Abstract
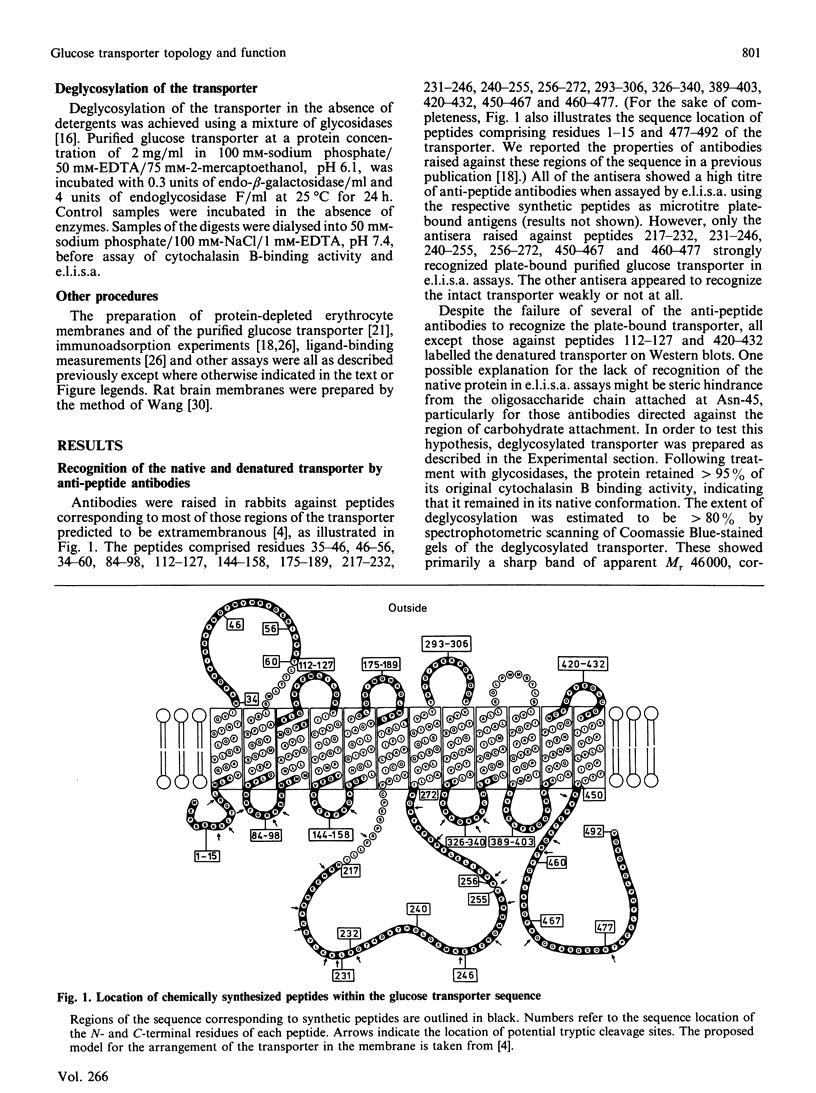
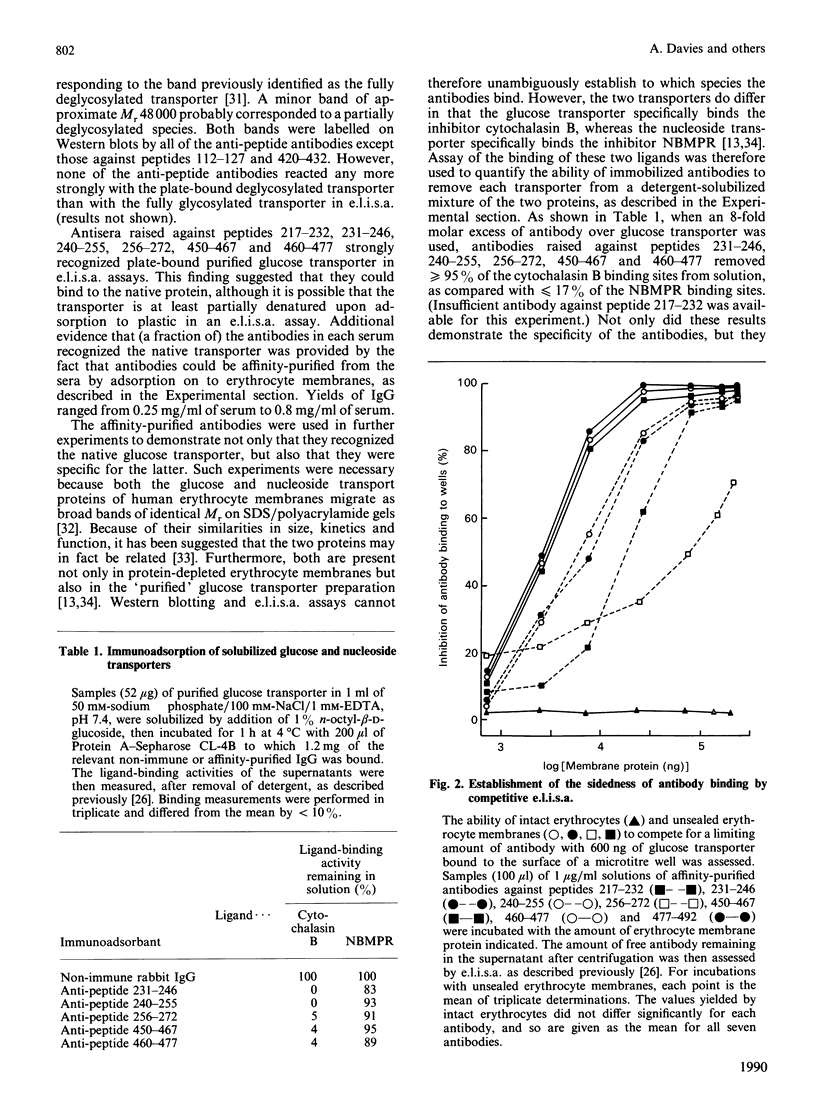
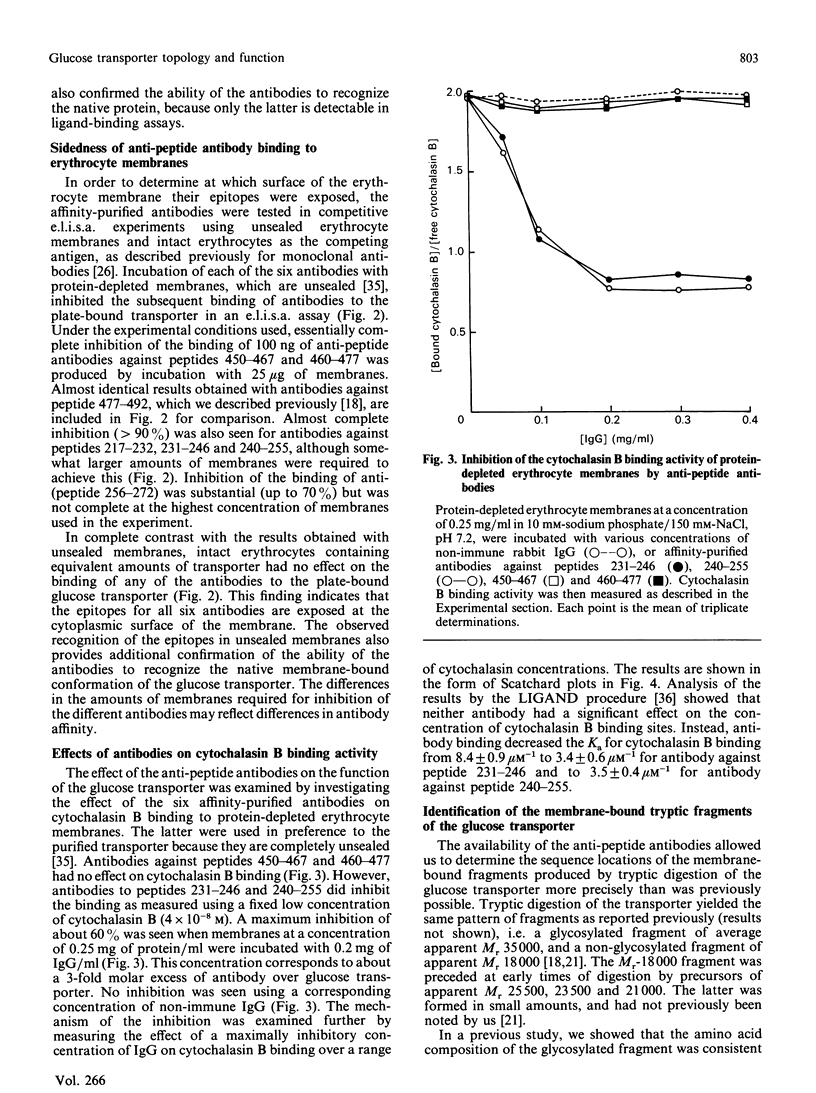
Antibodies were raised against synthetic peptides corresponding to most of the regions of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter predicted to be extramembranous in the model of Mueckler, Caruso, Baldwin, Panico, Blench, Morris, Lienhard, Allard & Lodish [(1985) Science 229, 941-945]. Most of the antibodies (17 out of a total of 19) recognized the intact denatured protein on Western blots. However, only seven of the antibodies recognized the native membrane-bound protein, even after its deglycosylation. These antibodies, against peptides encompassing residues 217-272 and 450-492 in the hydrophilic central and C-terminal regions of the transporter, bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the erythrocyte membrane. This finding is in agreement with the prediction of the model that these regions of the sequence are cytoplasmic. Antibodies against peptides from the central cytoplasmic loop of the transporter were found to inhibit the binding of cytochalasin B to the membrane-bound protein, whereas antibodies against the C-terminal region had no effect. The anti-peptide antibodies were then used to map the sequence locations of fragments of the transporter arising from tryptic digestion of the membrane-bound protein. This in turn enabled the epitopes for a number of anti-transporter monoclonal antibodies to be located within either the central cytoplasmic loop or the C-terminal region of the protein. Of those monoclonal antibodies which inhibited cytochalasin B binding to the protein, all but one were found to have epitopes within the central region of the sequence. In conjunction with the results of the anti-peptide antibody studies, these findings indicate the importance of this part of the protein for transporter function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E. Monoclonal antibodies to the glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. Identification of the transporter as a Mr = 55,000 protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8668–8675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J., Lee D. C., Baldwin S. A., Chapman D. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of the structure and conformational changes of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3502–3509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L., Lundahl P. C-terminal-specific monoclonal antibodies against the human red cell glucose transporter. Epitope localization with synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11414–11420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Takaku F., Akanuma Y., Oka Y. Cloning of a rabbit brain glucose transporter cDNA and alteration of glucose transporter mRNA during tissue development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1204–1211. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. M., Lienhard G. E., Baldwin S. A. The monosaccharide transport system of the human erythrocyte. Orientation upon reconstitution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):699–714. