Abstract
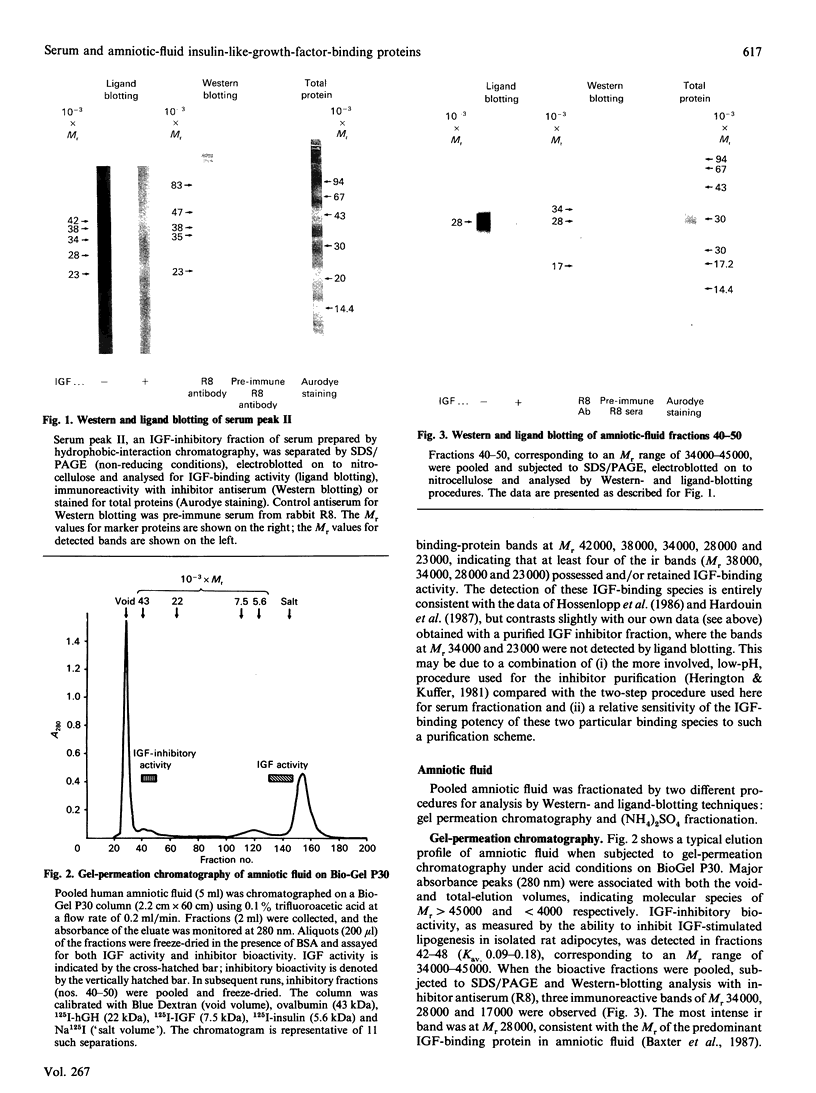
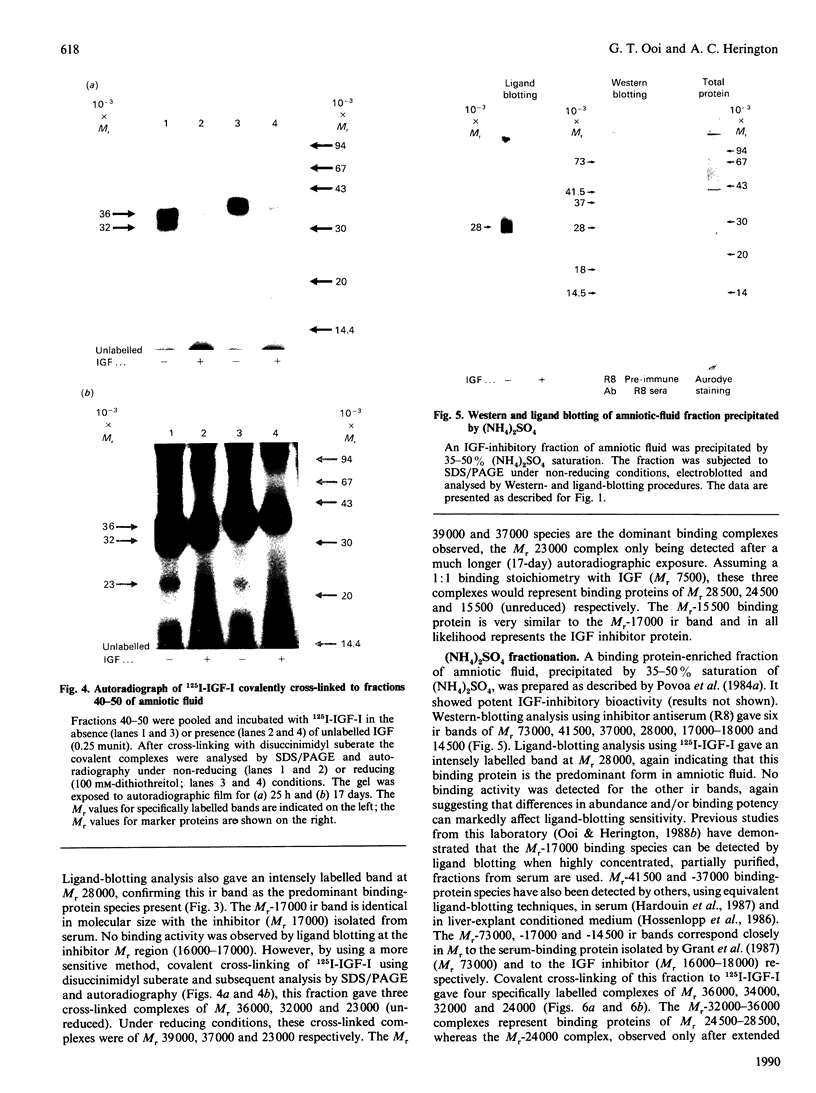
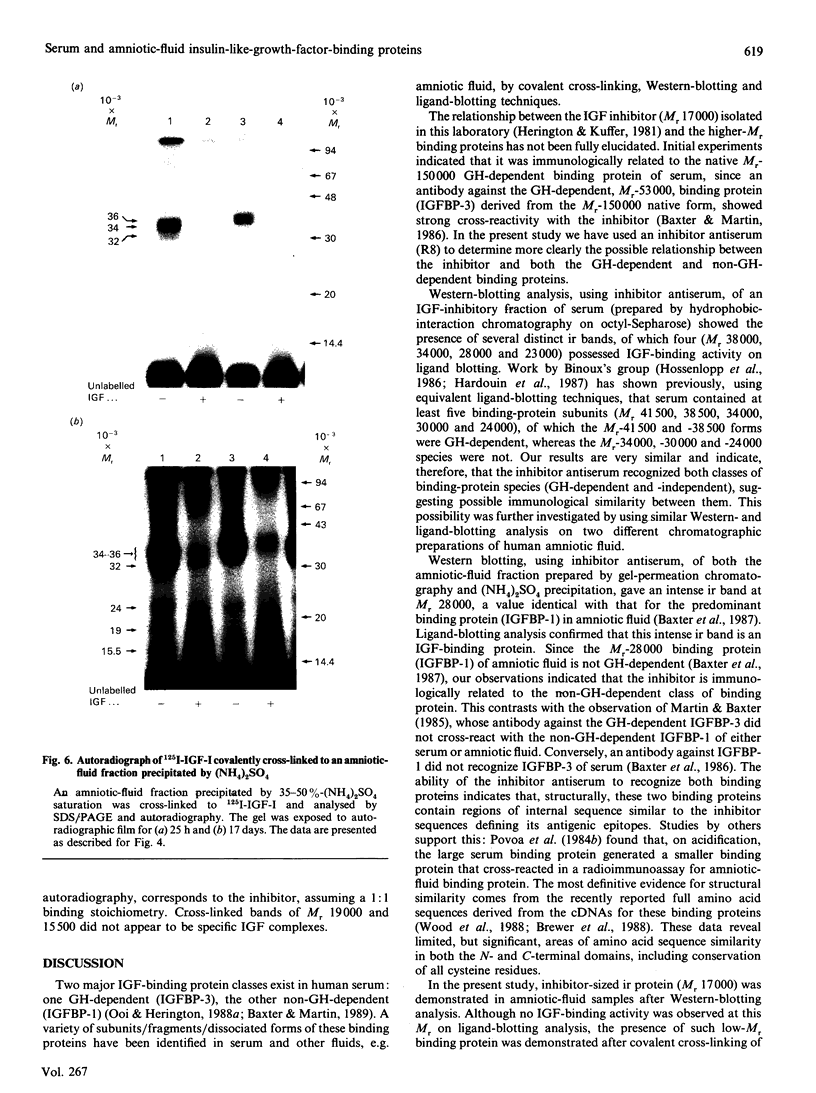
An antiserum (R8) raised against a purified specific low-Mr (16,000-18,000) insulin-like-growth-factor (IGF)-inhibitor/binding protein, which is immunologically related to the native growth hormone (GH)-dependent Mr-150,000 IGF-binding protein in serum, has been used to probe a possible additional relationship to the predominant non-GH-dependent IGF-binding protein (Mr approximately 30,000) of human amniotic fluid. Amniotic-fluid fractions and an IGF-inhibitory fraction of serum were analysed by covalent cross-linking, ligand-blotting and immunoblotting techniques. Western blotting of the serum fraction using the R8 antiserum gave five immunoreactive (ir) bands, of which at least three (Mr 38,000, 34,000 and 23,000) possessed IGF-binding activity, as indicated by ligand (125I-IGF-I) blotting. Western blotting of two differently prepared amniotic-fluid fractions, which both showed potent IGF-inhibitory bioactivity, gave several (Mr range 14,500-73,000) ir bands, of which two (Mr 28,000 and 17,000) were most prominent. Ligand-blotting analysis gave a single intensely labelled band at Mr 28,000, consistent with the major presence of the Mr-28,000-30,000 amniotic-fluid IGF-binding protein. Covalent cross-linking of the amniotic-fluid fractions to 125I-IGF-I gave three specifically cross-linked complexes (Mr 36,000, 32,000 and 23,000), which, assuming a 1:1 binding stoichiometry with IGF (Mr 7500), represent binding proteins of Mr 28,500, 24,500 and 15,500 respectively. The Mr-15,500 binding protein, very similar to the Mr-17,000 ir band, in all likelihood represents the IGF-inhibitor protein. Our results indicate that inhibitor-sized binding proteins and IGF-inhibitor bioactivity are present in human amniotic fluid, and that the IGF-inhibitor protein (Mr 16,000) and amniotic-fluid IGF-binding protein (Mr 28,000) are immunologically related. Since the IGF-inhibitor protein is also immunologically and structurally related to the native, GH-dependent, Mr-150,000 binding protein in serum, our data suggest a heretofore-unrecognized immunological similarity between the Mr-150,000 binding protein and the amniotic-fluid binding protein and its serum analogue, the Mr approximately 30,000, non-GH-dependent, binding protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors: structure, regulation and function. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulinlike growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI112742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Tyler M. I., Howden M. E. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human plasma differs from other human IGF binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Wood M. H. Two immunoreactive binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in human amniotic fluid: relationship to fetal maturity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Sep;65(3):423–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binkert C., Landwehr J., Mary J. L., Schwander J., Heinrich G. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a cDNA encoding a novel insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP-2). EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2497–2502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. T., Stetler G. L., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Busby W. H., Clemmons D. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a human insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A., Groffen C., Kortleve D. J., Geurts van Kessel A., Drop S. L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IBP-1). EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2417–2423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Elgin R. G., Han V. K., Casella S. J., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Cultured fibroblast monolayers secrete a protein that alters the cellular binding of somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1548–1556. doi: 10.1172/JCI112470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Bistrin M., Herington A. C. Differentiation between carrier-bound forms of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) in serum. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(9):1003–1008. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Enberg G., Herington A. C. Preferential association of the insulin-like growth factors I and II with metabolically inactive and active carrier-bound complexes in serum. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):745–750. doi: 10.1042/bj2410745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Herington A. C. Evidence for a biologically active, carrier-bound form of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) in human serum. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(4):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I-binding proteins in human amniotic fluid and in fetal and postnatal blood: evidence of immunological homology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):612–617. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vroede M. A., Tseng L. Y., Katsoyannis P. G., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Modulation of insulinlike growth factor I binding to human fibroblast monolayer cultures by insulinlike growth factor carrier proteins released to the incubation media. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI112343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J., Guyda H. J. Isolation of a somatomedin-binding protein from preterm amniotic fluid. Development of a radioimmunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):899–907. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Valiquette G., Guyda H. J., Corvol M. T., Posner B. I. Partial purification and characterization of a binding protein for insulin-like activity (ILAs) in human amniotic fluid: a possible inhibitor of insulin-like activity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Mar;90(3):505–518. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. B., Russell B., Harwood H. J., Jr, Merimee T. J. Separation of the insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in plasma and purification of the larger molecular weight species. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 May;64(5):1060–1065. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-5-1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Hossenlopp P., Segovia B., Seurin D., Portolan G., Lassarre C., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and relationships between structure and affinity. 