Abstract
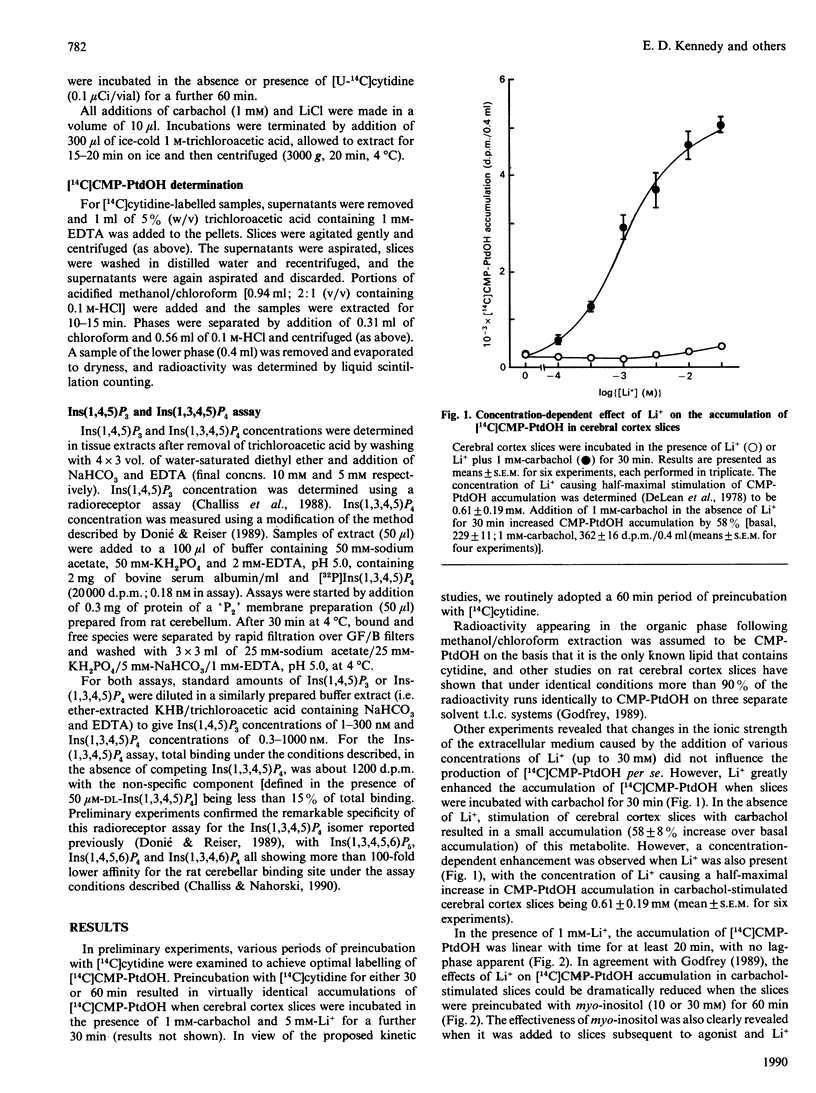
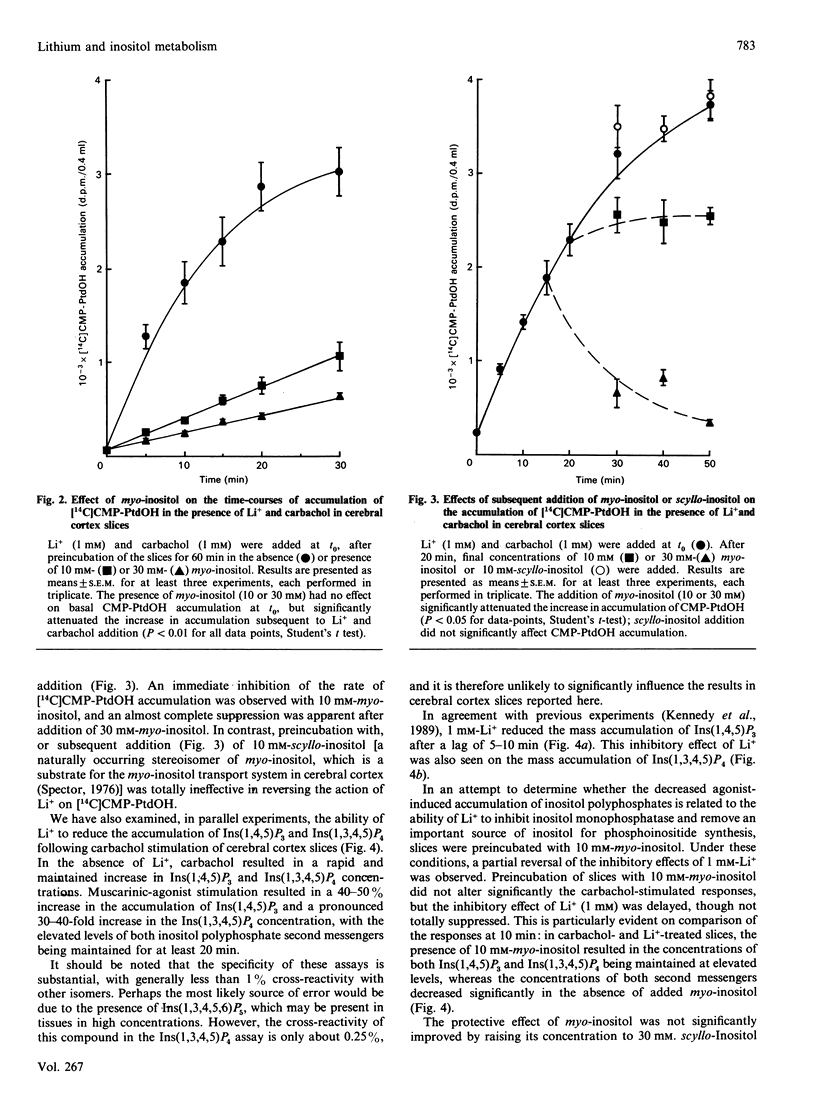
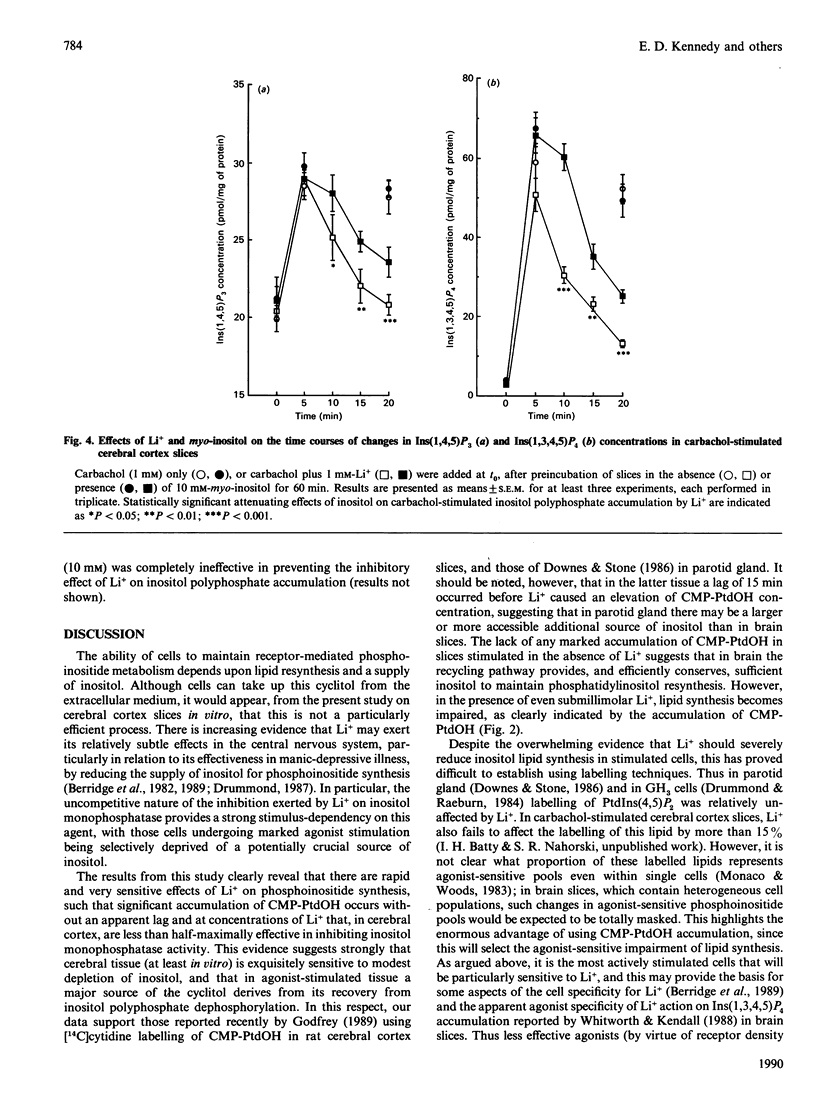
The ability of lithium to interfere with phosphoinositide metabolism in rat cerebral cortex slices has been examined by monitoring the accumulation of CMP-phosphatidate (CMP-PtdOH) and the reduction in Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 levels. A small accumulation of [14C]CMP-PtdOH was seen in slices prelabelled with [14C]cytidine and stimulated with carbachol (1 mM) or Li+ (1 mM). However, simultaneous addition of both agents for 30 min produced a 22-fold accumulation, with Li+ producing a half-maximal effect at a concentration of 0.61 +/- 0.19 mM. Kinetic studies revealed that the effects of carbachol and Li+ on CMP-PtdOH accumulation occurred with no initial lag apparent under these conditions and that preincubation with myo-inositol (10 or 30 mM) dramatically attenuated CMP-PtdOH accumulation. myo-Inositol could also attenuate the rate of accumulation of CMP-PtdOH when added 20 min after carbachol and Li+; these effects were not observed when equimolar concentrations of scyllo-inositol were added. Use of specific radioreceptor assays allowed the mass accumulations of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 to be monitored. Following a lag of 5-10 min, Li+ resulted in a marked reduction in the accumulation of both inositol polyphosphates resulting from muscarinic-cholinergic stimulation. Preincubation of cerebral cortex slices with myo- (but not scyllo-) inositol delayed, but did not prevent, the reduction in the accumulation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 or Ins(1,3,4,5)P4. The results suggest that cerebral cortex, at least in vitro, is very sensitive to myo-inositol depletion under conditions of muscarinic receptor stimulation. The relationship of such depletion to the generation of inositol polyphosphate second messengers is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. H., Stewart M. A. Reduced brain inositol in lithium-treated rats. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 27;233(43):267–268. doi: 10.1038/newbio233267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balla T., Baukal A. J., Guillemette G., Catt K. J. Multiple pathways of inositol polyphosphate metabolism in angiotensin-stimulated adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4083–4091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. H., Letcher A. J., Nahorski S. R. Accumulation of inositol polyphosphate isomers in agonist-stimulated cerebral-cortex slices. Comparison with metabolic profiles in cell-free preparations. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):23–32. doi: 10.1042/bj2580023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Rapid accumulation and sustained turnover of inositol phosphates in cerebral-cortex slices after muscarinic-receptor stimulation. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):237–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2600237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I., Nahorski S. R. Differential effects of lithium on muscarinic receptor stimulation of inositol phosphates in rat cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I., Nahorski S. R. Lithium inhibits muscarinic-receptor-stimulated inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2470797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Neural and developmental actions of lithium: a unifying hypothesis. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B., Gimlich R. L. Lithium-induced teratogenesis in frog embryos prevented by a polyphosphoinositide cycle intermediate or a diacylglycerol analog. Dev Biol. 1989 Apr;132(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90228-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donié F., Reiser G. A novel, specific binding protein assay for quantitation of intracellular inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP4) using a high-affinity InsP4 receptor from cerebellum. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Stone M. A. Lithium-induced reduction in intracellular inositol supply in cholinergically stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):199–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2340199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Raeburn C. A. The interaction of lithium with thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated lipid metabolism in GH3 pituitary tumour cells. Enhancement of stimulated 1,2-diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):129–136. doi: 10.1042/bj2240129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Sillers P. J. The role of the phosphatidylinositol cycle in mitosis in sea urchin zygotes. Lithium inhibition is overcome by myo-inositol but not by other cyclitols or sugars. Exp Cell Res. 1987 May;170(1):42–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., El Younsi C., Dawson M. C. Inter-relations between the phospholipids of rat pancreatic islets during glucose stimulation, and their response to medium inositol and tetracaine. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Ragan C. I., Watling K. J., Aspley S., Jackson R. G., Reid G. G., Gani D., Shute J. K. The purification and properties of myo-inositol monophosphatase from bovine brain. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):883–889. doi: 10.1042/bj2490883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey P. P. Potentiation by lithium of CMP-phosphatidate formation in carbachol-stimulated rat cerebral-cortical slices and its reversal by myo-inositol. