Abstract
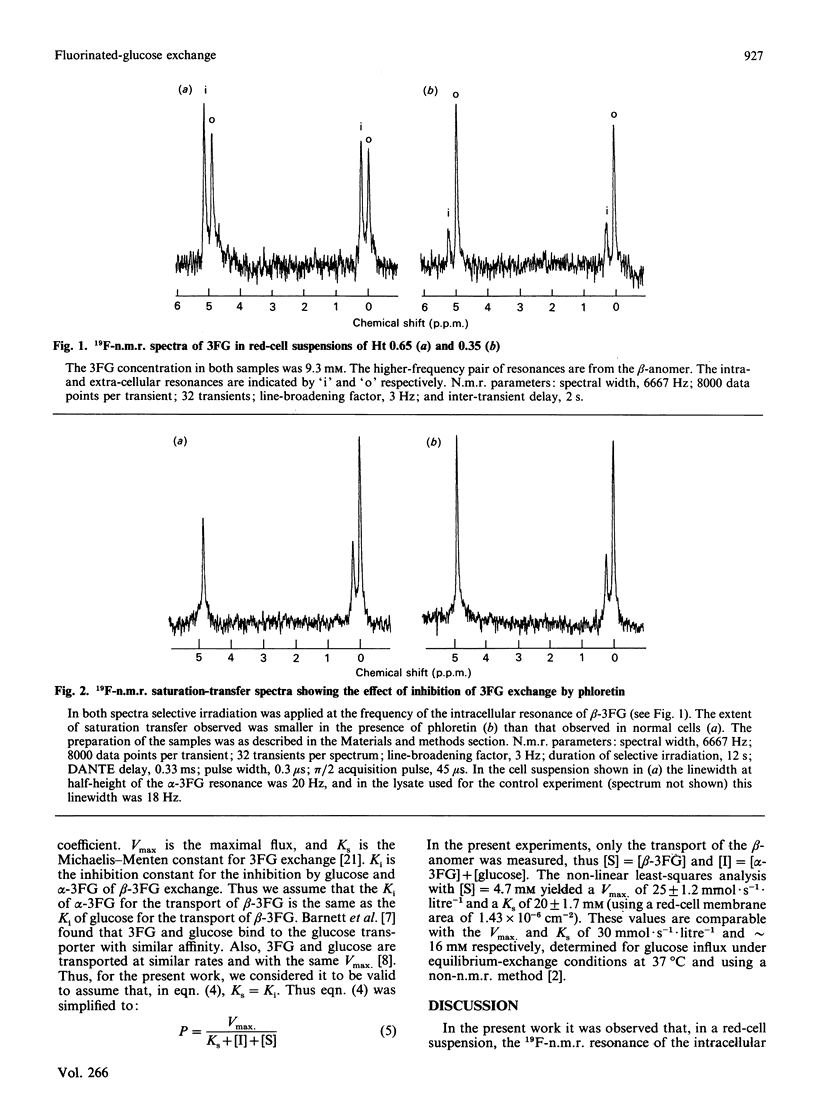
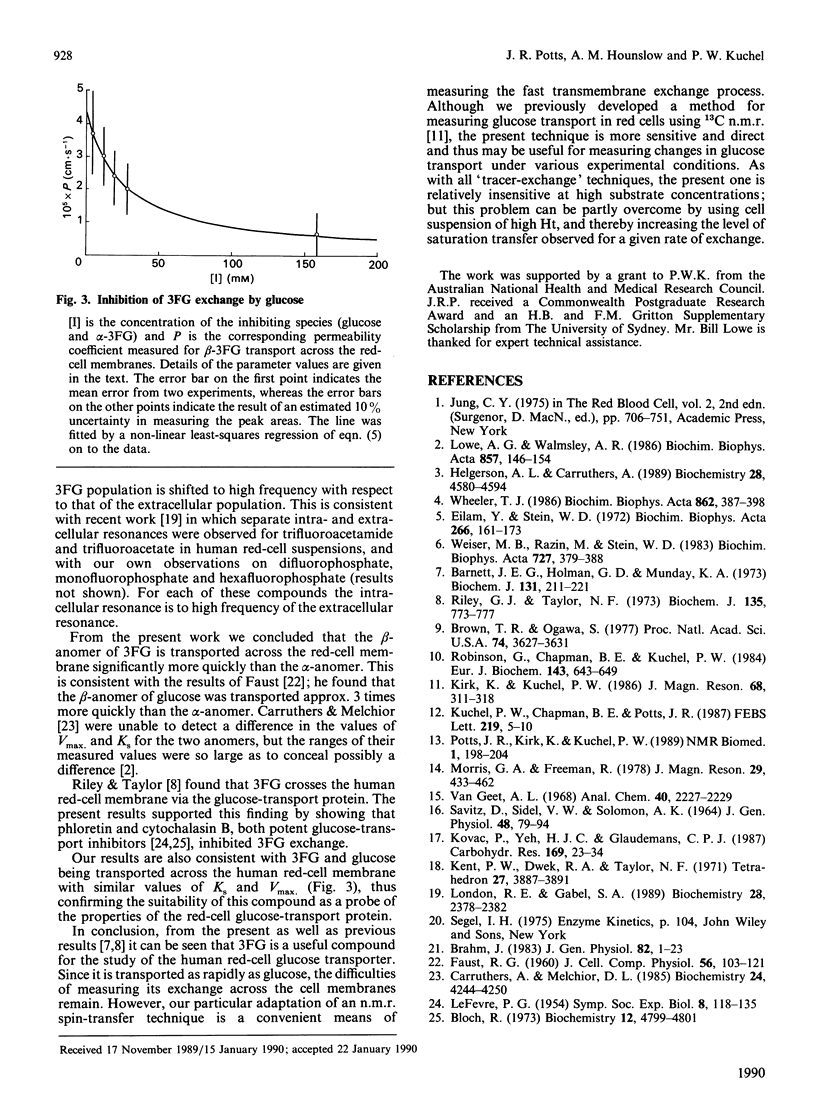
The 19F n.m.r. spectrum of 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-glucose (3FG) in a red-cell suspension was observed to contain separate resonances from the intra- and extra-cellular populations of both the alpha- and beta-anomers. This phenomenon was used with an n.m.r. spin-transfer procedure to measure the rate of exchange of the anomers across the human red-cell membrane under equilibrium-exchange conditions at 37 degrees C. The beta-anomer crossed the membrane significantly more quickly than the alpha-anomer. At a total 3FG concentration of 9.3 mM; the first-order rate constants for the efflux of the alpha- and beta-anomers were 0.41 +/- 0.15 and 0.88 +/- 0.20 s-1 respectively. The measurable 3FG exchange was inhibited by 75 and 100% respectively by the glucose-transport inhibitors cytochalasin B and phloretin. Glucose inhibited the exchange of 3FG, and the results were consistent with glucose and 3FG binding to the hexose-transport protein with similar affinity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett J. E., Holman G. D., Munday K. A. Structural requirements for binding to the sugar-transport system of the human erythrocyte. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):211–221. doi: 10.1042/bj1310211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R. Inhibition of glucose transport in the human erythrocyte by cytochalasin B. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4799–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahm J. Urea permeability of human red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jul;82(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. R., Ogawa S. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance kinetic measurements on adenylatekinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3627–3631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers A., Melchior D. L. Transport of alpha- and beta-D-glucose by the intact human red cell. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4244–4250. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilam Y., Stein W. D. A simple resolution of the kinetic anomaly in the exchange of different sugars across the membrane of the human red blood cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 14;266(1):161–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAUST R. G. Monosaccharide penetration into human red blood cells by an altered diffusion mechanism. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Oct;56:103–121. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030560205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgerson A. L., Carruthers A. Analysis of protein-mediated 3-O-methylglucose transport in rat erythrocytes: rejection of the alternating conformation carrier model for sugar transport. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4580–4594. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovác P., Yeh H. J., Glaudemans C. P. Synthesis and n.m.r. spectra of methyl 2-deoxy-2-fluoro- and 3-deoxy-3-fluoro-alpha- and beta-D-glucopyranosides. Carbohydr Res. 1987 Nov 15;169:23–34. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(87)80239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchel P. W., Chapman B. E., Potts J. R. Glucose transport in human erythrocytes measured using 13C NMR spin transfer. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 13;219(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London R. E., Gabel S. A. Determination of membrane potential and cell volume by 19F NMR using trifluoroacetate and trifluoroacetamide probes. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2378–2382. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe A. G., Walmsley A. R. The kinetics of glucose transport in human red blood cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 28;857(2):146–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90342-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. R., Kirk K., Kuchel P. W. Characterization of the transport of the nonelectrolyte dimethyl methylphosphonate across the red cell membrane. NMR Biomed. 1989 Apr;1(4):198–204. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940010408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley G. J., Taylor N. F. The interaction of 3-deoxy-3-fluoro-D-glucose with the hexose-transport system of the human erythrocyte. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):773–777. doi: 10.1042/bj1350773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G., Chapman B. E., Kuchel P. W. 31P NMR spin-transfer in the phosphoglyceromutase reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):643–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAVITZ D., SIDEL V. W., SOLOMON A. K. OSMOTIC PROPERTIES OF HUMAN RED CELLS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:79–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. B., Razin M., Stein W. D. Kinetic tests of models for sugar transport in human erythrocytes and a comparison of fresh and cold-stored cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 19;727(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J. Kinetics of glucose transport in human erythrocytes: zero-trans efflux and infinite-trans efflux at 0 degree C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 17;862(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


