Abstract
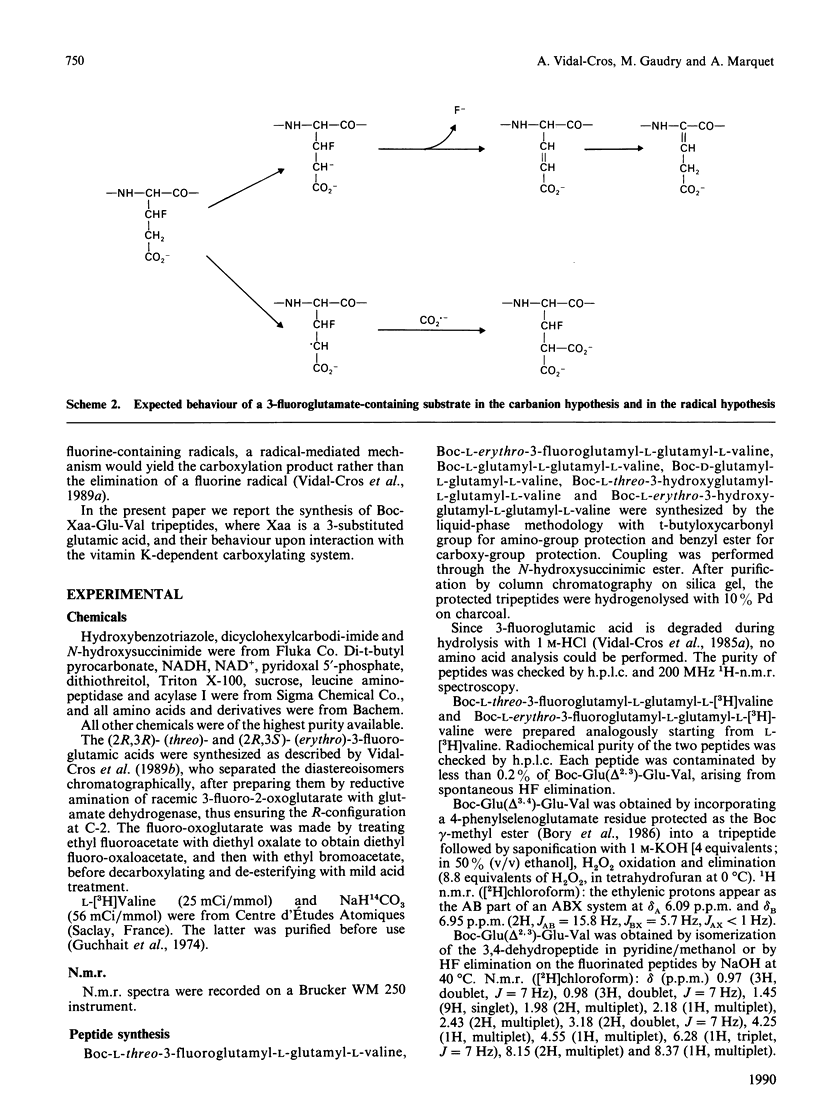
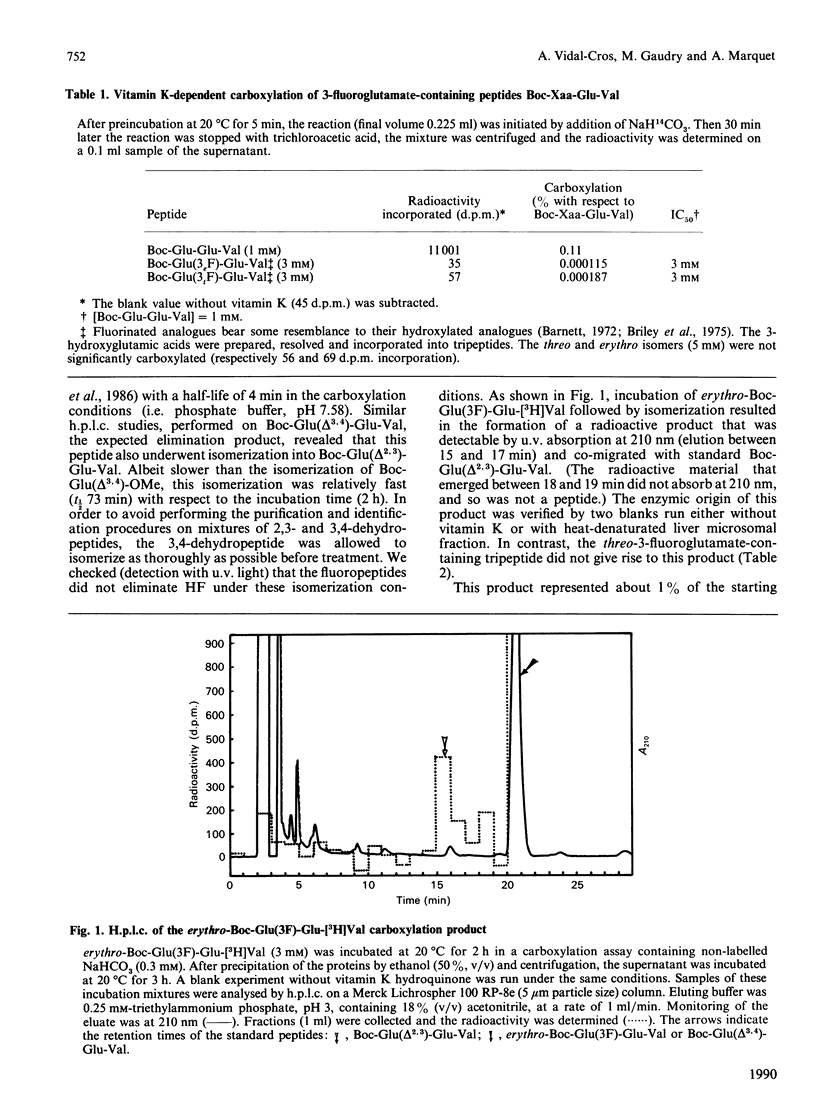
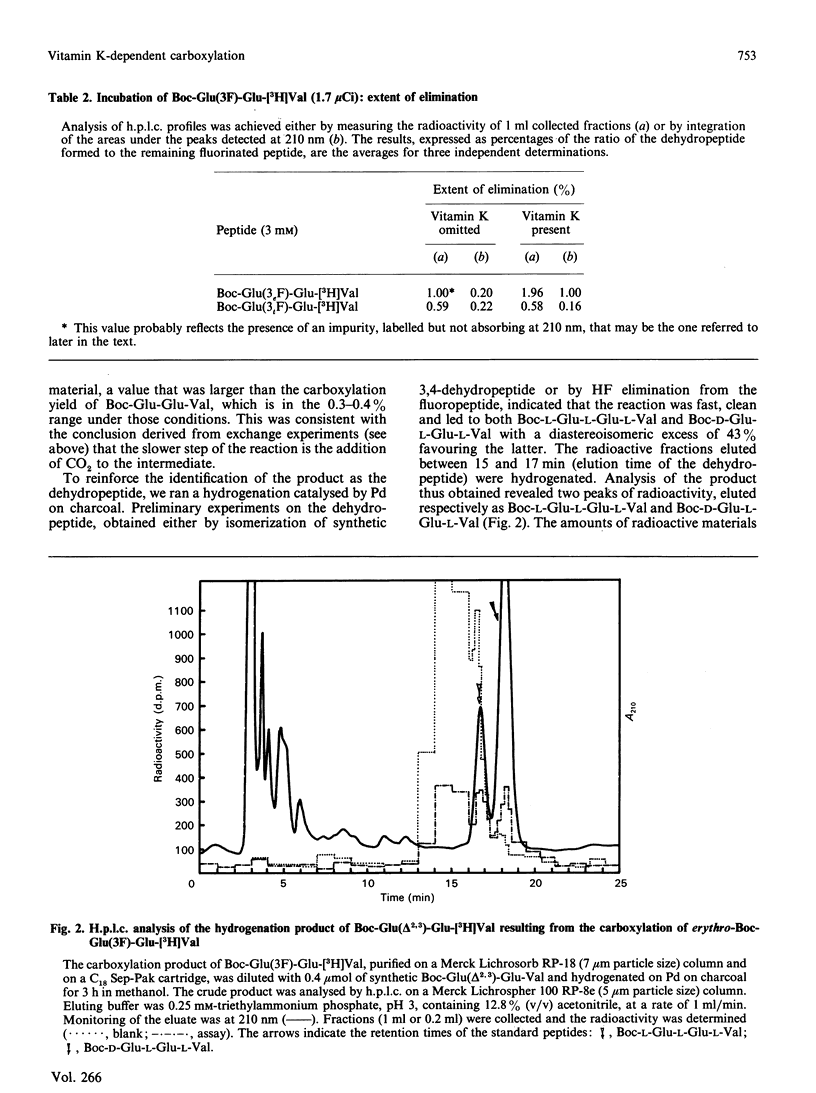
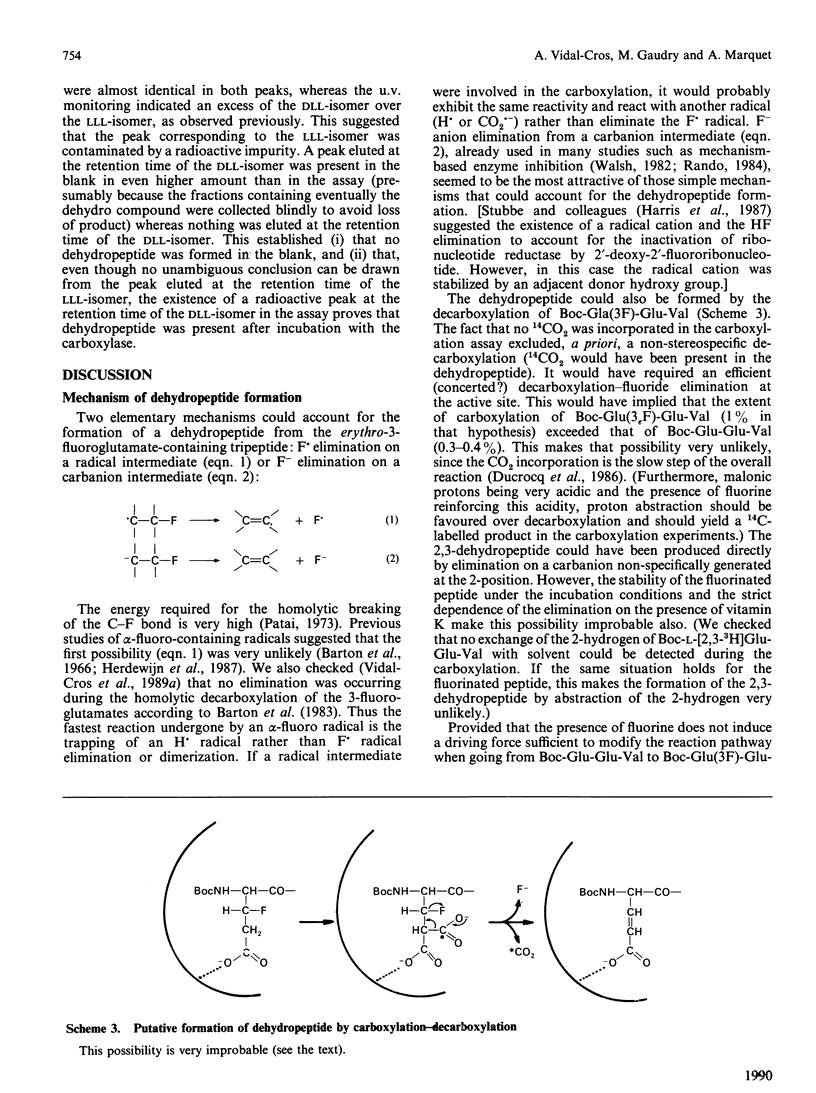
The tripeptides t-butyloxycarbonyl-Xaa-Glu-[3H]Val, where Xaa is either (2R,3S)- or (2R,3R)-3-fluoroglutamate (respectively the erythro and the threo isomer), were synthesized and their behaviour during vitamin K-dependent carboxylation was studied. Neither peptide was carboxylated. The erythro compound gave rise to an HF-elimination product representing 1% of the starting material. This HF elimination did not occur during incubation of the threo compound. The formation of the dehydropeptide, probably by elimination of an F- anion from an intermediate carbanion, favours the ionic pathway for vitamin K-dependent carboxylation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton D. L., Friedman P. A. Fate of the activated gamma-carbon-hydrogen bond in the uncoupled vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14084–14087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton D. H., Basu N. K., Hesse R. H., Morehouse F. S., Pechet M. M. Radical mechanisms in chromous ion reductions. An improved synthesis of 11-beta-hydroxy steroids. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Jul 5;88(13):3016–3021. doi: 10.1021/ja00965a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley P. A., Eisenthal R., Harrison R. Fluorine as a hydroxy analogue. Stereospecific phosphorylation of 2-deosy-2-fluoroglycerol by glucerol kinase. