E. L., Jr, Glimcher M. J., Gallop P. M. The presence of protein-bound gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in calcium-containing renal calculi. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1151–1157. doi: 10.1172/JCI108739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Bhown M., Cothran W. C., Höglund A., Butler W. T. Evidence for several gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing proteins in dentin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 4;704(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton R. A., Klass E. M. Human ingestion of a 'superwarfarin' rodenticide resulting in a prolonged anticoagulant effect. JAMA. 1984 Dec 7;252(21):3004–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Belagaje R. M., MacGillivray R. T. Cloning and sequencing of liver cDNA coding for bovine protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5653–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundwall A., Dackowski W., Cohen E., Shaffer M., Mahr A., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J., Wydro R. Isolation and sequence of the cDNA for human protein S, a regulator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of bovine prothrombin mRNA and its translation product. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1626–1634. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Morris H. R., Dell A. Primary structure of the vitamin K-dependent part of prothrombin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsu-ura S., Yamamoto S., Makita M. Determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in human urine by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 1;114(2):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90496-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. M., Olivera B. M., Cruz L. J., Gray W. R. Gamma-carboxyglutamate in a neuroactive toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14343–14346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTigue J. J., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Demonstration of a vitamin K- and O2-dependent exchange of 3H from 3H2O into glutamic acid residues. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12129–12131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon R. K., Gill D. S., Thomas M., Kernoff P. B., Dandona P. Impaired carboxylation of osteocalcin in warfarin-treated patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jan;64(1):59–61. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motohara K., Endo F., Matsuda I. Effect of vitamin K administration on acarboxy prothrombin (PIVKA-II) levels in newborns. Lancet. 1985 Aug 3;2(8449):242–244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa Y., Abram V., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T., Coe F. L. Purification and characterization of the principal inhibitor of calcium oxalate monohydrate crystal growth in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12594–12600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa Y., Abram V., Parks J. H., Lau H. S., Kawooya J. K., Coe F. L. Urine glycoprotein crystal growth inhibitors. Evidence for a molecular abnormality in calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1172/JCI112124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Zytkovicz T. H., Howard J. B. The mode of action of vitamin K. Identification of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid as a component of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6347–6350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson R. E. The function and metabolism of vitamin K. Annu Rev Nutr. 1984;4:281–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.04.070184.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan L. C., Price P. A. The propeptide of rat bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein shares homology with other vitamin K-dependent protein precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6109–6113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecci L., Cavallini D. A colorimetric procedure for the determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettifor J. M., Benson R. Congenital malformations associated with the administration of oral anticoagulants during pregnancy. J Pediatr. 1975 Mar;86(3):459–462. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preusch P. C., Suttie J. W. Relationship of dithiothreitol-dependent microsomal vitamin K quinone and vitamin K epoxide reductases inhibition of epoxide reduction by vitamin K quinone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 22;798(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Fraser J. D., Metz-Virca G. Molecular cloning of matrix Gla protein: implications for substrate recognition by the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8335–8339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Kaneda Y. Vitamin K counteracts the effect of warfarin in liver but not in bone. Thromb Res. 1987 Apr 1;46(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Otsuka A. A., Poser J. W., Kristaponis J., Raman N. Characterization of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein from bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Parthemore J. G., Deftos L. J. New biochemical marker for bone metabolism. Measurement by radioimmunoassay of bone GLA protein in the plasma of normal subjects and patients with bone disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):878–883. doi: 10.1172/JCI109954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Poser J. W., Raman N. Primary structure of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein from bovine bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3374–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A. Role of vitamin-K-dependent proteins in bone metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 1988;8:565–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.08.070188.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Urist M. R., Otawara Y. Matrix Gla protein, a new gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein which is associated with the organic matrix of bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91663-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Williamson M. K., Haba T., Dell R. B., Jee W. S. Excessive mineralization with growth plate closure in rats on chronic warfarin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7734–7738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Williamson M. K. Primary structure of bovine matrix Gla protein, a new vitamin K-dependent bone protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14971–14975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramotar K., Conly J. M., Chubb H., Louie T. J. Production of menaquinones by intestinal anaerobes. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):213–218. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels S. R., Gallaher K. J., Wallin R., Rannels D. E. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Lehrman S. R., Kawai M., Goodman H. L., Suttie J. W. Synthesis of peptide analogues of prothrombin precursor sequence 5-9. Substrate specificity of vitamin K dependent carboxylase. J Med Chem. 1981 Jun;24(6):706–711. doi: 10.1021/jm00138a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romberg R. W., Werness P. G., Riggs B. L., Mann K. G. Inhibition of hydroxyapatite crystal growth by bone-specific and other calcium-binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1176–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K., Priddle J. D., Offord R. E., Esnouf M. P. A mass-spectrometric method for the estimation of the ratio of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid to glutamic acid at specific sites in proteins. Application to the N-terminal region of bovine prothrombin. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):239–243. doi: 10.1042/bj1870239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski J. A., Schnoes H. K., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K epoxidase: properties and relationship to prothrombin synthesis. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3856–3863. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer M. J., McBurney A., Barkhan P. Studies on the absorption and metabolism of phylloquinone (vitamin K1) in man. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:513–542. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer M. J., Rahim S., Barkhan P., Stimmler L. Plasma vitamin K1 in mothers and their newborn babies. Lancet. 1982 Aug 28;2(8296):460–463. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90493-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R. B., Nandi D. L. Reduced thioredoxin: a possible physiological cofactor for vitamin K epoxide reductase. Further support for an active site disulfide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1248–1254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81274-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley D. M., Preusch P. C. Analysis of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid by reverse phase HPLC of its phenylthiocarbamyl derivative. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soute B. A., Balland A., Faure T., de la Salle H., Vermeer C. In vitro carboxylation of a blood coagulation factor IX precursor produced by recombinant-DNA technology. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Apr 25;61(2):238–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soute B. A., Müller-Esterl W., de Boer-van den Berg M. A., Ulrich M., Vermeer C. Discovery of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein in human spermatozoa. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 7;190(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80444-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soute B. A., Ulrich M. M., Vermeer C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: increased efficiency of the carboxylation reaction. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Feb 3;57(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soute B. A., Vermeer C., De Metz M., Hemker H. C., Lijnen H. R. In vitro prothrombin synthesis from a purified precursor protein. III. Preparation of an acid-soluble substrate for vitamin K-dependent carboxylase by limited proteolysis of bovine descarboxyprothrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 5;676(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speijer H., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Rosing J. Prothrombin activation by an activator from the venom of Oxyuranus scutellatus (Taipan snake). J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13258–13267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Jönsson M. Protein S, a new vitamin K-dependent protein from bovine plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 15;101(2):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Structure and function of protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):109–121. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Hageman J. M. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Development of a peptide substrate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5827–5830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Hoskins J. A., Engelke J., Hopfgartner A., Ehrlich H., Bang N. U., Belagaje R. M., Schoner B., Long G. L. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: possible role of the substrate "propeptide" as an intracellular recognition site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):634–637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Hoskins J. A., Engelke J., Hopfgartner A., Ehrlich H., Bang N. U., Belagaje R. M., Schoner B., Long G. L. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: possible role of the substrate "propeptide" as an intracellular recognition site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):634–637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Mummah-Schendel L. L., Shah D. V., Lyle B. J., Greger J. L. Vitamin K deficiency from dietary vitamin K restriction in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Mar;47(3):475–480. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/47.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Preusch P. C. Studies of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase and vitamin K epoxide reductase in rat liver. Haemostasis. 1986;16(3-4):193–215. doi: 10.1159/000215293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:459–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya H., Kawabata S., Nakagawa K., Yamamichi Y., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Bovine factor VII. Its purification and complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14868–14877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tans G., Govers-Riemslag J. W., van Rijn J. L., Rosing J. Purification and properties of a prothrombin activator from the venom of Notechis scutatus scutatus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9366–9372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thijssen H. H., Baars L. G., Vervoort-Peters H. T. Vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase: the basis for stereoselectivity of 4-hydroxycoumarin anticoagulant activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):675–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M. M., Furie B., Jacobs M. R., Vermeer C., Furie B. C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. A synthetic peptide based upon the gamma-carboxylation recognition site sequence of the prothrombin propeptide is an active substrate for the carboxylase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9697–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M. M., Knapen M. H., Herrmann-Erlee M. P., Vermeer C. Vitamin K is no antagonist for the action of warfarin in rat osteosarcoma UMR 106. Thromb Res. 1988 Apr 1;50(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M. M., Perizonius W. R., Spoor C. F., Sandberg P., Vermeer C. Extraction of osteocalcin from fossil bones and teeth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):712–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C., De Boer-Van den Berg M. A. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Haematologia (Budap) 1985;18(2):71–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Soute B. A., Lindhout M. J., Kop J., Hemker H. C. The role of blood clotting factor V in the conversion of prothrombin and a decarboxy prothrombin into thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 1;538(3):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C., Hendrix H., Daemen M. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylases from non-hepatic tissues. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80832-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C., Soute B. A., Hendrix H., de Boer-van den Berg M. A. Decarboxylated bone Gla-protein as a substrate for hepatic vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 2;165(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Protein S and the regulation of activated protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):131–138. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Hutson S. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Evidence that at least two microsomal dehydrogenases reduce vitamin K1 to support carboxylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1583–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Rannels S. R. Identification of vitamin K-dependent carboxylase activity in lung type II cells but not in lung macrophages. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):557–563. doi: 10.1042/bj2500557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zytkovicz T. H., Nelsestuen G. L. [3H]diborane reduction of vitamin K-dependent calcium-binding proteins. Identification of a unique amino acid. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2968–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer-van den Berg M. A., Uitendaal M. P., Vermeer C. Direct measurement of vitamin K-dependent enzymes in various isolated and cultured tumor and non-tumor cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 May;75(1):71–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00231610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer-van den Berg M. A., Verstijnen C. P., Vermeer C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase in skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Sep;87(3):377–380. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12524848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer-van den Berg M., Thijssen H. H., Vermeer C. The in vivo effects of oral anticoagulants in man: comparison between liver and non-hepatic tissues. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Apr 8;59(2):147–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Metz M., Vermeer C., Soute B. A., Hemker H. C. Identification of phospholipid as an essential part of bovine vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10843–10846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Metz M., Vermeer C., Soute B. A., van Scharrenburg G. J., Slotboom A. J., Hemker H. C. Partial purification of bovine liver vitamin K-dependent carboxylase by immunospecific adsorption onto antifactor X. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haarlem L. J., Knapen M. H., Hamulyák K., Vermeer C. Circulating osteocalcin during oral anticoagulant therapy. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Aug 30;60(1):79–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loo P. G., Soute B. A., van Haarlem L. J., Vermeer C. The effect of Gla-containing proteins on the precipitation of insoluble salts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90458-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


