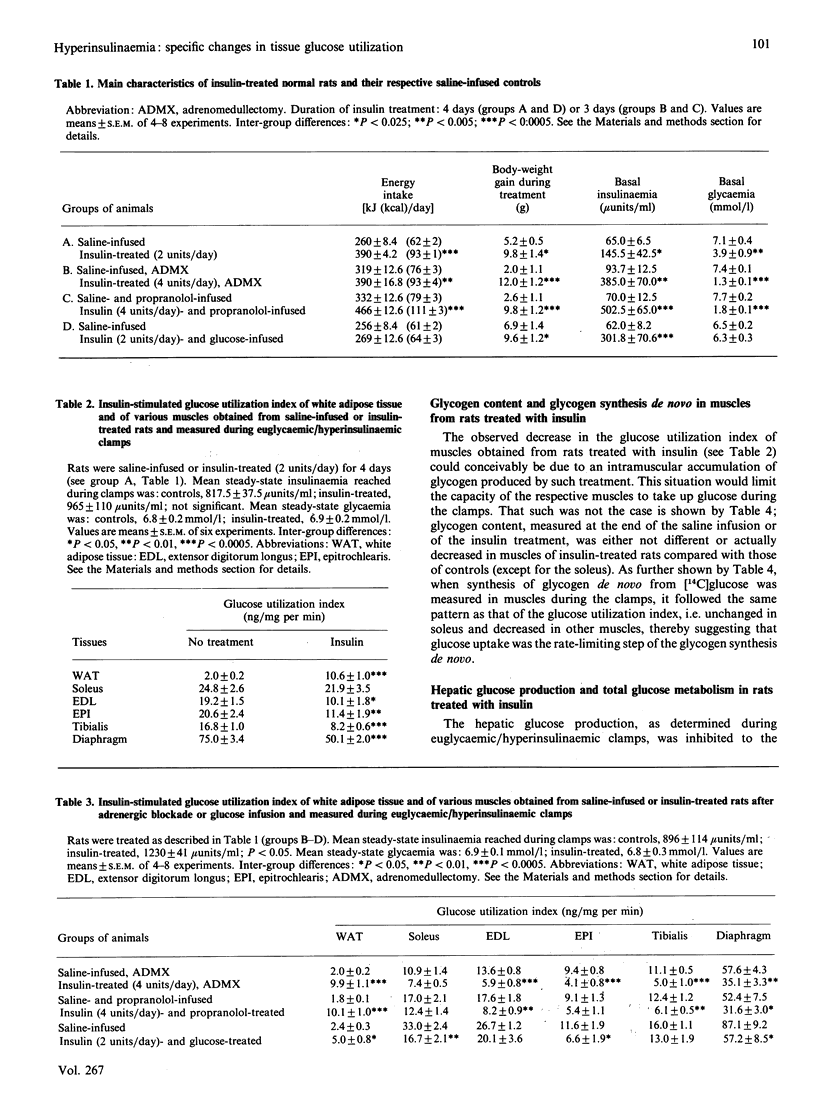
Abstract
The effects of hyperinsulinaemia imposed on normal rats on the subsequent insulin-responsiveness in vivo of 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake of white adipose tissue and of various muscle types were investigated. This was done by treating normal rats with insulin via osmotic minipumps, and by comparing them with saline-infused controls. Hyperinsulinaemia produced by prior insulin treatment resulted in a well-tolerated hypoglycaemia. At the end of the treatment, the glucose utilization index of individual tissues was determined by euglycaemic/hyperinsulinaemic clamps associated with the labelled 2-deoxy-D-glucose method. Prior insulin treatment resulted in increased insulin-responsiveness of the glucose utilization index of white adipose tissue, and in increased total lipogenesis in white adipose tissue and fat-pad weight. In contrast, prior insulin treatment resulted in a decreased glucose utilization index of several muscles. These opposite effects of hyperinsulinaemia on glucose utilization in white adipose tissue and muscles persisted when the hypoglycaemia-induced catecholamine output was prevented (adrenomedullectomy, propranolol treatment), as well as when hypoglycaemia was normalized by concomitant insulin treatment and glucose infusion. Insulin suppressed hepatic glucose production during the clamps in insulin-treated rats as in the respective controls, whereas total hepatic lipid synthesis and liver fat content were greater in rats treated with insulin than in controls. It is concluded that hyperinsulinaemia itself could be one of the driving forces responsible for producing increased glucose utilization by white adipose tissue, increased total lipid synthesis with fat accumulation in adipose tissue and the liver, together with an insulin-resistant state at the muscular level.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan T. M., Exton J. H. A rapid method for the determination of glycogen content and radioactivity in small quantities of tissue or isolated hepatocytes. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Rognstad R., Katz J. Lipogenesis in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2028–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré P., Leturque A., Burnol A. F., Penicaud L., Girard J. A method to quantify glucose utilization in vivo in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue of the anaesthetized rat. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2280103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Olefsky J. M., Marshall S. Insulin induces progressive insulin resistance in cultured rat adipocytes. Sequential effects at receptor and multiple postreceptor sites. Diabetes. 1986 Mar;35(3):258–267. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerre-Millo M., Lavau M., Horne J. S., Wardzala L. J. Proposed mechanism for increased insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipose cells from young, obese Zucker rats. Large intracellular pool of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2197–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issad T., Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Kandé J., Baudon M. A., Girard J. Effects of fasting on tissue glucose utilization in conscious resting rats. Major glucose-sparing effect in working muscles. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):241–244. doi: 10.1042/bj2460241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Burleigh K. M., Kraegen E. W. In vivo glucose metabolism in individual tissues of the rat. Interaction between epinephrine and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6366–6374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanrenaud B., Halimi S., van de Werve G. Neuro-endocrine disorders seen as triggers of the triad: obesity--insulin resistance--abnormal glucose tolerance. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(3):261–291. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Horton E. S., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for enhanced glucose transport response to insulin in adipose cells from chronically hyperinsulinemic rats. Increased translocation of glucose transporters from an enlarged intracellular pool. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):853–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI112894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Olefsky J. M. Effect of experimental hyperinsulinemia on insulin binding and glucose transport in isolated rat adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jul;235(1):E53–E62. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.1.E53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krief S., Bazin R., Dupuy F., Lavau M. Increased in vivo glucose utilization in 30-day-old obese Zucker rat: role of white adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):E342–E348. