Abstract
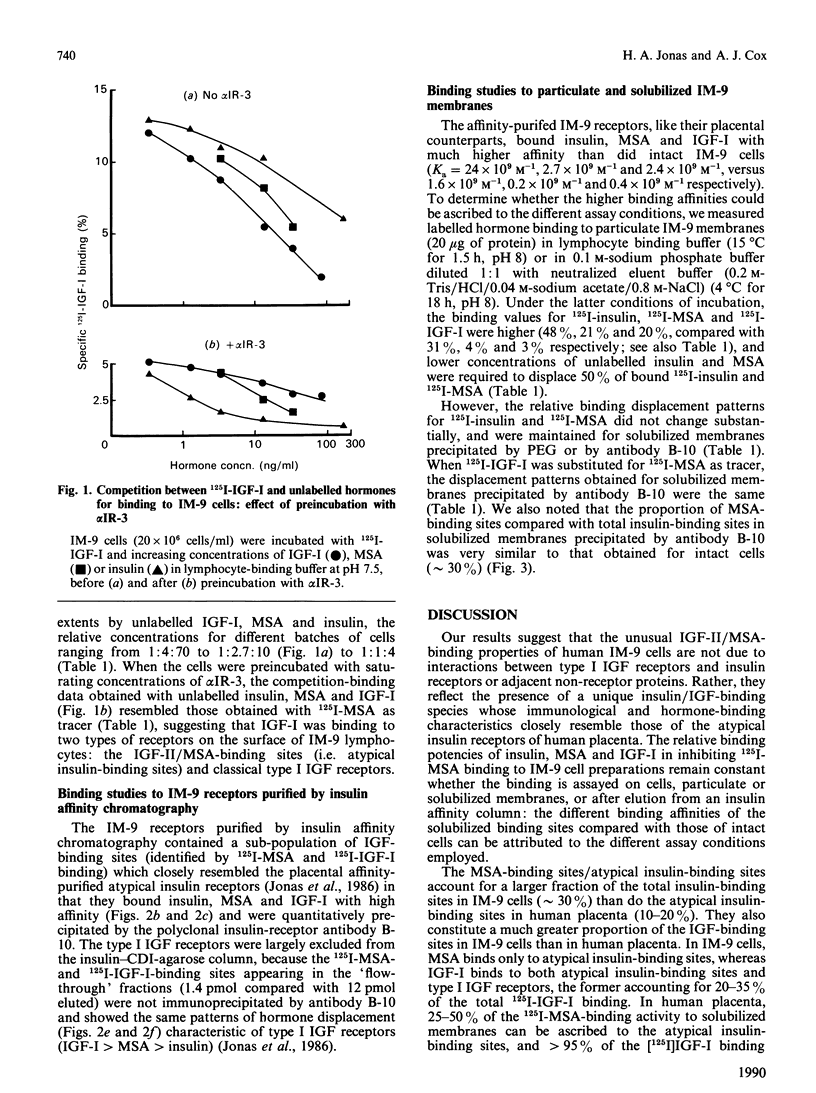
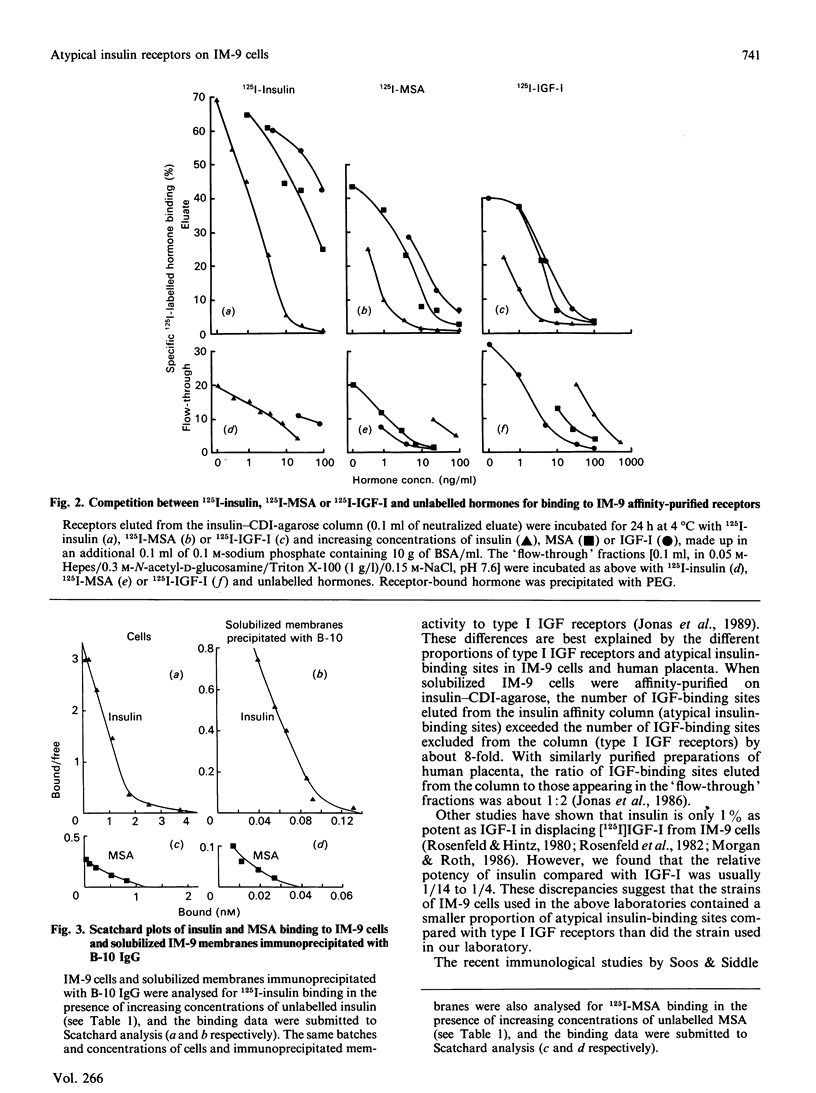
The cells of the IM-9 human lymphocyte-derived line contain a sub-population of insulin-binding sites whose immunological and hormone-binding characteristics closely resemble those of the atypical insulin-binding sites of human placenta. These binding sites, which have moderately high affinity for multiplication-stimulating activity [MSA, the rat homologue of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) II] and IGF-I, are identified on IM-9 cells by 125I-MSA binding. They account for approximately 30% of the total insulin-receptor population, and do not react with a monoclonal antibody to the type I IGF receptor (alpha IR-3). The relative concentrations of unlabelled insulin, MSA and IGF-I required to displace 50% of 125I-MSA from these binding sites (1:4.7:29 respectively) are maintained for cells, particulate membranes, Triton-solubilized membranes precipitated either by poly(ethylene glycol) or a polyclonal antibody (B-10) to the insulin receptor, and receptors purified by insulin affinity chromatography. Because the atypical insulin/MSA-binding sites outnumber the type I IGF receptors in IM-9 cells by approximately 10-fold, they also compete with the latter receptors for 125I-IGF-I binding. Thus 125I-IGF-I binding to IM-9 cells is inhibited by moderately low concentrations of insulin (relative potency ratios for insulin compared with IGF-I are approx. 1/14 to 1/4) and is partially displaced (65-80%) by alpha IR-3. When type I IGF receptors are blocked by alpha IR-3 or removed by B-10 immunoprecipitation or insulin affinity chromatography, the hormone-displacement patterns for 125I-IGF-I binding resemble those of the atypical insulin/MSA-binding sites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conover C. A., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Insulin-like growth factor II binding and action in human fetal fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Dec;133(3):560–566. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Pierce S. B., Morgan D. O., Sara V., Smith M. C., Roth R. A. The receptor for insulin-like growth factor II mediates an insulin-like response. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3367–3371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Thorsson A. V., Enberg G., Hall K. IGF-II binding on human lymphoid cells: demonstration of a common high affinity receptor for insulin like peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):774–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cook S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Interaction of the monoclonal antibodies alpha IR-1 and alpha IR-3 with insulin and somatomedin-C receptors. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):223–226. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Baxter R. C., Harrison L. C. Structural differences between insulin and somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors revealed by autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 30;109(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91744-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Cox A. J., Harrison L. C. Delineation of atypical insulin receptors from classical insulin and type I insulin-like growth factor receptors in human placenta. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 1;257(1):101–107. doi: 10.1042/bj2570101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Newman J. D., Harrison L. C. An atypical insulin receptor with high affinity for insulin-like growth factors copurified with placental insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra P., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Structural and immunological characterization of insulin-like growth factor II binding to IM-9 cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Dec;63(6):1400–1405. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-6-1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody which can distinguish between two distinct species of the type I receptor for insulin-like growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1341–1347. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. D., Harrison L. C. Homogeneous bivalent insulin receptor: purification using insulin coupled to 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole activated-agarose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91914-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Characterization of a specific receptor for somatomedin C (SM-C) on cultured human lymphocytes: evidence that SM-C modulates homologous receptor concentration. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1841–1848. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L., Dollar L. A. Insulin-induced loss of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors on IM-9 lymphocytes. Diabetes. 1982 May;31(5 Pt 1):375–381. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K. Immunological relationships between receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Evidence for structural heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor I receptors involving hybrids with insulin receptors. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):553–563. doi: 10.1042/bj2630553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Thompson K., Petersen D. J. Separation of the high affinity insulin-like growth factor I receptor from low affinity binding sites by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16461–16469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Graves D. C., Casella S. J., Jacobs S. Evidence from monoclonal antibody studies that insulin stimulates deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis through the type I somatomedin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):639–643. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


