Abstract
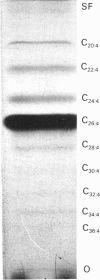
Rat brain was recently found to contain polyenoic very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) belonging to the n-3 and n-6 series with four, five and six double bonds and even-carbon chain lengths from 24 to 38 [Robinson, Johnson & Poulos (1990) Biochem. J. 265, 763-767]. In the present paper, the metabolism in vivo of hexacosatetraenoic acid (C26:4,n-6) was studied in neonatal rat brain. Rats were injected intracerebrally with [1-14C]C26:4,n-6 and the labelled metabolites were examined after 4 h. Radioactivity was detected mainly in non-esterified fatty acids, with smaller amounts in other neutral lipids and phospholipids. Radiolabelled fatty acid products included C28-36 tetraenoic and C26-28 pentaenoic VLCFA formed by elongation and desaturation of the substrate, and C14-24 saturated, C16-24 monoenoic, C18-24 dienoic, C18-22 trienoic and C20-24 tetraenoic fatty acids formed from released [1-14C]acetate either by synthesis de novo or by elongation of endogenous fatty acids. The data suggest that polyenoic VLCFA are synthesized in brain from shorter-chain precursor fatty acids and undergo beta-oxidation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson G. A. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of rat liver glycerophosphatides. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):478–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aveldaño M. I. A novel group of very long chain polyenoic fatty acids in dipolyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines from vertebrate retina. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1172–1179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aveldaño M. I., Sprecher H. Very long chain (C24 to C36) polyenoic fatty acids of the n-3 and n-6 series in dipolyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines from bovine retina. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1180–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges R. B., Coniglio J. G. The biosynthesis of delta-9,12,15,18-tetracosatetraenoic and of delta-6,9,12,15,18-tetracosapentaenoic acids by rat testes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavino V. C., Miller J. S., Dillman J. M., Milo G. E., Cornwell D. G. Polyunsaturated fatty acid accumulation in the lipids of cultured fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jan;22(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan W. M., Huth E. G. Biosynthesis of long-chain polyenoic acids from arachidonic acid in cultures of enriched spermatocytes and spermatids from mouse testis. Lipids. 1983 Apr;18(4):275–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02534702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan W. M. Metabolism of arachidonate in rat testis: characterization of 26-30 carbon polyenoic acids. Lipids. 1984 May;19(5):341–346. doi: 10.1007/BF02534785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inomata M., Takaku F., Nagai Y., Saito M. Assay for polyunsaturated fatty acids by argentation--thin-layer chromatography using commercial thin-layer plates. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naughton J. M. Supply of polyenoic fatty acids to the mammalian brain: the ease of conversion of the short-chain essential fatty acids to their longer chain polyunsaturated metabolites in liver, brain, placenta and blood. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Johnson D. W., Beckman K., White I. G., Easton C. Occurrence of unusual molecular species of sphingomyelin containing 28-34-carbon polyenoic fatty acids in ram spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):961–964. doi: 10.1042/bj2480961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A. Lipid metabolism in Zellweger's syndrome. Prog Lipid Res. 1989;28(1):35–51. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(89)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Sharp P., Johnson D., Easton C. The occurrence of polyenoic very long chain fatty acids with greater than 32 carbon atoms in molecular species of phosphatidylcholine in normal and peroxisome-deficient (Zellweger's syndrome) brain. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):645–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2530645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Sharp P., Johnson D., White I., Fellenberg A. The occurrence of polyenoic fatty acids with greater than 22 carbon atoms in mammalian spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):891–895. doi: 10.1042/bj2400891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Sharp P., Singh H., Johnson D., Fellenberg A., Pollard A. Detection of a homologous series of C26-C38 polyenoic fatty acids in the brain of patients without peroxisomes (Zellweger's syndrome). Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):607–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2350607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. S., Johnson D. W., Poulos A. Unique molecular species of phosphatidylcholine containing very-long-chain (C24-C38) polyenoic fatty acids in rat brain. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):763–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2650763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal M. D., Hill J. R. Human vascular endothelial cells synthesize and release 24- and 26-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 12;795(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotstein N. P., Aveldaño M. I. Synthesis of very long chain (up to 36 carbon) tetra, penta and hexaenoic fatty acids in retina. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):191–200. doi: 10.1042/bj2490191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Yoshida S., Takeshita M. Inhibitory effect of very-long-chain monounsaturated fatty-acyl-CoAs on the elongation of long-chain fatty acid in swine cerebral microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 15;960(3):410–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P., Poulos A., Fellenberg A., Johnson D. Structure and lipid distribution of polyenoic very-long-chain fatty acids in the brain of peroxisome-deficient patients (Zellweger syndrome). Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):61–67. doi: 10.1042/bj2480061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street J. M., Johnson D. W., Singh H., Poulos A. Metabolism of saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids by normal and Zellweger syndrome skin fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):647–655. doi: 10.1042/bj2600647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Ohno T., Miyatake T., Suzuki A., Yamakawa T. Fatty acid elongation activity in fibroblasts from patients with adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD). J Biochem. 1984 Oct;96(4):1241–1247. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Saitoh T., Takeshita M. Hydrogen transfer by NADPH-dependent reductases in elongation of very-long-chain saturated and polyunsaturated fatty-acyl-CoA in swine cerebral microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 19;958(3):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]