1. Circulating forms in man. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Kuffer A. D. Identification of a specific inhibitor of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in a partially purified human serum fraction. Endocrinology. 1981 Nov;109(5):1634–1640. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-5-1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhtala M. L., Koistinen R., Palomäki P., Partanen P., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Biologically active domain in somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):263–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinen R., Kalkkinen N., Huhtala M. L., Seppälä M., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Placental protein 12 is a decidual protein that binds somatomedin and has an identical N-terminal amino acid sequence with somatomedin-binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1375–1378. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Antibody against acid-stable insulin-like growth factor binding protein detects 150,000 mol wt growth hormone-dependent complex in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):799–801. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8754–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. H., Schalch D. S. Structure of somatomedin-binding protein: alkaline pH-induced dissociation of an acid-stable, 60,000 molecular weight complex into smaller components. Endocrinology. 1982 Sep;111(3):801–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-3-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. Covalent cross-linking of insulin-like growth factor-1 to a specific inhibitor from human serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. Recognition of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) serum binding proteins by an antibody raised against a specific IGF-inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):783–791. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. The biological and structural characterization of specific serum binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors. J Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;118(1):7–18. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1180007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Enberg G., Jörnvall H., Hall K. Isolation and characterization of a somatomedin-binding protein from mid-term human amniotic fluid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Isaksson M., Jörnvall H., Hall K. The somatomedin-binding protein isolated from a human hepatoma cell line is identical to the human amniotic fluid somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Roovete A., Hall K. Cross-reaction of serum somatomedin-binding protein in a radioimmunoassay developed for somatomedin-binding protein isolated from human amniotic fluid. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Dec;107(4):563–570. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1070563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Cachianes G., Henzel W. J., Winslow G. A., Spencer S. A., Hellmiss R., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Cloning and expression of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1176–1185. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







