Abstract
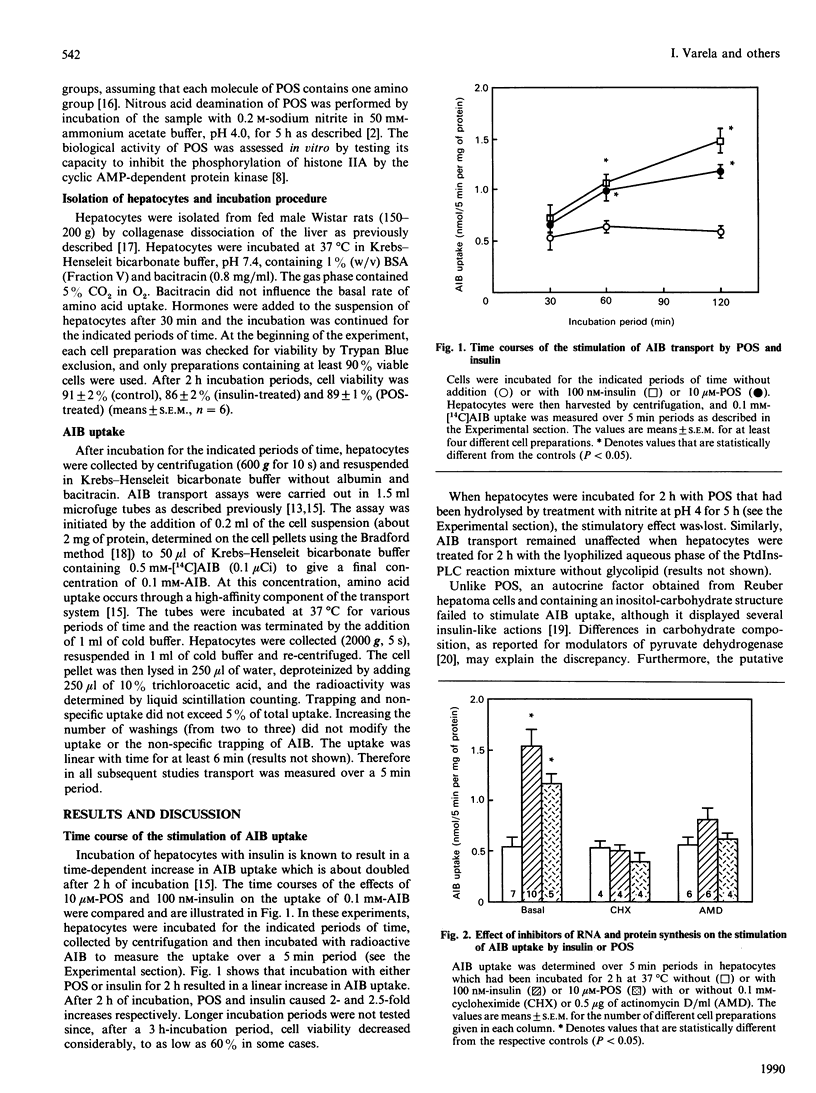
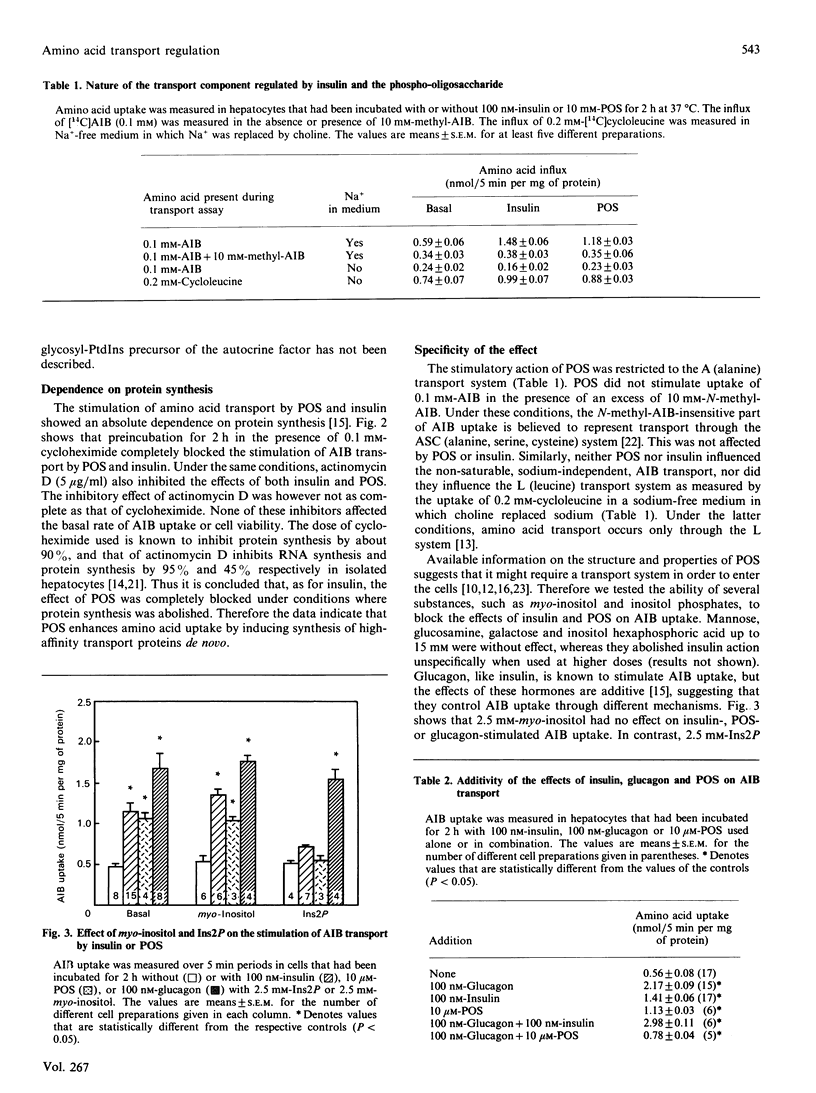
The ability of the insulin-induced phospho-oligosaccharide to stimulate amino acid transport was studied in isolated rat hepatocytes. At low alpha-aminoisobutyric acid concentrations (0.1 mM), both 100 nM-insulin and 10 microM-phospho-oligosaccharide doubled amino acid uptake after 2 h of incubation. This stimulation was prevented by 0.1 mM-cycloheximide or 5 micrograms of actinomycin D/ml, indicating that the phospho-oligosaccharide, like insulin, was acting via the synthesis of a high-affinity transport component. The effects of the phospho-oligosaccharide and of insulin were blocked by Ins2P (2.5 mM), but not by myo-inositol, inositol hexaphosphoric acid or several monosaccharides such as mannose, glucosamine and galactose. Both the temporal effect on amino acid entry and the extent of stimulation of this process by the phospho-oligosaccharide indicate that this molecule mimics, and may mediate, some of the long-term actions of insulin. However, the effects of phospho-oligosaccharide and insulin were not exactly the same, since the effect of insulin, but not of the phospho-oligosaccharide, was additive with that of glucagon.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany S., Mato J. M., Strålfors P. Phospho-dephospho-control by insulin is mimicked by a phospho-oligosaccharide in adipocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):77–79. doi: 10.1038/330077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J. F., Cabello M. A., Felíu J. E., Mato J. M. A phospho-oligosaccharide mimics insulin action on glycogen phosphorylase and pyruvate kinase activities in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90996-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J. F., Varela I., Ruiz-Albusac J. M., Mato J. M. Localisation of the insulin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol glycan at the outer surface of the cell membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80449-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J. F., Varela I., Ruiz-Albusac J. M., Mato J. M. Localisation of the insulin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol glycan at the outer surface of the cell membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80449-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Le Cam A., Freychet P. Insulin and glucagon stimulation of amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Synthesis of a high affinity component of transport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10431–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Kelly K. L., Pawlowski J., Mato J. M., Jarett L. Regulation and function of an insulin-sensitive glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol during T lymphocyte activation. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Franchi-Gazzola R., Gazzola G. C., Ronchi P. Regulation of amino acid transport in chick embryo heart cells. IV. Site and mechanisms of insulin action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 31;356(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Felíu J. E., Hers H. G. Control of gluconeogenesis and of enzymes of glycogen metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. A parallel study of the effect of phenylephrine and of glucagon. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):791–797. doi: 10.1042/bj1760791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Mato J. M., Merida I., Jarett L. Glucose transport and antilipolysis are differentially regulated by the polar head group of an insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6404–6407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Huang L. C., Schwartz C. F., Oswald A. S., Shen T. Y., Kinter M., Tang G. Z., Zeller K. Rat liver insulin mediator which stimulates pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate contains galactosamine and D-chiroinositol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1416–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Effect of insulin on amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetologia. 1978 Aug;15(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00422256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Glucagon stimulates the A system for neutral amino acid transport in isolated hepatocytes of adult rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):893–901. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Neutral amino acid transport. Characterization of the A and L systems in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Kelly K. L., Abler A., Jarett L. Identification of a novel insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid from H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2131–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Sorbara-Cazan L. R. Inositol glycan mimics the action of insulin on glucose utilization in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90519-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalba M., Kelly K. L., Mato J. M. Inhibition of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by the polar head group of an insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 18;968(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Watts T. D. An autocrine factor from Reuber hepatoma cells that stimulates DNA synthesis and acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Characterization of biologic activity and evidence for a glycan structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8027–8036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