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Baldwin J. M., Lienhard G. E. Monosaccharide transporter of the human erythrocyte. Characterization of an improved preparation. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3836–3842. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Henderson P. J. Homologies between sugar transporters from eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:459–471. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baly D. L., Horuk R. The biology and biochemistry of the glucose transporter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):571–590. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. M., Whetton A. D., Dexter T. M., Meeran K., Baldwin S. A. Characterisation of monoclonal antibodies which specifically recognise the human erythrocyte glucose transport protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3093–3098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
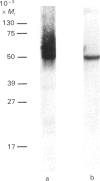
- Cairns M. T., Alvarez J., Panico M., Gibbs A. F., Morris H. R., Chapman D., Baldwin S. A. Investigation of the structure and function of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter by proteolytic dissection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 11;905(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns M. T., Elliot D. A., Scudder P. R., Baldwin S. A. Proteolytic and chemical dissection of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):179–188. doi: 10.1042/bj2210179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Herzlinger D., Danho W., Kaback H. R. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies and site-directed polyclonal antibodies against the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:453–467. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The yeast SNF3 gene encodes a glucose transporter homologous to the mammalian protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. J., Jung E. K., Jung C. Y. Structural basis of human erythrocyte glucose transporter function in reconstituted vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7101–7104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Meeran K., Cairns M. T., Baldwin S. A. Peptide-specific antibodies as probes of the orientation of the glucose transporter in the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9347–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deziel M. R., Rothstein A. Proteolytic cleavages of cytochalasin B binding components of band 4.5 proteins of the human red blood cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 19;776(1):10–20. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrink J., Bihler I. Membrane transport: its relation to cellular metabolic rates. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1177–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.1096301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorga F. R., Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E. The monosaccharide transporter from human erythrocytes is heterogeneously glycosylated. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91972-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorga F. R., Lienhard G. E. Equilibria and kinetics of ligand binding to the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. Evidence for an alternating conformation model for transport. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 1;20(18):5108–5113. doi: 10.1021/bi00521a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Rosenfeld M. G., Rosen O. M. Characterization of antisera to a synthetic carboxyl-terminal peptide of the glucose transporter protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Rees W. D. Photolabelling of the hexose transporter at external and internal sites: fragmentation patterns and evidence for a conformational change. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 12;897(3):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis S. M., Young J. D. Extraction and partial purification of the nucleoside-transport system from human erythrocytes based on the assay of nitrobenzylthioinosine-binding activity. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):331–339. doi: 10.1042/bj1940331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim A. R., Rees W. D., Holman G. D. Binding of cytochalasin B to trypsin and thermolysin fragments of the human erythrocyte hexose transporter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 3;902(3):402–405. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong F. Y., Baldwin S. A., Scudder P. R., Jarvis S. M., Choy M. Y., Young J. D. Erythrocyte nucleoside and sugar transport. Endo-beta-galactosidase and endoglycosidase-F digestion of partially purified human and pig transporter proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):349–356. doi: 10.1042/bj2400349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Crabb J. H., Ransome K. J. Endoglycosidase f cleaves the oligosaccharides from the glucose transporter of the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Möröy T., Wright J. K., Overath P. Anti-peptide antibodies and proteases as structural probes for the lactose/H+ transporter of Escherichia coli: a loop around amino acid residue 130 faces the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2403–2409. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Olson A. J., Lerner R. A., Hendrickson W. A. The reactivity of anti-peptide antibodies is a function of the atomic mobility of sites in a protein. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):127–134. doi: 10.1038/312127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. The D-glucose transporter is tissue-specific. Skeletal muscle and adipose tissue have a unique form of glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15689–15695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Jarvis S. M., Robins M. J., Paterson A. R. Photoaffinity labeling of the human erythrocyte nucleoside transporter by N6-(p-Azidobenzyl)adenosine and nitrobenzylthioinosine. Evidence that the transporter is a band 4.5 polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2202–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]