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.3.E342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Jeanrenaud B. Pre- and postweaning studies on development of obesity in mdb/mdb mice. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):E568–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.6.E568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand Y., Freychet P., Jeanrenaud B. Longitudinal study on the establishment of insulin resistance in hypothalamic obese mice. Endocrinology. 1978 Jan;102(1):74–85. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-1-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. E., Sullivan A. C. Glucose, insulin and sympathoadrenal activation. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Oct;20(3):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L., Baker B., Rizza R., Genest J., Gerich J. Infusion of insulin impairs human adipocyte glucose metabolism in vitro without decreasing adipocyte insulin receptor binding. Diabetologia. 1984 Sep;27(3):358–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00304850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Terretaz J., Kinebanyan M. F., Leturque A., Doré E., Girard J., Jeanrenaud B., Picon L. Development of obesity in Zucker rats. Early insulin resistance in muscles but normal sensitivity in white adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1987 May;36(5):626–631. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.5.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Kinebanyan M. F., Ferré P., Morin J., Kandé J., Smadja C., Marfaing-Jallat P., Picon L. Development of VMH obesity: in vivo insulin secretion and tissue insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):E255–E260. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.2.E255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Rohner-Jeanrenaud F., Jeanrenaud B. In vivo metabolic changes as studied longitudinally after ventromedial hypothalamic lesions. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):E662–E668. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.6.E662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohner-Jeanrenaud F., Jeanrenaud B. Involvement of the cholinergic system in insulin and glucagon oversecretion of genetic preobesity. Endocrinology. 1985 Feb;116(2):830–834. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-2-830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits J. F., Struyker-Boudier H. A. Steady-state disposition of propranolol and its total metabolites in the spontaneously hypertensive rat: chronic subcutaneous vs. intracerebroventricular infusion with osmotic minipumps. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jun;209(3):317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrettaz J., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Jeanrenaud B. Inhibition of hepatic glucose production by insulin in vivo in rats: contribution of glycolysis. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):E346–E351. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.4.E346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrettaz J., Jeanrenaud B. In vivo hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance in genetically obese (fa/fa) rats. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1346–1351. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Weir G. C., Gjinovci A., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Benzi R., Renold A. E. Increased insulin responsiveness in vivo and in vitro consequent to induced hyperinsulinemia in the rat. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):444–449. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Hirshman M., Pofcher E., Horton E. D., Mead P. M., Cushman S. W., Horton E. S. Regulation of glucose utilization in adipose cells and muscle after long-term experimental hyperinsulinemia in rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):460–469. doi: 10.1172/JCI111994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker J., Alberti K. G., York D. A., Singh J. The effects of chronic hyperinsulinaemia on insulin binding and glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):1055–1056. doi: 10.1042/bst0071055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Spaeth A. E. Perfusion in situ with tritium oxide to measure hepatic lipogenesis and lipid secretion. Normal and orotic acid-fed rats. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 25;241(12):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Uhl J. J., Cartee G. D., Holloszy J. O. Activation of glucose transport in muscle by prolonged exposure to insulin. Effects of glucose and insulin concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16049–16053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