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):501–507. doi: 10.1042/bj1450501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decottignies-Le Maréchal P., Rikong-Aide H., Azerad R., Gaudry M. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of synthetic substrates. Nature of the products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):700–707. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91884-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardot J. M., Mack D. O., Floyd R. A., Johnson B. C. Evidence for vitamin K semiquinone as the functional form of vitamin K in the liver vitamin K-dependent protein carboxylation reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guchhait R. B., Polakis S. E., Dimroth P., Stoll E., Moss J., Lane M. D. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase system of Escherichia coli. Purification and properties of the biotin carboxylase, carboxyltransferase, and carboxyl carrier protein components. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6633–6645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G., Ashley G. W., Robins M. J., Tolman R. L., Stubbe J. 2'-Deoxy-2'-halonucleotides as alternate substrates and mechanism-based inactivators of Lactobacillus leichmannii ribonucleotide reductase. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):1895–1902. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdewijn P., Pauwels R., Baba M., Balzarini J., De Clercq E. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of various 2'- and 3'-substituted 2',3'-dideoxyadenosines: a structure-activity analysis. J Med Chem. 1987 Nov;30(11):2131–2137. doi: 10.1021/jm00394a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTigue J. J., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Demonstration of a vitamin K- and O2-dependent exchange of 3H from 3H2O into glutamic acid residues. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12129–12131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Mechanism-based enzyme inactivators. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Jun;36(2):111–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbe J., Abeles R. H. Biotin carboxylations--concerted or not concerted? That is the question! J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8338–8340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbe J., Fish S., Abeles R. H. Are carboxylations involving biotin concerted or nonconcerted? J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):236–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Cros A., Gaudry M., Marquet A. Interaction of L-threo and L-erythro isomers of 3-fluoroglutamate with glutamate decarboxylase from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 1;229(3):675–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2290675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