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2580621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. J., Drummond A. H. Formation of inositol phosphate isomers in GH3 pituitary tumour cells stimulated with thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Acute effects of lithium ions. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):463–470. doi: 10.1042/bj2480463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. D., Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Lithium reduces the accumulation of inositol polyphosphate second messengers following cholinergic stimulation of cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1989 Nov;53(5):1652–1655. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb08566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantelli L., Capanni L., Corti V., Bennardini F., Matucci R., Ledda F. Influence of lithium on the positive inotropic effect of phenylephrine and isoprenaline in guinea-pig heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 20;150(1-2):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90757-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E., Woods D. Characterization of the hormone-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pool in WRK-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15125–15129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Pösö H., Iivanainen A., Andersson L. C. myo-Inositol reverses Li+-induced inhibition of phosphoinositide turnover and ornithine decarboxylase induction during early lymphocyte activation. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jul;16(7):859–861. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Nahorski S. R. Developmental aspects of muscarinic-induced inositol polyphosphate accumulation in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 5;172(6):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P., Munsell L. Y. Effects of lithium on phosphoinositide metabolism in vivo. Fed Proc. 1986 Oct;45(11):2639–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector R. Inositol accumulation by brain slices in vitro. J Neurochem. 1976 Nov;27(5):1273–1276. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Egawa K. CDP-diglyceride:inositol transferase from rat liver. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5419–5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitworth P., Kendall D. A. Lithium selectively inhibits muscarinic receptor-stimulated inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in mouse cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):258–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Heller W. A., Snyder S. H., Baraban J. M. Lithium blocks a phosphoinositide-mediated cholinergic response in hippocampal slices. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1428–1429. doi: 10.1126/science.2831626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


