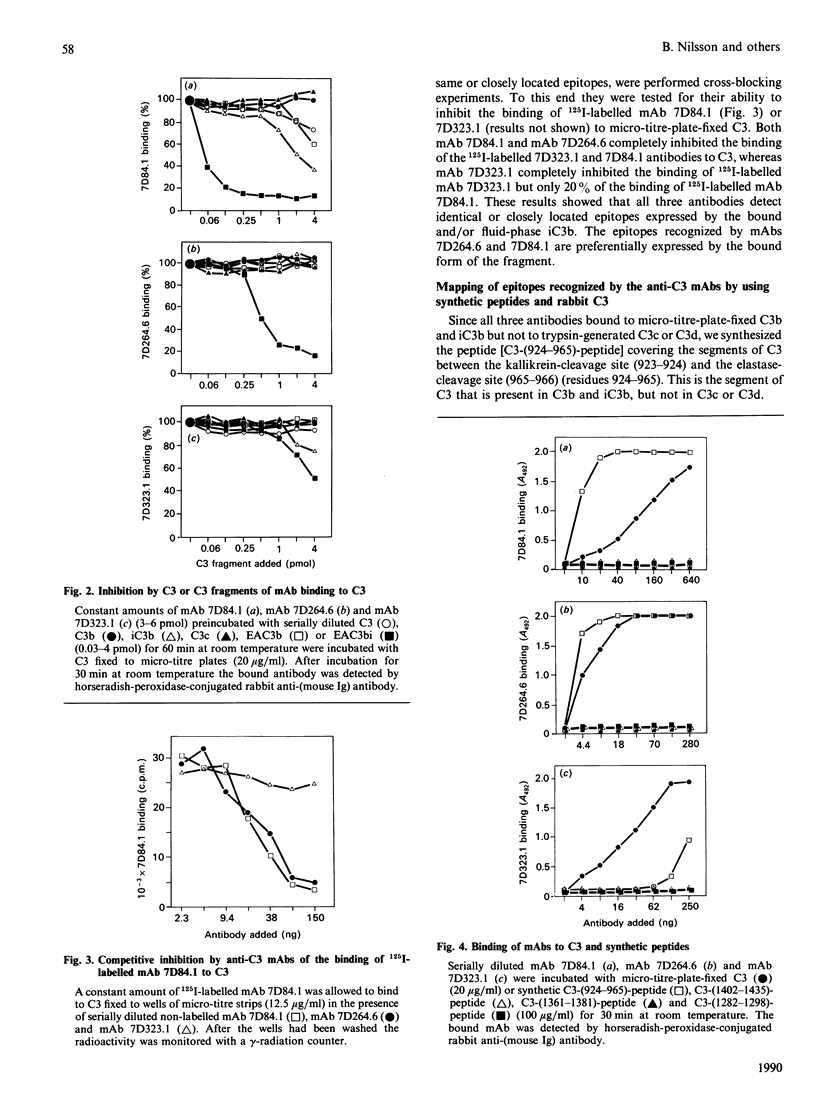
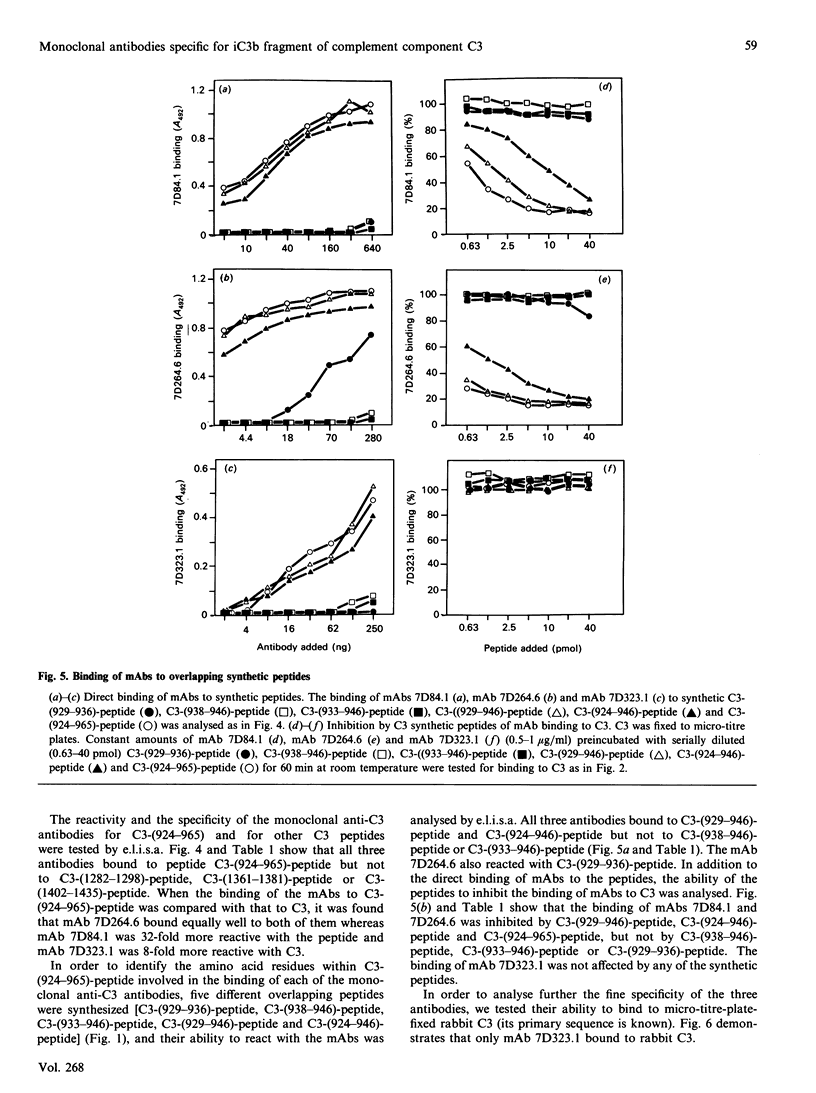
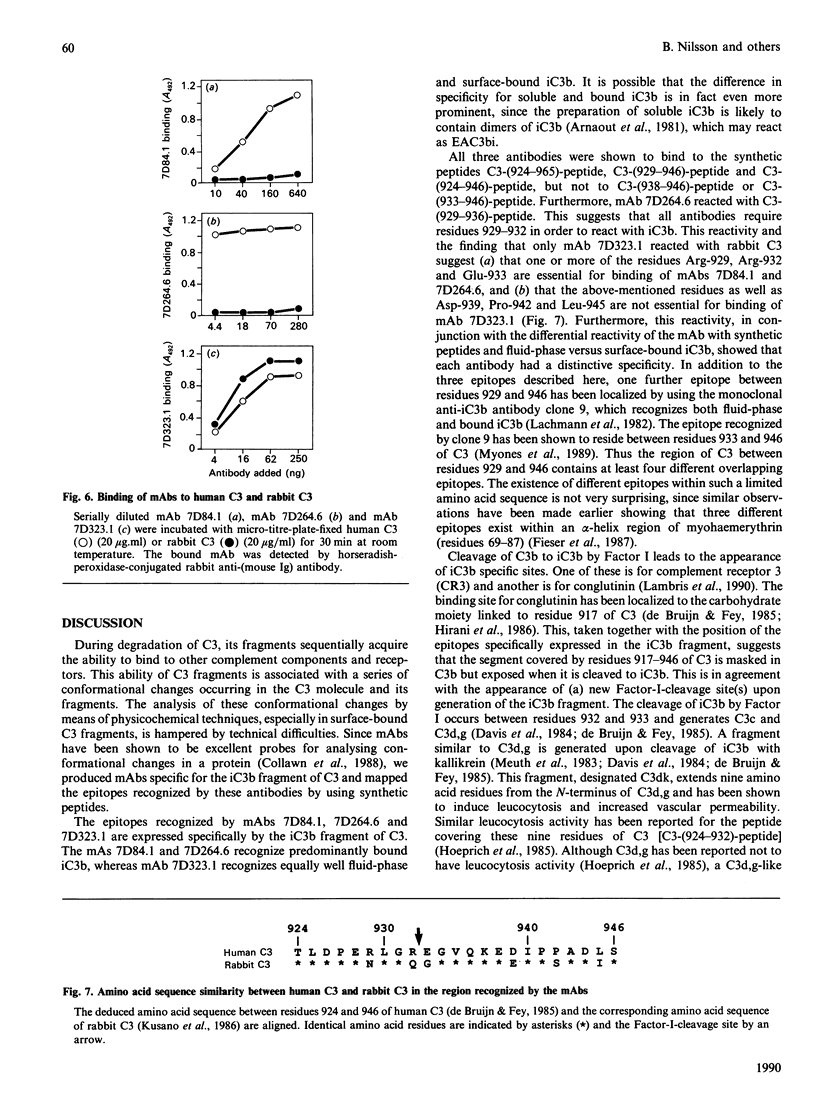
Abstract
The different fragments of the third complement component, C3, generated upon complement activation/inactivation have the ability to bind to several other complement components and receptors as well as to proteins of foreign origin. These multiple reactivities of C3 fragments are associated with a series of conformational changes occurring in the C3 molecule during its degradation. The conformations acquired by the different C3 fragments are also associated with the exposure of neoantigenic epitopes that are specific for (a) particular fragment(s). In order to study these epitopes and thus the conformational changes occurring in C3, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognizing such epitopes were produced in Balb/c mice after immunization with denatured human C3. Two of the three antibodies (7D84.1 and 7D264.6) presented in this study recognized predominantly surface-bound iC3b, and one mAb (7D323.1) recognized both surface-bound and fluid-phase iC3b. Although none of the mAbs recognized any other fluid-phase C3 fragment, all three antibodies detected micro-titre-plate-fixed C3b and iC3b, but not C3c or C3d. In addition to the reaction with human C3, mAb 7D323.1 also bound to micro-titre-plate-fixed rabbit C3. The epitopes recognized by the three mAbs were further localized by using synthetic peptides that were designed on the basis of the differential binding of the mAbs to the C3 fragments. All three antibodies reacted with C3-(924-965)-peptide, which represents the region of C3 between the kallikrein-cleavage site (923-924) and the elastase-cleavage site (965-966). On the basis of the binding of the mAbs to five different overlapping peptides spanning the region between residues 924 and 965 of the human C3 sequence, and the sequence similarity between human C3 and rabbit C3 within this area, the epitopes recognized by these antibodies are mapped. The contribution of the individual amino acid residues in the formation of the epitopes is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado M. T., Lambris J. D., Tsokos G. C., Burger R., Bitter-Suermann D., Tamerius J. D., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Monoclonal antibodies against complement 3 neoantigens for detection of immune complexes and complement activation. Relationship between immune complex levels, state of C3, and numbers of receptors for C3b. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1418–1426. doi: 10.1172/JCI112119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A., Melamed J., Tack B. F., Colten H. R. Characterization of the human complement (c3b) receptor with a fluid phase C3b dimer. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1348–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becherer J. D., Alsenz J., Servis C., Myones B. L., Lambris J. D. Cell surface proteins reacting with activated complement components. Complement Inflamm. 1989;6(3):142–165. doi: 10.1159/000463091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becherer J. D., Lambris J. D. Identification of the C3b receptor-binding domain in third component of complement. