Abstract
1. We examined the isolated mouse skeletal-muscle model in vitro, commonly used by many investigators, for its suitability for metabolic studies. 2. Despite the fact that pH, O2 saturation, osmolality and the release of the enzyme creatine kinase remained stable, histochemical studies showed large cores devoid of glycogen, suggesting that the incubated muscle had lost its viability. 3. This study indicates that caution should be exercised when interpreting the results of studies with intact isolated mouse muscles.
Full text
PDF
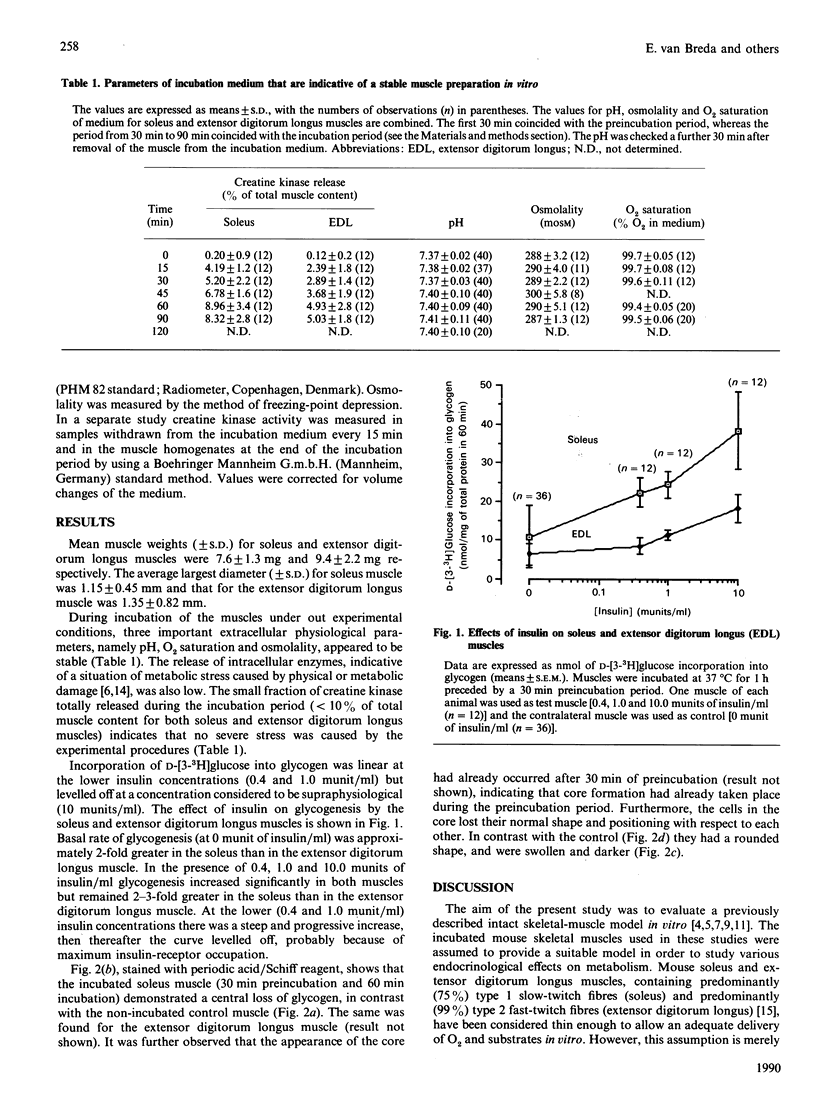
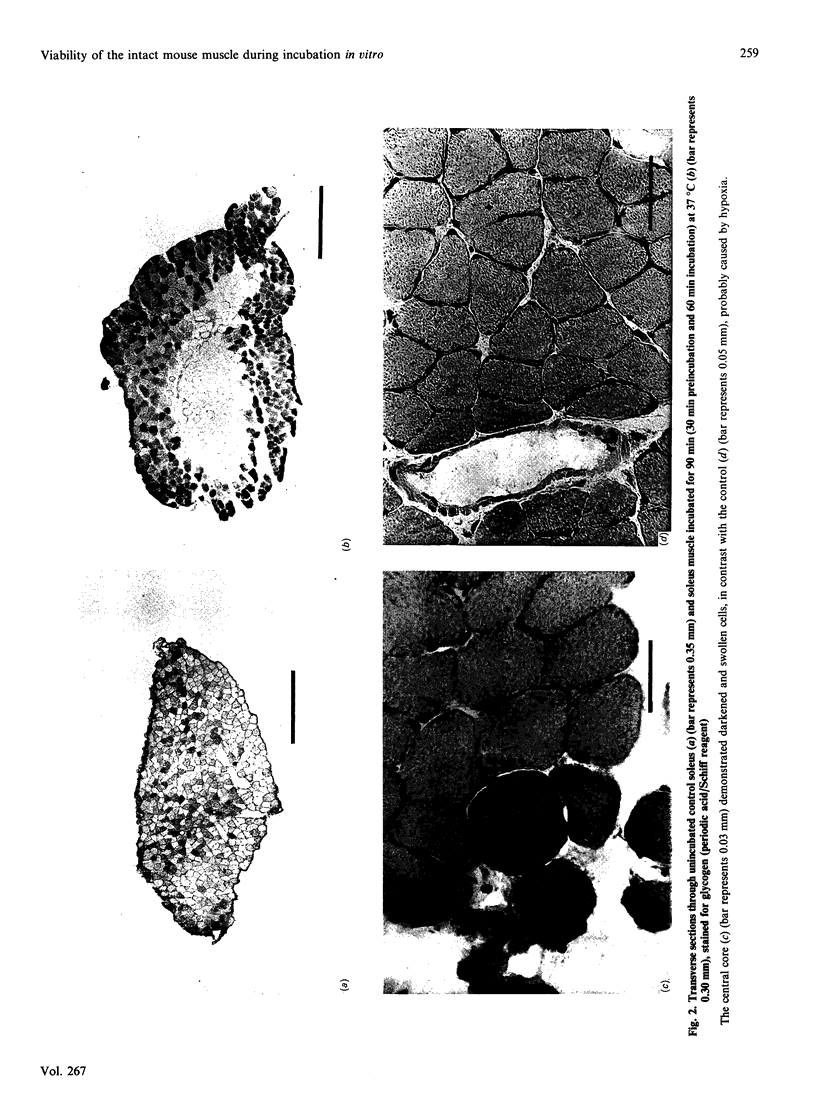

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonen A., Tan M. H., Watson-Wright W. M. Effects of exercise on insulin binding and glucose metabolism in muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;62(12):1500–1504. doi: 10.1139/y84-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen A., Tan M. H., Watson-Wright W. M. Insulin binding and glucose uptake differences in rodent skeletal muscles. Diabetes. 1981 Aug;30(8):702–704. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.8.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Dietz M. R., Shikama H., Wootten M., Exton J. H. Insulin regulation of skeletal muscle glycogen metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):E69–E74. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.1.E69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. T., Kushmerick M. J. Chemical energetics of slow- and fast-twitch muscles of the mouse. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):147–166. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R. Hormonal control of muscle growth. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Sep;10(7):577–598. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A., Jackson M. J., McPhail G., Edwards R. H. Experimental mouse muscle damage: the importance of external calcium. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Mar;66(3):317–322. doi: 10.1042/cs0660317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Jeanrenaud B., Freychet P. Insulin binding and effects in isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):E348–E358. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.4.E348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltin C. A., Harris C. I. Morphological observations and rates of protein synthesis in rat muscles incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):927–930. doi: 10.1042/bj2320927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Leighton B., Challiss R. A., Lozeman F. J. Assessment of biochemical viability of isolated incubated muscle preparations. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):621–622. doi: 10.1042/bj2380621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington R. J. Clinical biochemistry of muscular dystrophy. Br Med Bull. 1980 May;36(2):123–126. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puah J. A., Bailey C. J. Effect of ovarian hormones on glucose metabolism in mouse soleus muscle. Endocrinology. 1985 Oct;117(4):1336–1340. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-4-1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S. S., Faulkner J. A. Temperature-dependent physiological stability of rat skeletal muscle in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C265–C270. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan M. H., Bonen A. The in vitro effect of corticosterone on insulin binding and glucose metabolism in mouse skeletal muscles. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;63(9):1133–1138. doi: 10.1139/y85-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson-Wright W. M., Tan M. H., Bonen A. Insulin binding and 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in fast- and slow-twitch mouse skeletal muscle at 18 and 37 degrees C. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;62(12):1460–1465. doi: 10.1139/y84-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuurveld J. G., Veerkamp J. H., Wirtz P. Isolated myofibers from rat skeletal muscle in suspension: cellular morphology and calcium homeostasis. Muscle Nerve. 1985 Nov-Dec;8(9):750–759. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]