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14586–14591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R., Deubel U., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D. Identification of functionally relevant determinants on the complement component C3 with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2042–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R., Zilow G., Bader A., Friedlein A., Naser W. The C terminus of the anaphylatoxin C3a generated upon complement activation represents a neoantigenic determinant with diagnostic potential. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collawn J. F., Wallace C. J., Proudfoot A. E., Paterson Y. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of conformational changes in protein-engineered cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8625–8634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoudaki M. E., Becherer J. D., Lambris J. D. A 34-amino acid peptide of the third component of complement mediates properdin binding. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1577–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. Physiologic inactivation of fluid phase C3b: isolation and structural analysis of C3c, C3d,g (alpha 2D), and C3g. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1960–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiScipio R. G. The binding of human complement proteins C5, factor B, beta 1H and properdin to complement fragment C3b on zymosan. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):485–496. doi: 10.1042/bj1990485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggertsen G., Hellman U., Lundwall A., Folkersen J., Sjöquist J. Characterization of tryptic fragments of human complement factor C3. Mol Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(8):833–841. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway due to resistance of zymosan-bound amplification convertase to endogenous regulatory mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1683–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieser T. M., Tainer J. A., Geysen H. M., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Influence of protein flexibility and peptide conformation on reactivity of monoclonal anti-peptide antibodies with a protein alpha-helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8568–8572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Nussenzweig V. The role of C4-binding protein and beta 1H in proteolysis of C4b and C3b. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):267–276. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadd K. J., Reid K. B. The binding of complement component C3 to antibody-antigen aggregates after activation of the alternative pathway in human serum. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):471–480. doi: 10.1042/bj1950471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garred P., Mollnes T. E., Lea T., Fischer E. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody MoAb bH6 reacting with a neoepitope of human C3 expressed on C3b, iC3b, and C3c. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Mar;27(3):319–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirani S., Lambris J. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Structural analysis of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharides of human complement component C3. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):613–616. doi: 10.1042/bj2330613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of rabbit C3, Factor B, and Factor H and comparison of their properties with those of the human analog. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1094–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Mitomo K., Fujita T., Tamura N. Characterization of three monoclonal antibodies against C3 with selective specificities. Immunology. 1987 Nov;62(3):413–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E. Conformational changes accompanying proteolytic cleavage of human complement protein C3b by the regulatory enzyme factor I and its cofactor H. Spectroscopic and enzymological studies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4238–4244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Cooper N. R. The structure and function of the third component of human complement--I. The nature and extent of conformational changes accompanying C3 activation. Mol Immunol. 1981 Apr;18(4):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J. Detection of disulphide bonds and localization of interchain linkages in the third (C3) and the fourth (C4) components of human complement. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):819–825. doi: 10.1042/bj2330819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Pangburn M. K., Oldroyd R. G. Breakdown of C3 after complement activation. Identification of a new fragment C3g, using monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):205–216. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Avila D., Becherer J. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A discontinuous factor H binding site in the third component of complement as delineated by synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12147–12150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Ganu V. S., Hirani S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mapping of the C3d receptor (CR2)-binding site and a neoantigenic site in the C3d domain of the third component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4235–4239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The multifunctional role of C3: structural analysis of its interactions with physiological ligands. Mol Immunol. 1986 Nov;23(11):1237–1242. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D. The multifunctional role of C3, the third component of complement. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Covalent binding and hemolytic activity of complement proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7194–7198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Seya T., Nagasawa S. Location of the inter-chain disulfide bonds of the third component of human complement. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):264–269. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Iida K., Mold C., Nussenzweig V. Unique role of the complement receptor CR1 in the degradation of C3b associated with immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1739–1754. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth J. L., Morgan E. L., DiSipio R. G., Hugli T. E. Suppression of T lymphocyte functions by human C3 fragments. I. Inhibition of human T cell proliferative responses by a kallikrein cleavage fragment of human iC3b. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2605–2611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitomo K., Fujita T., Iida K. Functional and antigenic properties of complement receptor type 2, CR2. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1424–1429. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar J. L., Helder A. W., Müller M. A., Goris-Mulder M., Jonker L. S., Brouwer M., Pondman K. W. Physico-chemical and antigenic properties of human C3. Immunochemistry. 1975 May;12(5):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Ekdahl K. N., Svensson K. E., Bjelle A., Nilsson U. R. Distinctive expression of neoantigenic C3(D) epitopes on bound C3 following activation and binding to different target surfaces in normal and pathological human sera. Mol Immunol. 1989 Apr;26(4):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Nilsson U. R. An assessment of the extent of antigenic analogy between physiologically bound C3 and C3 denatured by sodium dodecyl sulphate. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Dec;22(6):703–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Svensson K. E., Borwell P., Nilsson U. R. Production of mouse monoclonal antibodies that detect distinct neoantigenic epitopes on bound C3b and iC3b but not on the corresponding soluble fragments. Mol Immunol. 1987 May;24(5):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Mandle R. J., Jr, McConnell-Mapes J. A. Human C3 and C5: subunit structure and modifications by trypsin and C42-C423. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):815–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Nilsson B. Analogous antigenic alterations elicited in C3 by physiologic binding and by denaturation in the presence of sodium dodecylsulfate. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2594–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Kinetic and thermodynamic analysis of the control of C3b by the complement regulatory proteins factors H and I. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):178–185. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Sim R. B. Molecular modelling of human complement component C3 and its fragments by solution scattering. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):155–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Medof M. E. Membrane complement receptors specific for bound fragments of C3. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:217–267. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Nagasawa S., Atkinson J. P. Generation of the bioactive kallikrein-derived fragment, C3d-k, by HANE-plasma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):208–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Turner J. R., Atkinson J. P. Purification and characterization of a membrane protein (gp45-70) that is a cofactor for cleavage of C3b and C4b. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):837–855. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamerius J. D., Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Detection of a neoantigen on human C3bi and C3d by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2015–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamerius J. D., Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Selective inhibition of functional sites of cell-bound C3b by hybridoma-derived antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):512–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Fey G. H. Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


